Functional overview
Understand the key concepts, components, and architecture
of Federated Directory Server.
The following diagram illustrates the various components of Federated Directory Server, which
are described next.
Federated Directory Server components
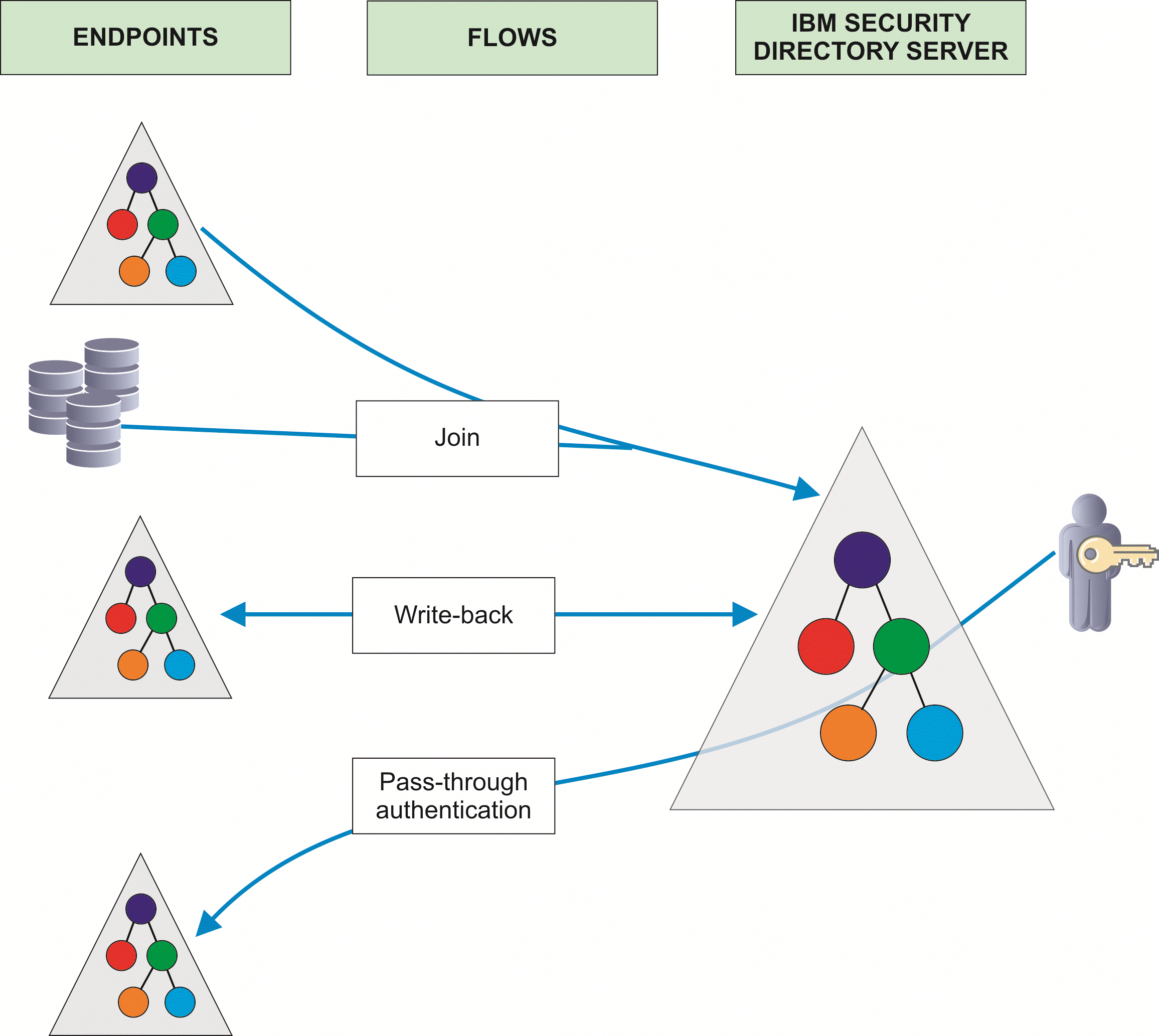
- Directory Server
- The Security Directory Server,
which is the target for all flows in the project.
- Endpoint
- A configured source system that can provide data in a flow. The endpoint types that are currently available are Active Directory,
Custom AssemblyLine, File, JDBC, LDAP, IBM Security Directory Server and
Sun Directory.
- Flow
- A configuration that defines the relationship between the endpoints
and the target IBM Security Directory Server.
You must create flows only after you configure the target Directory Server connection settings and add one or more endpoints.
- Attribute maps
- A map used to convert the attribute from the source schema
to the corresponding attribute in the target schema. In Federated Directory Server you
can apply one of the ready-to-use attribute maps or a customized attribute
map to a flow operation.
- Join
- A configured source system that provides data that augments and
enriches the data from the endpoint. If you configure a flow to specify
a join with the endpoint, the entries are processed in the following
manner:
- An entry comes in from the endpoint.
- The flow looks it up on the join data source.
- The entry is merged with the data from the endpoint.
- The merged data is added to the target directory server.
- Pass-through authentication
- A feature of IBM Security Directory Server where
a user can be authenticated by delegating authentication to a different
LDAP server. A flow contains a section for pass-through authentication.
When you enable pass-through authentication for a flow, it configures IBM Security Directory Server to
use the credentials that are stored in the endpoint for authenticating
users that originate from that flow.
Parent topic:
Overview
