IBM BPM, V8.0.1, All platforms > Migrating and upgrading your IBM BPM environment > Migrating to new hardware
Migrating an ND environment to the same version on new hardware with full downtime
Use this procedure to migrate an ND environment to the same version on new hardware, while incurring full downtime.
Review Migrating to the same version on new hardware.
Procedure
Follow these steps to migrate an ND environment while incurring full downtime.
- Install the migration
target product(s).
Install the identical version and fix packs for the products on the target system as are installed on the source system.
You must either install the target version with the same user ID as that used for installing the source version or have permission to access the configuration and data on the source installation.
Important: To migrate from source profiles augmented by multiple products, the new version of those products must be installed into the same target installation directory.
For example, if the source profile is augmented by IBM BPM and IBM Business Monitor, both of those products must be installed into the same target installation directory.
- To prepare to stop all Java Virtual Machines (JVMs) in the cell, identify all clusters, node agents, non-clustered servers, and the dmgr.
For example, in the topology illustrated, you would need to stop the following.
- The three clusters
- The node agents for nodes one and two
- The non-clustered server in node three
- The dmgr for the cell
Figure 1. Example topology with three clusters across two nodes plus a third node for non-clustered servers

- Stop the clusters, node agents, non-clustered servers, and dmgr.
- Stop all cluster members.
- Stop all node agents.
- Stop all non-clustered servers.
- Stop the dmgr.
Stop the source dmgr using the stopManager command from the profile_root/bin directory on the migration source system or from the profile's First steps console.
Use the following syntax:
-

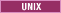
stopManager.sh -username user_name -password password
-
 stopManager.bat -username user_name -password password
stopManager.bat -username user_name -password password
If the profile has security enabled, the user name provided must be a member of the operator or administrator role.
If security is enabled, you do not have to specify the -username and -password parameters if the server is running as a Windows service. In this case, the parameters are automatically passed into the script that the Windows service uses to shut down the server.
If the profile does not have security enabled, the -username and -password parameters are unnecessary.
For more information about the stopManager command, see
 stopManager command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
stopManager command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- Back up the migration source profiles and the migration source product databases.
- Back up the migration source profiles.
Repeat this step for each profile that will be migrated, including the dmgr, each non-clustered managed node, and each managed node.
Back up the profile configuration on the migration source server using the backupConfig command.
Use the following syntax to back up a profile named profile1 to /ProfileBackups/profile1.zip:
-


backupConfig.sh /ProfileBackups/profile1.zip -profileName profile1
-
 backupConfig.bat c:\ProfileBackups\profile1.zip
-profileName profile1
backupConfig.bat c:\ProfileBackups\profile1.zip
-profileName profile1
For more information about the backupConfig command, see
 backupConfig command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
backupConfig command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- Back up the migration source product databases.
Back up the following databases that are configured by any of the migration source profiles according to the documentation for your database:
- Business Process Choreographer Database
- Business Space database
- Common database
- Common Event Infrastructure Database
- Messaging Engine Database
- Performance Data Warehouse database
- Process Server or Process Center database
- Back up the migration source profiles.
- Migrate the dmgr profile. Perform the Migrating a profile to the same version on a remote system (new hardware) procedure.
- Start the target dmgr.
Start the target dmgr using the startManager command from the profile_root/bin directory on the dmgr system or from the First steps console for the dmgr profile.
Use the following syntax:
-


startManager.sh
-
 startManager.bat
startManager.bat
For more information about the startManager command, see
 startManager command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
startManager command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- Migrate the managed nodes by performing Migrating a profile to the same version on a remote system (new hardware) for all nodes that are federated under the dmgr.
- Synchronize the migration target custom profiles with the dmgr profile. Synchronize all the clustered nodes that participate in the clusters migrated in previous steps to update the target cluster configuration.
- Secure the changes made up
to this point by making a new back up of your managed profiles. Back up the profile configuration on the clustered managed node using the backupConfig command. Use the following syntax to back up a profile named profile1 to /ProfileBackups/profile1.zip:
-


backupConfig.sh /ProfileBackups/profile1.zip -profileName profile1
-
 backupConfig.bat c:\ProfileBackups\profile1.zip
-profileName profile1
backupConfig.bat c:\ProfileBackups\profile1.zip
-profileName profile1
For more information about the backupConfig command, see
 backupConfig command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
backupConfig command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- Synchronize the managed nodes. Synchronize the node with the target dmgr using the syncNode command from the profile_root/bin directory of the migration target profile or from the target profile's First
steps console. Use the following syntax:
-


syncNode.sh deployment_manager_machine_name_or_ip_address deployment_manager_port_no
-
 syncNode.bat deployment_manager_machine_name_or_ip_address
deployment_manager_port_no
syncNode.bat deployment_manager_machine_name_or_ip_address
deployment_manager_port_no
For more information about the syncNode command, see
 syncNode command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
syncNode command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- If the syncNode command did not complete successfully, perform the following actions.
- Resolve the issues reported by the syncNode command.
- If necessary, restore the managed profiles that you backed up before running the syncNode command.
- Run the syncNode command again.
- Secure the changes made up
to this point by making a new back up of your managed profiles. Back up the profile configuration on the clustered managed node using the backupConfig command. Use the following syntax to back up a profile named profile1 to /ProfileBackups/profile1.zip:
- Start the migrated custom profiles.
Repeat this step for each clustered managed node for each cluster that was migrated.
Start the migration target node agent using the startNode command from the profile_root/bin directory of the migration target server.
Use the following syntax:
-


startNode.sh
-
 startNode.bat
startNode.bat
For more information about the startNode command, see
 startNode command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
startNode command in the WebSphere Application Server information center.
-
- Start the clusters. To start the clusters in your deployment environment, Deployment_Environment_Name, in the preferred sequence, perform the following actions using the administrative console:
- Click Servers > Clusters > WebSphere application server clusters.
- If your topology includes a messaging cluster, click the cluster name (typically Deployment_Environment_Name.Messaging) then click Start.
- If your topology includes a support cluster, click the cluster name (typically Deployment_Environment_Name.Support) then click Start.
- If your topology includes a web cluster, click the cluster name (typically Deployment_Environment_Name.Web) then click Start.
- If your topology includes an application deployment target cluster, click the cluster name (typically Deployment_Environment_Name.AppTarget) then click Start.
- Start the non-clustered servers. Using the administrative console, start each server by clicking Servers > Server Types > WebSphere application servers, then the name of the server, and Start.
- Optional: Uninstall the source
dmgr.
Once the migration is complete, the migration source dmgr can be uninstalled.
Results
The ND environment is migrated to the new hardware.
What to do next
Perform Postmigration tasks for migrating to new hardware.
Migrating to the same version on new hardware
Related tasks:
