Configure a Web server and an appserver on separate machines (remote)
Overview
When multiple profiles exist, the plug-ins installer configures only the default profile.
WAS provides a binary plug-ins for...
If the WAS product family does not provide a binary plug-in for a particular brand of Web server, then the Web server is not supported. The purpose of the binary plug-in is to provide the communication protocol between the Web server and the appserver.
For each new profile install a new Web server for the new profile and use the Plug-ins installation wizard to install the binary plug-in module and to configure both the Web server and the appserver.
This topic describes how to create the following topology:
If you are planning to add the appserver node into a deployment manager cell but have not done so yet, start the deployment manager and federate the node before installing the plug-in. You cannot add an appserver with a Web server definition into the deployment manager cell.
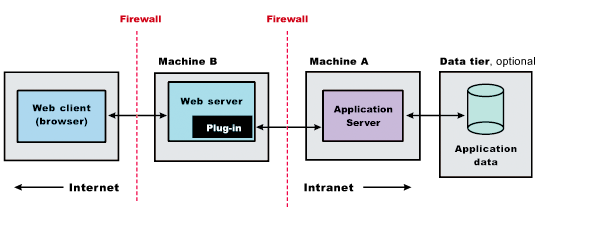
The following topology is considered a remote topology because the Web server is on a separate machine. The diagram shows a typical remote topology for a distributed environment:
This topic describes the installation of a Web server on one machine and the appserver on a separate machine. In this situation, the Plug-ins installation wizard on one machine cannot create the Web server definition in the appserver configuration on the other machine.
In such a case, the Plug-ins installation wizard creates a script on the Web server machine that you can copy to the appserver machine. Run the script on the appserver machine to create the Web server configuration definition within the appserver configuration.
Perform the following procedure to install the plug-in and configure both the Web server and the appserver.
Procedure
- Log on to the operating system.
On *nix systems select a umask that would allow the owner to read/write to the files, and allow others to access them according to the prevailing system policy. For root, a umask of 022 is recommended. For non-root users a umask of 002 or 022 could be used, depending on whether or not the users share the group. To verify the umask setting,...
umask
To set the umask setting to 022,...umask 022
![[Windows]](../../windows.gif) When installing on a Windows system, a Windows service is automatically created to autostart the appserver if your installer user account has the following advanced user rights:
When installing on a Windows system, a Windows service is automatically created to autostart the appserver if your installer user account has the following advanced user rights:
- Act as part of the operating system
- Log on as a service
For example, on some Windows systems, click...
Administrative Tools | Local Security Policy | User Rights Assignments
...to set the advanced options. See your Windows documentation for more information.
On Windows, if you plan to run the appserver as a Windows service, do not install from a user ID that contains spaces. A user ID with spaces cannot be validated. Such a user ID is not allowed to continue the installation. To work around this problem, install with a user ID that does not contain spaces.
- Act as part of the operating system
- Install WAS ND on appserver machine.
- Install the IBM HTTP Server or another supported Web server on webserver machine.
- Launch the Plug-ins installation wizard on the machine with the Web server.
Select the Plug-ins installation wizard from the launchpad or change directories to the plugin directory on the product disc or in the downloaded installation image and issue the install command.
- Clear the check box for the roadmap or select the check box to view the roadmap, then click Next.
- Read the license agreement and accept the agreement it if you agree to its terms. Click Next when you are finished.
- If your system does not pass the prerequisites check, stop the installation, correct any problems, and restart the installation.
If your system passes the prerequisites check, click Next.
- If you stop the installation, see the file...
/tmp/temporaryPluginInstallLog.txt
...might exist if the root user installed the plug-ins on an operating system such as AIX or Linux.
- If you continue the installation in spite of warnings about missing prerequisites, see the file...
plugins_root/logs/install/log.txt
...after the installation is complete.
- If you stop the installation, see the file...
- Select the type of Web server that you are configuring and click Next.
