Configure a Web server and an application server profile on the same machine
Overview
This topic describes installing a Web server plug-in that WAS (WAS) provides to communicate with a particular brand of Web server. This procedure describes installing the Web server and its Web server plug-in for WAS and the Application Server on the same machine .
The wizard performs three steps to properly configure a Web server for V6. The wizard performs the steps in the following order:
- The wizard installs the unique binary plug-in module for the supported Web server after collecting the following information:
- The type of Web server
- The location of the configuration file for the Web server that the wizard configures
- The plug-ins installation root directory for the Web server plug-in modules that the wizard installs
- The installation root directory of the WAS product, where the wizard creates a Web server definition
- The wizard prompts you for the location of the configuration file or files for the Web server. You must browse for and select the correct file.
The wizard edits the configuration file or files for a Web server by creating directives that point to the location of the binary plug-in module and the plug-in configuration file.
The name of the binary plug-in module varies per Web server type. The plug-in configuration file is always the plugin-cfg.xml file.
- The wizard creates a Web server definition in the configuration of the application server unless one already exists.
Use the administrative console to manage the Web server configuration. For example, when you install an application on the application server, one can also choose to install it on the Web server definition. If so, the updated plugin-cfg.xml file shows that the new application is available. When the Web server reads the updated plug-in configuration file, the Web server becomes aware of the new application that it can serve to Web clients.
If you choose not to install the new application on the Web server definition, the application is not added to the plug-in configuration file. The Web server is not aware of the application and cannot serve it to Web clients.
Use the following procedure to install the Web server plug-in, configure the Web server, and create a Web server definition in the default application server profile.
Before you begin
If the WAS product family supports a particular brand of Web server, such as IBM HTTP Server or IIS, then your WAS product provides a binary plug-in for the Web server that install.
If you are downloading install images from PartnerWorld, the WAS ND distro C5886ML contains the installation wizard.
If the WAS product family does not provide a binary plug-in for a particular brand of Web server, then the Web server is not supported. The purpose of the binary plug-in is to provide the communication protocol between the Web server and the application server.
Suppose that you create a new profile. Suppose also that you want to use a Web server. You must install a new Web server for the new profile and use the Plug-ins installation wizard to install the binary plug-in module and to configure both the Web server and the application server.
If the Web server is not already installed, one can still install the plug-ins for future use. If the WAS product is not installed, one can still install the plug-ins. However, it is recommended that you install the Web server and the WAS product before installing the plug-ins for the supported Web server.
This procedure configures the application server profile that is the default profile on the machine. A one-to-one relationship exists between a Web server and the application server.
This topic describes how to create the following topology:
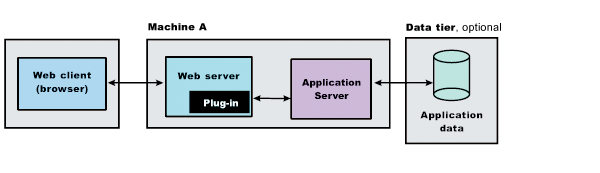
The set of steps leading up to the next diagram show how to configure a stand-alone application server. The set of steps after the next diagram show how to configure an application server that is federated into a deployment manager cell.
Procedure
- Log on as root on a Linux or UNIX operating system, or as a member of the administrator group on a Windows system.
- In addition, verify that the
umask setting is 022. To verify the umask setting, issue the following command
umask
To set the umask setting to 022, issue the following command
umask 022
- Some steps of the installation on a Windows
platform require the administrator group user to have the following advanced
user rights:
- Act as part of the operating system
- Log on as a service
For example, on some Windows systems, click...
Administrative Tools | Local Security Policy | User Rights Assignments
...to see the advanced options. See your Windows documentation for more information.
The installation wizard grants your Windows user ID the advanced user rights, if the user ID belongs to the administrator group. The silent installation does not grant these rights. If you create a new user ID on a Windows platform to perform a silent installation, restart the system to activate the proper authorizations for the user ID before we can perform a successful silent installation.
When installing the WAS as a Windows service, do not use a user ID that contains spaces. A user ID with spaces cannot be validated. Such a user ID is not allowed to continue the installation. To work around this problem, install with a user ID that does not contain spaces, or do not choose to install Windows services.
- Install WAS Network Deployment on Machine A.
- Install the IBM HTTP Server or another supported Web server on Machine A.
