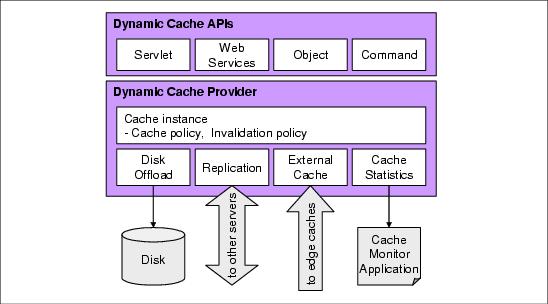
6.2.1 Dynamic cache service
The biggest performance gains for an application are found when data can be held ready for use or even where business logic or page rendering simply does not need to be done.
The dynamic cache service (dynacache) within the WebSphere Application Server stores dynamically generated web pages.
You tell WAS...
- Which pages can be cached
- Under what conditions
- For how long it is valid to cache it
The dynamic cache service is not restricted to just web content. The dynamic cache service has a number of APIs that can be used in a variety of ways for separate parts of an enterprise Java application.
- Web content
We can provide an XML file, cachespec.xml, in a web module to list a range of dynamic web pages and web fragments that can be cached. This includes all types of dynamically generated web content such as servlets, JSPs, JSFs, portlets, and AJAXs. This option does not require code change to use dynamic caching.
- Web services
Web services are naturally also web content, but it is worth mentioning them separately as there is specific support for being able to cache web service responses based on varying data in SOAP headers and parameters. This option does not require code change to use dynamic caching.
- Java objects
WebSphere Application Server provides an API for storing Java objects called the DistributedMap API. An application can use the DistributedMap to cache data to reduce expensive data accesses from data sources such as web services or databases.
- Java commands
WebSphere Application Server provides the Command cache API to cache the output of business logic methods. When the API has been implemented, the cache can be configured and tuned with the cachespec.xml file in the same way as the web content.
All of the dynamic cache service APIs can benefit from the services that the dynamic cache provider implements...
- Cache replication copies data between application servers. It is configurable as to how much data is replicated, from cache invalidations to replicating all cache content.
- Cache invalidation management is available through automatic time-based, memory-based invalidation, programmatic or manual invalidation through the cache monitor, and specifying URLs that can invalidate a cache entry.
- Disk offload for when you need to cache more data than can be contained in the application server JVM.
The dynamic cache service can be used by any WAS application.
WebSphere Commerce makes good use of the dynamic cache service to optimize the web store browsing experience and for storing user-related data in object caches. The dynamically generated content is stored in an instance of the dynamic cache called a servlet cache. The Java objects are stored in instances of the dynamic cache called an object cache. These cache instances can be created and managed under the Resources section of the administrative console. By default, all cached data is stored in the cache instance created by default, called baseCache.
Error 404 - Not Found
The document you are looking for may have been removed or re-named. Please contact the web site owner for further assistance.