The Plug-ins installation wizard panel prompts you to identify the Web servers to configure. Actually you can select only one Web server each time you run the Plug-ins installation wizard.
Stop any Web server while you are configuring it. A step later in the procedure directs you to start the Web server as you begin the snoop servlet test.
If you select the Web server identification option labeled None, the Web server installs the binary plug-ins but does not configure the Web server.
- Select Web server machine (remote) and click Next.
- Accept the default location for the installation root directory for the plug-ins. Click Next.
You can type another new directory or click Browse to select an empty directory. The fully qualified path identifies the plug-ins installation root directory.
The default location is shown in Directory conventions.
A possibility exists that the Web server might run on a platform that WAS does not support.
- Click Browse to select the configuration file for your Web server, verify that the Web server port is correct, and then click Next when you are finished.
Select the file and not just the directory of the file. Some Web servers have two configuration files and require you to browse for each file. The following list shows configuration files for supported Web servers:
The wizard displays a naming panel for the nickname of the Web server definition.
- Specify a nickname for the Web server. Click Next when you are finished.
The wizard uses the value to name configuration folders in the plug-ins installation root directory. The wizard also uses the name in the configuration script for the appserver to name the Web server definition.
If the appserver profile already has a Web server definition, delete the Web server definition before continuing...
$AdminTask deleteServer { -serverName webserver1 -nodeName webserver1_node }
$AdminTask removeUnmanagedNode { -nodeName webserver1_node }
$AdminConfig saveIn these commands, webserver1 is the Web server name.
- Accept the default location for the plugin-cfg.xml file that the wizard creates on the Web server machine, then click Next.
You can type a change to the value or click Browse to select a file in another location. If you do not accept the default location, the plugin-cfg.xml file must exist.
- Identify the host name or IP address of the appserver machine, then click Next.
- Examine the summary panel. Click Next when you are finished.
The panel notifies you that you have manual steps to perform to complete the installation and configuration. The type of Web server, the nickname of the Web server, and the location of the plugin-cfg.xml file displays on the panel.
The Plug-ins installation wizard creates the script...
configureWeb_server_name/plugins_root/bin/
...on webserver machine.
The Plug-ins installation wizard also creates the file...
plugins_root/config/Web_server_name/plugin-cfg.xml
The Web server reads the plugin-cfg.xml file to determine the applications that the appserver on appserver machine can serve to the Web server on webserver machine. Whenever the configuration changes, the appserver regenerates the file.
When regeneration occurs, propagate the new plugin-cfg.xml file from the appserver machine to the Web server machine.
You can automatically propagate the file to an IBM HTTP Server instance.
- Click Next on the pre-installation summary panel to begin the installation or click Back to change any characteristics of the installation.
The panel specifies the...
- Plug-ins installation root directory
- Web server plug-ins
- Disc size of the code
- After the wizard installs the code and creates the uninstaller program, examine the post-installation summary panel. Click Next when you are finished to display the Plug-ins installation roadmap.
The Plug-ins installation wizard installs the binary plug-in module. On a Linux system, for example, the installation creates...
plugins_root
The directory...
plugins_root/config/Web_server_name
...contains the plugin-cfg.xml file.
The wizard displays the name and location of the configuration script and the plugin-cfg.xml file. The wizard also displays the type of Web server that is configured and the nickname of the Web server.
If a problem occurs and the installation is unsuccessful, examine the logs in...
plugins_root/logs
Correct any problems and reinstall.
- Close the road map and click Finish to exit the wizard.
Log files from the installation are in...
plugins_root/logs/install
- Copy...
plugins_root/bin/configureWeb_server_name[sh|bat]
...from webserver machine to...
app_server_root/bin
...on appserver machine.
Web_server_name is the nickname of the Web server specified in step 12. Web_server_name is not a vendor name, such as IIS or Apache.
- If one platform is a system such as AIX or Linux and the other is a Windows platform, copy the script from the crossPlatformScripts directory. For example:
- For *nix...
plugins_root/bin/configureWeb_server_name.sh
- For Windows...
plugins_root/bin/crossPlatformScripts/configureWeb_server_name.bat
Compensate for file encoding differences to prevent script failure.