- Launch the Plug-ins installation wizard on the machine with the Web server.
- Select the Plug-ins installation wizard from the launchpad or change directories to the plugin directory on the product disc or in the downloaded installation image and issue the install command.
- Stop the stand-alone application server before installing the Web server plug-ins. For example,...
/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer/profiles/default/bin/stopServer.sh server1
- Clear the check box for the roadmap or select the check box to view the roadmap, then click Next.
- If you are unsure of which installation scenario to follow, display the roadmap instead. Print and keep the roadmap as a handy overview of the installation steps.
- Press Ctrl-P to print the roadmap if the Web browser navigation controls and the menu bar are not present on the browser window that displays the Plug-ins roadmap. Press Ctrl-W to close the browser window if the navigation controls and the menu bar do not display. Or close the browser window with the window control in the title bar.
- Read the license agreement and accept the agreement it if you agree to its terms. Click Next when you are finished.
- If your system does not pass the prerequisites check, stop the installation, correct any problems, and restart the installation. If your system passes the prerequisites check, click Next.
- Look for the appropriate log file for information about missing prerequisites:
- If you stop the installation, see the temporaryPluginInstallLog.txt file in the temporary directory of the user who installed the plug-ins. For example, the /tmp/temporaryPluginInstallLog.txt file might exist if the root user installed the plug-ins on a Linux or UNIX system.
- If you continue the installation in spite of warnings about missing prerequisites, see the plugins_install_root/logs/install/log.txt file after the installation is complete.
See Troubleshooting installation for more information about log files.
- Select the type of Web server that you are configuring and click Next.
The Plug-ins installation wizard panel prompts you to identify the Web servers to configure. Actually one can select only one Web server each time you run the Plug-ins installation wizard.
- Stop any Web server while you are configuring it. A step later in the procedure directs you to start the Web server as you begin the snoop servlet test.
If you select the Web server identification option labeled None, the Web server installs the binary plug-ins but does not configure the Web server. A known problem in the wizard panel causes the English word None to appear in translated versions of the wizard. However, the selectable option is functional in every locale in spite of the missing translation.
- Select Application Server machine (local) and click Next.
Accept the default location for the installation root directory for the plug-ins. Click Next.
We can type another new directory or click Browse to select an empty directory. The fully qualified path identifies the plug-ins installation root directory.
The default location is:
- /usr/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins
- C:\Program Files\IBM\WebSphere\Plugins
A possibility exists that the Web server might run on a platform that WAS does not support.
- Click Browse on the Application Server installation location panel to browse for the location of the Application Server profile, if necessary. Click Next when the installation root directory is correct.
The fully qualified path identifies the installation root directory for the WAS product.
The default location is:
- /usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/AppServer
- C:\Program Files\IBM\WebSphere\AppServer
- Click Browse to select the configuration file for your Web server, verify that the Web server port is correct, and then click Next when you are finished.
- Select the file and not just the directory of the file. Some Web servers have two configuration files and require you to browse for each file.
The following list shows configuration files for supported Web servers:
- Apache HTTP Server
- apache_install_root/config/httpd.conf
- Domino Web Server
- names.nsf and Notes.jar
- The wizard prompts for the notes.jar file. The actual name is Notes.jar.
The Plug-ins installation wizard verifies that the files exist but the wizard does not validate either file.
- The wizard prompts for the notes.jar file. The actual name is Notes.jar.
- IBM HTTP Server
- ihs_install_root/conf/httpd.conf
- Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS)
- The Plug-ins installation wizard can determine the correct files to edit.
- Sun ONE Web Server 6.0 or Sun Java System Web Server, V6.1
- obj.conf and magnus.conf
The wizard displays a naming panel for the nickname of the Web server definition.
- Specify a nickname for the Web server. Click Next when you are finished.
- The wizard uses the value to name configuration folders in the plug-ins installation root directory. The wizard also uses the name in the configuration script for the application server to name the Web server definition.
- If the application server profile already has a Web server definition, delete the Web server definition before continuing. Use the following commands to delete the Web server definition
$AdminTask deleteServer { -serverNamewebserver1 -nodeName webserver1_node } $AdminTask removeUnmanagedNode { -nodeName webserver1_node } $AdminConfig save
- Specify the location for the plugin-cfg.xml file and click Next.
This is a critical selection.
