Web Services Addressing SPI
The Web Services Addressing (WS-Addressing) system programming interface (SPI) extends the application programming interface to enable you to create and reason about the contents of endpoint references and other WS-Addressing artifacts, and to set or retrieve WS-Addressing message addressing properties (MAPs) on or from Web service messages.
The programming interfaces in this topic are described in more detail in the WS-Addressing SPI documentation.
Creating, refining, and reasoning about the contents of endpoint references
The SPIs for creating, refining, and reasoning about the contents of endpoint references are contained in the com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing package and are summarized in the following illustration (the first two interfaces are API interfaces that are extended by the SPIs):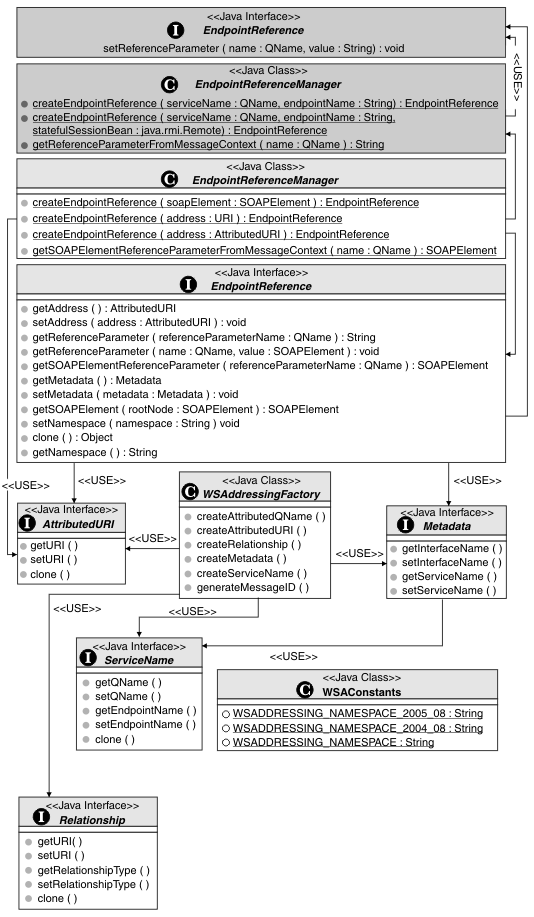
The SPI extends the WS-Addressing com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference API to provide a number of additional methods through the com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.EndpointReference interface. You can cast instances of com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference to com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.EndpointReference to access this additional functionality.
Similarly, the SPI com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.EndpointReferenceManager extends the functionality that is provided in the com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReferenceManager API. You can perform the following actions using the additional methods that are provided by the EndpointReference and EndpointReferenceManager SPIs:
- Create endpoint references
- Create EndpointReference objects by specifying the URI of the endpoint that the EndpointReference object is to represent, using the createEndpointReference(URI) operation, or the EndpointReferenceManager.createEndpointReference(AttributedURI) operation. These methods differ from the createEndpointReference method that is provided at the API level, in that they do not automatically generate the URI for the EndpointReference instance. You might use these methods when you know that the URI of the endpoint is stable, for example in a test environment with no deployment considerations.
- Map between XML and Java representations of an endpoint reference
- You can serialize instances of the EndpointReference interface to their corresponding SOAP element instances using the EndpointReference.getSOAPElement operation. Conversely, you can deserialize SOAP elements of type EndpointReferenceType into their corresponding EndpointReference Java representation, by using the EndpointReference.createEndpointReference(SOAPElement) operation. You might find these serialization and deserialization interfaces useful if you are creating custom binders for types that contain EndpointReference instances.
- Use more complex reference parameter types
-
The interfaces that are provided at the API level are restricted to reference parameters of type xsd:string to allow for a simpler programming model. The
SPIs extend this support to allow reference parameters of type <xsd:any>.
The EndpointReference interface provides mechanisms for getting and setting reference parameters as SOAP elements. Additionally, the EndpointReferenceManager class provides the getSOAPElementReferenceParameterFromMessageContext operation, which enables receiving endpoints to acquire reference parameters that are not of type String from the incoming message.
When invoking a service with an EndpointReference object that contains a reference parameter, create the reference parameter using a complete QName object, with all parts present: namespace, localpart, and prefix. If the QName object is not complete, service invocations will fail.
- Set and reason about endpoint reference contents
- The EndpointReference interface provides operations for you to set and reason about the contents of an EndpointReference instance, such as its WS-Addressing [address] and [metadata] properties. Additional interfaces are provided to represent the artifacts making up an endpoint reference: Metadata, AttributedURI, and ServiceName. You create instances of these interfaces using operations that are provided by the WSAddressingFactory class.
