Web services security architecture
The Web services security model employed by WAS is the declarative model. There are no APIs in for programmatically interacting with Web services security, but there are a few Server Provider Interfaces (SPIs) for extending some security-related behaviors.
Figure 1: Web services security model

The security constraints for Web services security are specified in the IBM deployment descriptor extension for Web services. The Web services security run time acts on the constraints to enforce Web services security for the SOAP message. The scope of the IBM deployment descriptor extension is at the module level (EJB module or Web module). Bindings are also associated with each of the following IBM deployment descriptor extensions:
- Client (A Web services client be either a stand-alone client or a Web service that acts as a client to another Web service.)
- ibm-webservicesclient-ext.xmi
- ibm-webservicesclient-bnd.xmi
- Server
- ibm-webservices-ext.xmi
- ibm-webservices-bnd.xmi
Use the tools provided by IBM (such as the Application Server Toolkit, WebSphere Studio Application Developer, or WebSphere Development Client for iSeries) to create the IBM deployment descriptor extension and bindings. After the bindings are created, you can use the tools or the WebSphere administrative console to specify the bindings.
Note: The binding information is collected after the application has been deployed, not during deployment itself. The alternative is to specify the required binding information before deploying your application.
Figure 2: Web services security message interpretation
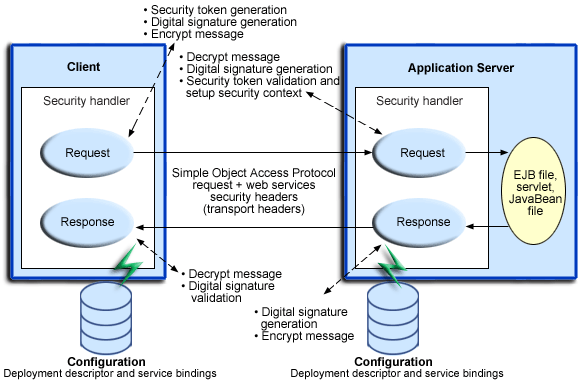
The Web services security run time enforces or applies Web services security based on the defined security constraints in the deployment descriptor and binding files. In Figure 2, Web services security has the following points where it intercepts the message and acts on the security constraints that are defined:
- Request sender
- Is defined in the ibm-webservicesclient-ext.xmi and ibm-webservicesclient-bnd.xmi files.
- Applies the appropriate security constraints to the SOAP message (such as signing or encryption) before the message is sent across the wire, generating the time stamp or the required security token.
- Request receiver
- Is defined in the ibm-webservices-ext.xmi and ibm-webservices-bnd.xmi files.
- Verifies that the Web services security constraints are met.
- Verifies the freshness of the message based on the time stamp.
- Verifies the required signature.
- Verifies that the message is encrypted and decrypts the message if encrypted.
- Validates the security tokens and sets up the security context for the down-stream call.
- Response sender
- Is defined in the ibm-webservices-ext.xmi and ibm-webservices-bnd.xmi files.
- Applies the appropriate security constraints to the SOAP message response, like signing the message, encrypting the message, or generating the time stamp.
- Response receiver
- Is defined in the ibm-webservicesclient-ext.xmi or ibm-webservicesclient-bnd.xmi file.
- Verifies that the Web services security constraints are met.
- Verifies the freshness of the message based on the time stamp.
- Verifies the required signature.
- Verifies that the message is encrypted and decrypts the message, if encrypted.
Web services security programming interfaces
SPIs are provided to extend the capability of the Web services security run time. The following SPIs and application programming interfaces (APIs) are available:
-
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.config.KeyLocator
This SPI is an abstract class for obtaining the keys for digital signature and encryption. The following implementations are the defaults:-
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.config.KeyStoreKeyLocator
Implements the Java key store. -
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.config.WSIdKeyStoreMapKeyLocator
Provides a mapping of authenticated identity to a key for encryption, or uses the default key that is specified. This is typically used in the response sender configuration. -
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.config.CertInRequestKeyLocator
Provides the capability of using the signer key for encryption in the response message. This is typically used in the response sender configuration.