See Configuration behavior of the Plug-ins installation wizard for a description of the logic that determines what path is configured by default. The following possibilities exist for the default location of the plug-in configuration file. The wizard determines the characteristics of the application server to determine the best path for the file:
- An application server that has an existing Web server definition has the
following path
plug-ins_install_root/config/server/plugin-cfg.xml
- A stand-alone application server that does not have a Web server definition
has the following path
was_install_root/profiles/profile/config/cells/cell/nodes/server/servers/server/plugin-cfg.xml
- An application server that has an existing Web server definition has the
following path
- We can accept the default value if the application server does
not have a Web server definition.
Using an existing Web server definition
If the application server has a Web server definition, the wizard cannot create a new Web server definition within the application server configuration. However, the wizard can reconfigure the Web server. Click Browse and select the existing plugin-cfg.xml file in the application server configuration.
To find the plug-in configuration file in a stand-alone application server, follow this file path
was_install_root/profiles/profile /config/cells/cell/nodes/ Web_servername_node/servers/ Web_servername/plugin-cfg.xml
If the existing Web_servername is different than the nickname that you gave the Web server in the wizard, click Back to return to the naming panel for the Web server and change the name to match the existing Web server definition name.
If one cannot find an existing plugin-cfg.xml file after all, install the temporary plugin-cfg.xml file. In such a case, type the path to the plug-ins installation root directory so that the wizard can install the temporary plug-in configuration file
plug-ins_install_root/config/server/plugin-cfg.xml
- Click Next after verifying the characteristics of the plug-ins
installation or click Back to make changes.
Once created, a Web server definition on a stand-alone application server node cannot be removed except through scripting. (See Uninstalling the Web server plug-ins for WAS for the procedure.)
We can, however, reuse the same definition for a different type of Web server. Run the Plug-ins installation wizard to configure a new Web server in that situation. The Plug-ins installation wizard configures the new Web server to use the existing plugin-cfg.xml file.
- Click Next on the pre-installation summary panel to begin the installation or click Back to change any characteristics of the installation. The wizard begins installing the plug-ins and configuring the Web server and the application server.
The wizard shows an installation status panel as it installs the plug-ins.
The wizard displays the Installation summary panel at the completion of the installation.
- Verify the success of the installation on the Installation summary
panel and click Finish to exit the wizard.
If a problem occurs and the installation is unsuccessful, examine the logs in the plug-ins_install_root/logs directory. Correct any problems and reinstall.
- Domino Web Server only: Set the WAS_PLUGIN_CONFIG_FILE environment variable.
To configure Domino, set the WAS_PLUGIN_CONFIG_FILE environment variable. On Linux and UNIX-based platforms, sourcing a script to the parent shell allows child processes to inherit the exported variables. On Windows systems, run the script as you would run any other command. Sourcing is automatic on Windows systems.
- Open a command window.
- Change directories to the plug-ins installation root directory.
- Issue the appropriate command for the plug-ins_install_root/bin/setupPluginCfg.sh script:
- . plug-ins_install_root/bin/setupPluginCfg.sh (Notice the space between the period and the installation root directory.)
- source plug-ins_install_root/bin/setupPluginCfg.sh
The script is also in the lotus_install_root/notesdata directory on Linux and UNIX systems.
Issue the appropriate command for the script before starting the Domino Web Server.
- Start the Snoop servlet to verify the ability of the Web server to retrieve an application from the Application Server.
- Test your environment by starting your Application Server, your Web server, and using the snoop servlet with an IP address.
- Start the Application Server. In a Network Deployment environment, the Snoop servlet is available in the cell only if you included the DefaultApplication when adding the Application Server to the cell. The -includeapps option for the addNode command migrates the DefaultApplication to the cell. If the application is not present, skip this step.
Change directories to the install_root/profiles/profile/bin directory and run the startServer command:
- ./startServer.sh server1
- startServer server1
- Start the IBM HTTP Server or the Web server that you are using.
Use a command window to change the directory to the IBM HTTP Server installed image, or to the installed image of your Web server. Issue the appropriate command to start the Web server, such as these commands for IBM HTTP Server:
To start the IBM HTTP Server from the command line:
Access the apache and apachectl commands in the IBMHttpServer/bin directory.
- ./apachectl start
- apache
- Point your browser to http://localhost:9080/snoop to test the internal HTTP transport provided by the Application Server. Point your browser to http://Host_name_of_Web_server_machine/snoop to test the Web server plug-in.
