Configure inbound transports
Overview
You can configure a different transport for inbound security versus outbound security.
- To select the type and SSL settings for an inbound transport, click...
Security | Secure administration, applications, and infrastructure | RMI/IIOP security | CSIv2 inbound transport
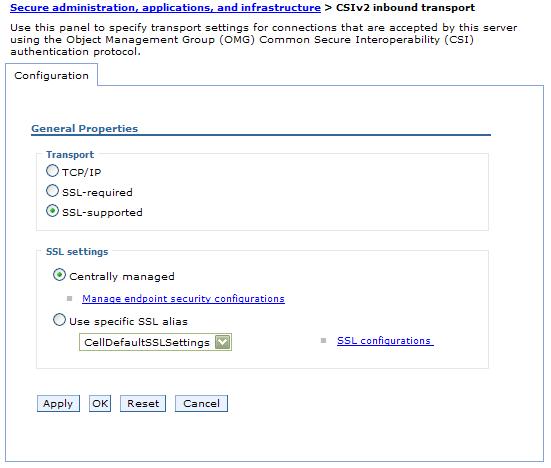
By selecting the type of transport, as noted previously, you choose which listener ports you want to open. In addition, you disable the SSL client certificate authentication feature if you choose TCP/IP as the transport.
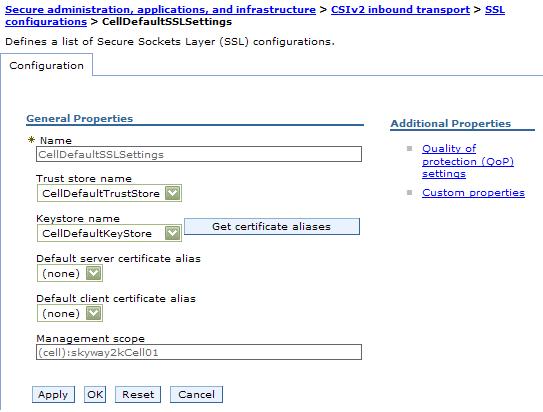
- Access the SSL configurations panel to select the SSL settings that correspond to an SSL transport.
- Click Apply in the CSIv2 inbound transport panel.
- Consider fixing the listener ports that you configured. You complete this action in a different panel, but think about this action now. Most endpoints are managed at a single location, which is why they do not display in the Inbound transport panels. Managing end points at a single location helps you decrease the number of conflicts in the configuration when you assign the endpoints. The location for SSL end points is at each server. The following port names are defined in the End points panel and are used for Object Request Broker (ORB) security:
- CSIV2_SSL_MUTUALAUTH_LISTENER_ADDRESS - CSIv2 Client Authentication SSL Port
- CSIV2_SSL_SERVERAUTH_LISTENER_ADDRESS - CSIv2 SSL Port
-
![[This information applies to V6.0.x and previous servers only that are federated in a V6.1 cell.]](images/v6app.gif) SAS_SSL_SERVERAUTH_LISTENER_ADDRESS - SAS SSL Port
SAS_SSL_SERVERAUTH_LISTENER_ADDRESS - SAS SSL Port
- ORB_LISTENER_PORT - TCP/IP Port
For an appserver, click Servers > Application servers > server. Under Communications, click Ports. The Ports panel is displayed for the specified server.
For a node agent, go to System administration > Node agents > node. Under Additional properties, click Ports. The Ports panel for the node agent and deployment manager already are fixed, but you might consider reassigning the ports. For the deployment manager, click System Administration > Deployment manager. Under Additional properties, click Ports.