-
-
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.id.TrustedIDEvaluator
An interface that used to evaluate the trust for identity assertion. The following implementation is the default:-
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.id.TrustedIDEvaluatorImpl
Enables you to define a list of trusted identities.
-
-
JAAS CallbackHandler APIs
Used for token generation by the request sender. These APIs can be extended to generate a custom token that is inserted in the Web services security header. The following implementations are the defaults that are provided by WAS:-
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.auth.callback.GUIPromptCallbackHandler
Presents a login prompt to gather the basic authentication data. Use this implementation in the client environment only. -
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.auth.callback.StdinPromptCallbackHandler
Collects the basic authentication data with Standard in (stdin). Use this implementation in the client environment only. -
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.auth.callback.NonPromptCallbackHandler
Reads the basic authentication data from the application binding file. This may be used on the server side to generate a user name token. -
com.ibm.wsspi.wssecurity.auth.callback.LTPATokenCallbackHandler
Generates an LTPA token in the Web services security header as binary security token. If there is basic authentication data that is defined in the application binding file, this implementation is used to perform a login, extract the LTPA token from the WebSphere credentials, and insert the token in the Web services security header. Otherwise, it extracts the LTPA security token from the invocation credentials (RunAs identity) and inserts the token in the Web services security header.
-
-
JAAS LoginModule API
Used for token validation of the request receiver side of the message. You can implement a custom LoginModule to perform validation of the custom token on the request receiver of the message. After the token is verified and validated, the token is set as the caller (the RunAs identity in the WebSphere run time) and the identity is used for authorization checks by the containers before a J2EE resource is invoked.The following configurations are the default AuthMethod configurations that are provided by WAS:
-
BasicAuth
Validates a user name token. -
Signature
Maps a distinguished name (DN) of a verified certificate to a JAAS subject. -
IDAssertion
Maps a trusted identity to a JAAS subject. -
LTPA
Validates an LTPA token received in the message and creates a JAAS subject.
-
Default configuration (ws-security.xml) for WAS
In the WAS, each application server has a copy of ws-security.xml, the file that defines the default binding information for Web services security. The following is a list of defaults defined in the ws-security.xml file:
-
Trust Anchors
Identifies the trusted root certificates for signature verification. -
Certificate Stores
Contains certificate revocation lists (CRLs) and non-trusted certificates for verification. -
KeyLocators
Locates the keys for digital signature and encryption. -
TrustedIDEvaluators
Evaluates the trust of the received identity before identity assertion. -
LoginMappings
Contains the JAAS configurations for AuthMethod token validation.
If the Web services security constraints that are specified in the deployment descriptors and the required bindings are not defined in the bindings file, the default constraints in the ws-security.xml file are used.
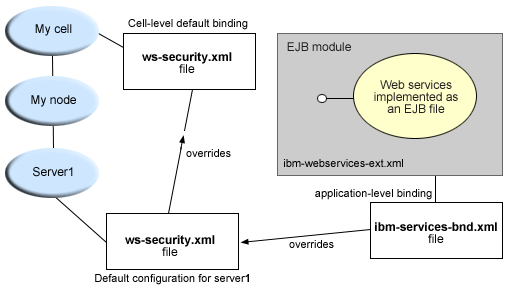
Default configuration (ws-security.xml) for WAS Network Deployment
In the WAS Network Deployment installation, the ws-security.xml file is at the cell level and defines the default binding information for Web services security for the entire cell. But each application server can have its own ws-security.xml file to override the cell default; similarly, each Web service can override the default in its binding files. The following is a list of defaults defined in ws-security.xml file:
-
Trust Anchors
Identifies the trusted root certificates for signature verification. -
Certificate Stores
Contains CRLs and non-trusted certificates for verification. -
KeyLocators
Locates the keys for digital signature and encryption. -
TrustedIDEvaluators
Evaluates the trust of the received identity before identity assertion. -
LoginMappings
Contains the JAAS configurations for AuthMethod token validation.
The Web services security run time reads the configuration from the application bindings first, then tries the server-level, and finally tries the cell level. Figure 4 depicts the run time configuration process.
Figure 4: Runtime configuration