The HTTP Transport port is 9080 by default and must be unique for every profile. The port is associated with a virtual host named default_host, which is configured to host the installed DefaultApplication and any installed Samples. The snoop servlet is part of the DefaultApplication. Change the port to match your actual HTTP Transport port.
- Verify that snoop is running.
Either Web address should display the Snoop Servlet - Request/Client Information page.
- Remote IBM HTTP Server only: Verify that the automatic propagation function can work on a remote IBM HTTP Server by using the following steps. This procedure is not necessary for local Web servers.
- Create a user=adminUser, password=adminPassword in the IHS_install_root /conf/admin.passwd file. For example: c:\ws\ihs60\bin\htpasswd -cb c:\ws\ihs60\conf\admin.passwd adminUser adminPassword
- Use the administrative console of the deployment manager or the Application Server to enter the User ID and password information that you created for the administrative user of IBM HTTP Server. Go to Servers > Web server > Web_server_definition > Remote Web server administration. Set the following values: admin Port=8008, User Id=adminUser, Password=adminPassword.
- Set the correct read/write permissions for the httpd.conf file and the plugin-cfg.xml file. See the IHS_install_root /logs/admin_error.log file for more information.
Automatic propagation of the plug-in configuration file requires the IBM HTTP administrative server to be up and running. If you are managing an IBM HTTP Server using the WAS administrative console, the following error might display
"Could not connect to IHS Administration server error"
Perform the following procedure to correct the error:
- Verify that the IBM HTTP Server administration server is running.
- Verify that the Web server host name and the port that is defined in the WAS administrative console matches the IBM HTTP Server administration host name and port.
- Verify that the fire wall is not preventing you from accessing the IBM HTTP Server administration server from the WAS administrative console.
- Verify that the user ID and password that is specified in the WAS administrative console under remote managed, is created in the admin.passwd file, using the htpasswd command.
- If you are trying to connect securely, verify that you export the IBM HTTP Server administration server keydb personal certificate into the WAS key database as a signer certificate. This key database is specified by the com.ibm.ssl.trustStore directive in the sas.client.props file in the profile where your administrative console is running. This consideration is primarily for self-signed certificates.
- If you still have problems, check the IBM HTTP Server admin_error.log file and the WAS logs (trace.log file) to determine the cause of the problem.
Configure a Web server and a distributed application server profile on the same machine.
The rest of these steps describe how to configure an application server that is federated into a deployment manager cell.
The following topology is considered a local distributed topology because it involves a cell:
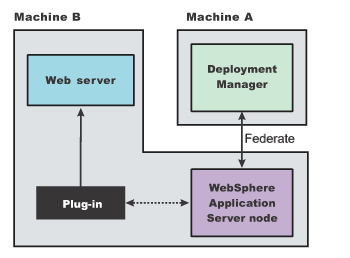
This part of the procedure assumes that you have already installed the Network Deployment product on both machines. Also assumed is that you have already configured a deployment manager profile on Machine A and an application server profile on Machine A.
If you are planning to add the application server node into a deployment manager cell but have not done so yet, start the deployment manager and federate the node before installing the plug-in. We cannot add an application server with a Web server definition into the deployment manager cell.
A Web server definition on a federated application server is installed on the same managed node as the application server. There is one node, but with two server processes, the application server and the Web server definition.
If you are installing the plug-ins for use with a federated application server, start the deployment manager. Verify that the node agent process on the managed node is also running. Both the deployment manager and the node agent must be running to successfully configure a managed node.
- Start the Application Server. In a Network Deployment environment, the Snoop servlet is available in the cell only if you included the DefaultApplication when adding the Application Server to the cell. The -includeapps option for the addNode command migrates the DefaultApplication to the cell. If the application is not present, skip this step.
- Install IBM HTTP Server or another supported Web server on Machine A.
See Installing IBM HTTP Server or refer to the product documentation for your Web server for more information.
- Launch the Plug-ins installation wizard on the machine with the Web server.
- Clear the check box for the roadmap or select the check box to view the roadmap, then click Next.
- Read the license agreement and accept the agreement it if you agree to its terms, then click Next.
- If your system does not pass the prerequisites check, stop the installation, correct any problems, and restart the installation. If your system passes the prerequisites check, click Next.
