Product overview > Cache > Database integration
|
| |
|
|
In-line caching
In-line caching uses eXtreme Scale as the primary means for interacting with the data. When eXtreme Scale is used as an in-line cache, the application interacts with the backend using a Loader plug-in.
The in-line caching option simplifies data access because it allows applications to access the eXtreme Scale APIs directly. WebSphere eXtreme Scale supports several in-line caching scenarios, as follows.
- Read-through
- Write-through
- Write-behind
Read-through caching scenario
A read-through cache is a sparse cache that lazily loads data entries by key as they are requested. This is done without requiring the caller to know how the entries are populated. If the data cannot be found in the eXtreme Scale cache, eXtreme Scale will retrieve the missing data from the Loader plug-in, which loads the data from the back-end database and inserts the data into the cache. Subsequent requests for the same data key will be found in the cache until it is removed, invalidated or evicted.Figure 1. Read-through caching
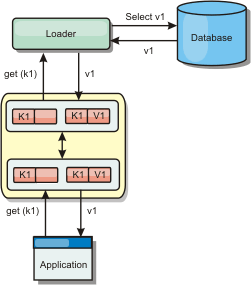
Write-through caching scenario
In a write-through cache, every write to the cache synchronously writes to the database using the Loader. This method provides consistency with the back end, but decreases write performance since the database operation is synchronous. Since the cache and database are both updated, subsequent reads for the same data will be found in the cache, avoiding the database call. A write-through cache is often used in conjunction with a read-through cache.Figure 2. Write-through caching
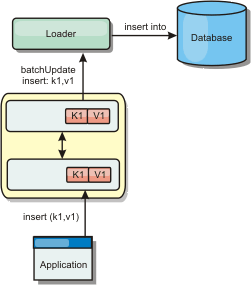
Write-behind caching scenario
Database synchronization can be improved by writing changes asynchronously. This is known as a write-behind or write-back cache. Changes that would normally be written synchronously to the loader are instead buffered in eXtreme Scale and written to the database using a background thread. Write performance is significantly improved because the database operation is removed from the client transaction and the database writes can be compressed. See Write-behind caching for more information.Figure 3. Write-behind caching
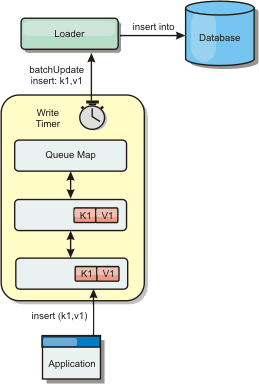
See Write-behind caching for further information.
Parent topic:
Database integration: Write-behind, in-line, and side caching
Related concepts
Database synchronization techniques
Configure write-behind support
Plug-ins for communicating with persistent stores