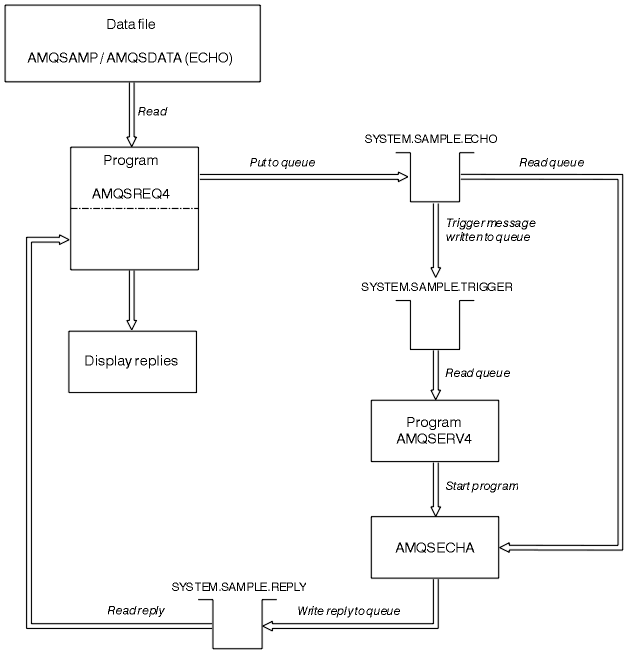
Design of the Request sample program
The program opens the target server queue so that it can put messages. It uses the MQOPEN call with the MQOO_OUTPUT option. If it cannot open the queue, the program displays an error message containing the reason code returned by the MQOPEN call.
The program then opens the reply-to queue called SYSTEM.SAMPLE.REPLY so that it can get reply messages. For this, the program uses the MQOPEN call with the MQOO_INPUT_EXCLUSIVE option. If it cannot open the queue, the program displays an error message containing the reason code returned by the MQOPEN call.
For each line of input, the program then reads the text into a buffer and uses the MQPUT call to create a request message containing the text of that line. On this call the program uses the MQRO_EXCEPTION_WITH_DATA report option to request that any report messages sent about the request message will include the first 100 bytes of the message data. The program continues until either it reaches the end of the input or the MQPUT call fails.
The program then uses the MQGET call to remove reply messages from the queue, and displays the data contained in the replies. The MQGET call uses the MQGMO_WAIT, MQGMO_CONVERT, and MQGMO_ACCEPT_TRUNCATED options. The WaitInterval is 5 minutes in the COBOL version, and 1 minute in the C version, for the first reply (to allow time for a server application to be triggered), and 15 seconds for subsequent replies. The program waits for these periods if there is no message on the queue. If no message arrives before this interval expires, the call fails and returns the MQRC_NO_MSG_AVAILABLE reason code. The call also uses the MQGMO_ACCEPT_TRUNCATED_MSG option, so that messages longer than the declared buffer size are truncated.
The program demonstrates how to clear the MsgId and CorrelId fields of the MQMD structure after each MQGET call because the call sets these fields to the values contained in the message it retrieves. Clearing these fields means that successive MQGET calls retrieve messages in the order in which the messages are held in the queue.
The program continues until either the MQGET call returns the MQRC_NO_MSG_AVAILABLE reason code or the MQGET call fails. If the call fails, the program displays an error message that contains the reason code.
The program then closes both the target server queue and the reply-to queue using the MQCLOSE call.