- Acquire and change the supported namespace
- The WS-Addressing support in WAS supports multiple namespaces. The setNamespace and getNamespace operations that are provided on the EndpointReference interface enable you to change and acquire the namespace that is associated with a particular EndpointReference object. Serialization to SOAP elements is in accordance with the namespace of the EndpointReference object. By default, the namespace of the destination endpoint reference (the endpoint reference set as the com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.WSAConstants.WSADDRESSING_DESTINATION_EPR property on the JAX-RPC Stub or Call object), defines the namespace of the message addressing properties of the message.
Setting and Retrieving WS-Addressing message addressing properties
The WS-Addressing SPI provides a number of constants that identify JAX-RPC properties to set WS-Addressing MAPs on outbound messages, and message context properties to retrieve MAPs on inbound messages. These constants are shown in the following diagram in the com.wsspi.wsaddresssing.WSAConstants class. The diagram also shows the interfaces that are required for generating instances of the appropriate property value types AttributedURI and Relationship. The first WSAConstants interface is an API interface.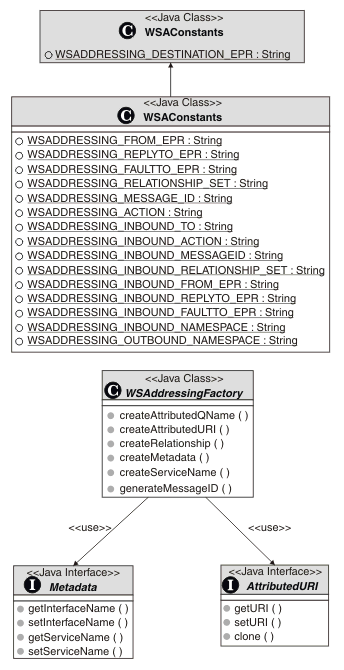
Setting WS-Addressing message addressing properties on outbound messages You can add WS-Addressing message information headers to outgoing messages by setting the appropriate properties on the JAX-RPC Stub or Call interface prior to invoking a message in the Stub or Call object. The following table summarizes the relevant properties and their types.
| Property name (of type String) | Java type of property value | Abstract WS-Addressing MAP name or names | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WSADDRESSING_DESTINATION_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference |
[destination] URI
| Not set
Note that this property comes from the API. |
| WSADDRESSING_FROM_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [source endpoint] | Not set |
| WSADDRESSING_REPLYTO_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [reply endpoint] | Not set, unless the message is a one-way message with no reply |
| WSADDRESSING_FAULTTO_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [fault endpoint] | Not set |
| WSADDRESSING_RELATIONSHIP_SET | java.util.Set containing instances of com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.Relationship | [relationship] | Not set |
| WSADDRESSING_MESSAGE_ID | com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.AttributedURI | [message id] | Generated and set to a unique value |
| WSADDRESSING_ACTION | com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.AttributedURI | [action] | Generated and set, according to the WS-Addressing specification |
| WSADDRESSING_OUTBOUND_NAMESPACE | String | none | The WS-Addressing namespace of the WSADDRESSING_DESTINATION_EPR property, if specified, otherwise the default namespace |
Retrieving WS-Addressing message addressing properties from inbound messages WS-Addressing message information headers that correspond to the last inbound message are available from the inbound properties that are defined in the WSAConstants class. The following table summarizes the available inbound properties. You acquire reference parameters from the message context using the EndpointReferenceManager.getReferenceParameter interface.
| Message context property name (of type String) | Java type of property value | Abstract WS-Addressing MAP name |
|---|---|---|
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_TO | com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.AttributedURI | [destination] |
| No specific property. Use the EndpointReferenceManager.getReferenceParameter(QName name) method to obtain the associated MAP. | Any type | [reference parameters]* |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_FROM_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [source endpoint] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_REPLYTO_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [reply endpoint] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_FAULTTO_EPR | com.ibm.websphere.wsaddressing.EndpointReference | [fault endpoint] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_RELATIONSHIP | java.util.Set containing instances of com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.Relationship | [relationship] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_MESSAGE_ID | com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.AttributedURI | [message id] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_ACTION | com.ibm.wsspi.wsaddressing.AttributedURI | [action] |
| WSADDRESSING_INBOUND_NAMESPACE | String | The WS-Addressing namespace of the incoming message |
Related concepts
Web Services Addressing support
Web Services Resource Framework support
Related tasks
Creating stateful Web services using the Web Services Resource Framework
Use the WS-Addressing SPI: Performing more advanced Web Service Addressing tasks
Related Reference
Example: Creating a Web service that uses the Web Services Addressing API to access a generic Web service resource instance
Related information
Reference: Generated API documentation