The content of...
configureWeb_server_name.sh|bat
...can be corrupt if the default file encoding of the two machines differs. This scenario is possible when one machine is set up for a double-byte character set (DBCS) locale and the other machine is not.
Determine the file encoding and use one of the following procedures to circumvent the failure. To determine the default file encoding, run the appropriate command.
- For *nix run the following command on a system such as AIX or Linux:
locale
- For Windows run the following command on a Windows machine:
CHCP
Use the result of the command on each machine as the value of the variable...
web_server_machine_encoding
...and the variable...
application_server_machine_encoding
...in one of the following procedures.
Procedures for compensating for encoding differences...
Suppose that the Web server is running on a Linux machine and ND is running on a Windows machine.
Web server running on a system such as AIX or Linux...
Run the following command on the system to encode the script file that configures the Web server definition, before you FTP the file to the Windows machine in binary mode:
iconv -f web_server_machine_encoding \ -t application_server_machine_encoding \ configureWeb_server_name.batThe nickname of the Web server is used in the name of the script file. The name cannot contain characters from a DBCS if you intend to set up IBM HTTP Server for automatic propagation.
Suppose that the Web server is running on a Windows machine and ND is running on a machine with a system such as AIX or Linux.
Web server running on a Windows machine...
Run the following command on the machine with a system such as AIX or Linux to encode the script file that configures the Web server definition, after you FTP the file in binary mode:
iconv -f web_server_machine_encoding \ -t application_server_machine_encoding \ configureWeb_server_name.shIf the conversion mapping is not supported by the iconv command on your system, copy the contents of the Web server configuration script to a clip board and paste it onto the machine where the appserver is running.
- For *nix...
-
Start the appserver on appserver machine.
If running a managed node, start using the dmgr console. If running a stand-alone appserver...
-
profile_root/bin/startServer.sh server1
- Open a command window and change to the profile directory where the Web server should be assigned. Run the script that you copied to appserver machine. You will need the following parameters:
Profile Name (Optional) Admin user ID (Optional) Admin user password
For example:
configurewebserver1.sh Dmgr01 myUserID myPassword
The webserver will be configured via wsadmin.
- From the console of the deployment manager, click...
System administration | Save Changes to Master Repository | Synchronize changes with Nodes | Save
- For Domino Web server only set the environment variable...
WAS_PLUGIN_CONFIG_FILE
- Regenerate the plugin-cfg.xml file on appserver machine using the console.
Click...
Servers | Web server | Web server | Generate Plug-in
During the installation of the plug-ins, the default plugin-cfg.xml file is installed on webserver machine in...
plugins_root/config/Web_server_name
The Web server plug-in configuration service regenerates the plugin-cfg.xml file automatically. To use the current plugin-cfg.xml file from the appserver, propagate the plugin-cfg.xml file.
WAS is configured to automatically regenerate the file each time a significant event occurs . Such events include...
- Installing applications on the appserver and the Web server
- Creating a new virtual host
- Propagate the plugin-cfg.xml file from the appserver to the Web server using the console. Click...
Servers | Web server | Web server | Propagate Plug-in
The Web server plug-in configuration service propagates the plugin-cfg.xml file automatically for IBM HTTP Server 6.0 only.
Web servers other than IBM HTTP Server require manual propagation.
For all other Web servers, propagate the plug-in configuration file by manually copying the plugin-cfg.xml file from...
profile_root/config/cells/cell_name/nodes/node_name/servers/Web_server_name
...on appserver machine to...
plugins_root/config/Web_server_name
...on webserver machine.
- Start the Snoop servlet to verify the ability of the Web server to retrieve an application from the Application Server.
Test your environment by starting your Application Server, your Web server, and using the snoop servlet with an IP address.
- Start the Application Server.