The Object Request Broker (ORB) on WAS uses a listener port for Remote Method Invocation over the Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (RMI/IIOP) communications, and is statically specified using configuration dialogs or during migration. If you are working with a firewall, specify a static port for the ORB listener and open that port on the firewall so that communication can pass through the specified port. The endPoint property for setting the ORB listener port is: ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS. In the WAS ND environment, the ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS end point is specified on the node agent. The location service daemon resides on the node agent and piggybacks onto the ORB listener port, which results in needing the port fixed. Also, add the ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS to the other appservers to set their ORB listener port. Each ORB has a distinct listener port. In WAS ND, specify a different listener port. For example, you might specify the following ports:
- Node agent: ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS=9000
- Server1: ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS=9811
- Server2: ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS=9812
Federated servers can run without the node agent running. When ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS is set to a value of zero (0) or greater, the server does not depend on the location service daemon to redirect connections to the server. When you set ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS, all object references in the namespace specify the connection to the server, not the location service daemon. When the server is running without the node agent, all applications must be accessed through the name server that runs on the appserver. The client must change the Java Naming Directory Interface (JNDI) reference to use the host and port of the appserver.
Table 1. ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS value = 0 The server starts on any available port and does not use the location service daemon. value > 0 The server starts on the port that is specified by the value you enter. The location service daemon is not used. Work load management might not work without the node agent running.
Complete the following steps using the console to specify the ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS port or ports.
Complete the following steps for the node agent and the deployment manager.
- Click Servers > Application Servers > server.
Under Communications, click Ports > New.
- Select ORB_LISTENER_ADDRESS from the Port name field in the Configuration panel.
- Enter the IP address, the fully qualified Domain Name System (DNS) host name, or the DNS host name by itself in the Host field.
For example, if the host name is myhost, the fully qualified
DNS name can be myhost.myco.com and the IP address can be 1.5.123.88.201.
- Enter the port number in the Port field. The port number specifies the port for which the service is configured to accept client requests. The port value is used with the host name. Using the previous example, the port number might be 9000.
Click Security > Secure administration, applications, and infrastructure. Under RMI/IIOP security, click CSIv2 inbound transport to select the SSL settings that are used for inbound requests from CSIv2 clients. Remember that the CSIv2 protocol is used to inter-operate with previous releases. When configuring the keystore and truststore files in the SSL configuration, these files need the right information for inter-operating with previous releases of WAS. For example, a previous release has a different truststore file than the V6 release. If you use the V6 keystore file, add the signer to the truststore file of the previous release for those clients connecting to this server.
- CSIV2_SSL_MUTUALAUTH_LISTENER_ADDRESS - CSIv2 Client Authentication SSL Port
Results
The inbound transport configuration is complete. With this configuration, you can configure a different transport for inbound security versus outbound security. For example, if the appserver is the first server that is used by users, the security configuration might be more secure. When requests go to back-end enterprise bean servers, you might lessen the security for performance reasons when you go outbound. With this flexibility you can design the right transport infrastructure to meet your needs.
What to do next
When you finish configuring security, perform the following steps to save, synchronize, and restart the servers:- Click Save in the console to save any modifications to the configuration.
- Synchronize the configuration with all node agents.
- Stop and restart all servers, when synchronized.
V6.0.x and previous servers federated in a V6.1 cell
For V6.0.x and previous servers federated in a V6.1 cell inbound transports refer to the types of listener ports and their attributes that are opened to receive requests for this server. Both CSIv2 and SAS have the ability to configure the transport.SAS is supported only between V6.0.x and previous version servers federated in a V6.1 cell.
However, the following differences between the two protocols exist:

- CSIv2 is much more flexible than SAS, which requires SSL; CSIv2 does not require SSL.
- SAS does not support SSL client certificate authentication, while CSIv2 does.
- CSIv2 can require SSL connections, while SAS only supports SSL connections.
- SAS always has two listener ports open: TCP/IP and SSL.
- CSIv2 can have as few as one listener port and as many as three listener ports. You can open one port for just TCP/IP or when SSL is required. You can open two ports when SSL is supported, and open three ports when SSL and SSL client certificate authentication is supported.
Common Secure Interoperability V2 transport inbound settings
Secure Authentication Service inbound transport settings
Related tasks
Configure RMI over IIOP
Related Reference
Ports settings