- Select the type of Web server that you are configuring, then click Next.
- Select Application Server machine (local) and click Next.
- Accept the default location for the installation root directory for the plug-ins, then click Next.
- Click Browse on the Application Server installation location panel to browse for the location of the Application Server profile, if necessary. Click Next when the installation root directory is correct.
- Click Browse to select the configuration file for your Web server, verify that the Web server port is correct, and then click Next.
- Specify a nickname for the Web server, then click Next.
- Specify the location for the plugin-cfg.xml file and click Next.
This is a critical selection. A federated application server that does not have a Web server definition has the following path
was_install_root/profiles/profile/config/cells/cell/nodes/node/servers/Web_servername/plugin-cfg.xml
An application server that has an existing Web server definition has the following path
plug-ins_install_root/config/server/plugin-cfg.xml
See Configuration behavior of the Plug-ins installation wizard for a description of the logic that determines what path is configured by default.
- Click Next after verifying the characteristics of the plug-ins installation or click Back to make changes.
Use the administrative console of the deployment manger to delete an existing Web server or to create new ones. Federated nodes can have more than one Web server definition.
- Click Next on the pre-installation summary panel to begin the installation or click Back to change any characteristics of the installation.
The wizard begins installing the plug-ins and configuring the Web server and the application server.
The wizard shows an installation status panel as it installs the plug-ins.
The wizard displays the Installation summary panel at the completion of the installation.
- Verify the success of the installation on the Installation summary panel and click Finish to exit the wizard.
- Complete the installation by creating the Web server definition.
Use the administrative console of the deployment manager to create the Web server definition on a federated node. Or, one can run the configuration script that the Plug-ins installation wizard created.
The script already contains all of the information that gather when using the administrative console option.
Select one of the following options:
- Using the administrative console
Click Servers > Web servers > New and use the Create new Web server entry wizard to create the Web server definition.
- Run the configuration script
Issue the appropriate command from a command window:
- ./plug-ins_install_root/bin/configureWeb_servername.sh
- plug-ins_install_root\bin\configureWeb_servername.bat
If you have enabled security or changed the default JMX connector type, edit the script and include the appropriate parameters on the wsadmin command.
- Using the administrative console
- From the administrative console of the deployment manager, click System administration > Save Changes to Master Repository > Synchronize changes with Nodes > Save.
- Source the Domino Web server script if necessary.
Start the snoop servlet.
See the snoop procedure for the stand-alone application server for the full procedure.
Result
The installation of the binary plug-in modules results in the creation of the Plugins directory and several subdirectories. The following directories are among those created on a Linux system, for example:
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/_uninstPlugin/_jvmForPlugin contains the WAS SDK, Java technology edition used to uninstall the product
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/_uninstPlugin contains the uninstaller program
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/bin contains the binary plug-ins for all supported Web servers
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/logs contains log files
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/properties contains version information
- /opt/IBM/WebSphere/Plugins/roadmap contains the roadmap for the Plug-ins installation wizard
The Plug-ins installation wizard creates a Web server definition within the application server profile unless one already exists.
The Plug-ins installation wizard configures the Web server to use...
profiles_install_root/profile/plugin-cfg.xml
The application server regenerates the Web server plug-in configuration file, plugin-cfg.xml whenever an event occurs that affects the file. Such events include the addition or removal of an application, server, or virtual host. The stand-alone application server regenerates the file in the following location
was_install_root/profiles/profile/config/cells/cell/nodes/server/servers/server/plugin-cfg.xml
On a federated node, the creation or removal of clusters and cluster members also causes file regeneration. The deployment manager regenerates the file for a federated application server in the following location
was_install_root/profiles/profile/config/cells/cell/nodes/node/servers/server/plugin-cfg.xml
What to do next
We can start a stand-alone application server and the Web server immediately after installing of the binary plug-in for the local Web server. Open the administrative console of the application server after you start the server and save the changed configuration.
After installing the binary plug-in for the local Web server, one can start a federated application server and the Web server after running the configuration script that completes the installation. Open the administrative console of the deployment manager. Wait for node synchronization to occur. Save the changed configuration that includes the new Web server definition.
See Also
Select a Web server topologyConfiguration behavior of the Plug-ins installation wizard
Web server configuration
Edit Web server configuration files
Install Web server plug-ins
Configuration behavior of the Plug-ins installation wizard
Web server configuration