In a ND environment, the Snoop servlet is available in the cell only if you included the DefaultApplication when adding the Application Server to the cell. The -includeapps option for the addNode command migrates the DefaultApplication to the cell.
If the application is not present, skip this step.
If running a managed node, start using the dmgr console. If running a stand-alone appserver...
- cd profile_root/bin
./startServer.sh server1 - Start the IBM HTTP Server or the Web server that you are using.
Use a command window to change the directory to the IBM HTTP Server installed image, or to the installed image of your Web server. Issue the appropriate command to start the Web server, such as these commands for IBM HTTP Server:
To start the IBM HTTP Server...
- *nix
./apachectl start
- Windows
apache
- *nix
- Point your browser to...
http://localhost:9080/snoop
...to test the internal HTTP transport provided by the Application Server. Point your browser to...
http://Host_name_of_Web_server_machine/snoop
..to test the Web server plug-in.
The HTTP Transport port is 9080 by default and must be unique for every profile. The port is associated with a virtual host named default_host, which is configured to host the installed DefaultApplication and any installed Samples. The snoop servlet is part of the DefaultApplication. Change the port to match your actual HTTP Transport port.
- Verify that snoop is running.
Either Web address should display the Snoop Servlet - Request/Client Information page.
- Remote IBM HTTP Server only:
Verify that the automatic propagation function can work on a remote IBM HTTP Server by using the following steps. This procedure is not necessary for local Web servers.
- Create a user=adminUser, password=adminPassword in the...
/conf/admin.passwd
For example:
c:\ws\ihs60\bin\htpasswd -cb c:\ws\ihs60\conf\admin.passwd adminUser adminPassword
- Use the console of the deployment manager or the Application Server to enter the User ID and password information that you created for the administrative user of IBM HTTP Server. Go to...
Servers | Web server | Web_server_definition | Remote Web server administration
Set the following values:
- admin Port=8008
- User Id=adminUser
- Password=adminPassword
- Set the correct read/write permissions for the httpd.conf file and the plugin-cfg.xml file. See...
IHS_root/logs/admin_error.log
Automatic propagation of the plug-in configuration file requires the IBM HTTP administrative server to be up and running. If you are managing an IBM HTTP Server using the console, the following error might display:
"Could not connect to IHS Administration server error"
Perform the following procedure to correct the error:- Verify that the IBM HTTP Server administration server is running.
- Verify that the Web server host name and the port that is defined in the
console matches the IBM HTTP Server administration host name and port.
- Verify that the fire wall is not preventing you from accessing the IBM
HTTP Server administration server from the WAS administrative console.
- Verify that the user ID and password that is specified in the WebSphere
Application Server console under remote managed, is created in the admin.passwd file, using the htpasswd command.
- If you are trying to connect securely, verify that you export the IBM
HTTP Server administration server keydb personal certificate into the WebSphere
Application Server key database as a signer certificate. This key database is specified by the com.ibm.ssl.trustStore directive in the sas.client.props file in the profile where your console is running. This consideration is primarily for self-signed certificates.
- If you still have problems, check the IBM HTTP Server admin_error.log file and the WAS logs (trace.log file) to determine the cause of the problem.
- Create a user=adminUser, password=adminPassword in the...
- Start the Application Server.
Results
This procedure results in the installation of the Web server plug-ins for WAS on a Web server machine. The Plug-ins installation wizard also configures the Web server to support an appserver on a separate machine. The installation of the binary plug-in modules results in the creation of the Plugins directory and several subdirectories. The following directories are among those created on a Linux system...
- plugins_root/uninstall contains the uninstaller program
- plugins_root/bin contains the binary plug-ins for all supported Web servers
- plugins_root/logs contains log files
- plugins_root/properties contains version information
- plugins_root/roadmap contains the roadmap for the Plug-ins installation wizard
What to do next
- Select a Web server topology diagram and roadmap
- Web server configuration
- Plug-ins configuration
- Edit Web server configuration files
Related tasks
Installing Web server plug-ins