IBM BPM, V8.0.1, All platforms > Authoring services in Integration Designer > Services and service-related functions > Building mediation flows
Contributing your own mediation primitive plug-in
You can develop your own mediation primitives, and contribute them to the Mediation Flow editor palette. Integration developers can then use these mediation primitives in the same way that you use the supplied mediation primitives, for example Message Filter.
The following topics briefly describe the actions that you have to perform to develop your own mediation primitive, contribute the primitive to the palette in the mediation flow editor, and deploy the primitives. We then use an example to show the steps required, and provide links to reference documentation.
- Create a plug-in project
- Generate the mediation metadata
- Author Java code
- Deploy the plug-in
- Deploy the primitives to the run time
- Example
- Elements of the properties xml file
- Mediation primitive property group schema definition
- References
These steps might change in future releases, and effort might be required to re-enable your contributions for future releases.
Create a plug-in project
Create a plug-in for your primitives in the eclipse plug-in development environment (PDE), with these definitions:
- Create a plug-in project.
- Create these extensions in the plugin.xml:
- com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveHandlers - defines the terminals of your primitive, and identifies the properties file where the properties of the primitive are defined, and the .mednode file that you will generate in topic "Generate the mediation metadata".
- com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveUIContribution - builds on medationPrimitiveHandler and adds information to contribute the medationPrimitiveHandler to the palette in the mediation flow editor.
- The typeName and typeNamespace of the medationPrimitiveHandler and the mediationPrimitiveUIContribution must be the same in order to allow the mediationPrimitiveUIContribution to be associated with the medationPrimitiveHandler .
- The typeNamespace must begin with mednode://mednodes, and end with FileName.mednode. A file of this name will be created when we generate the mediation metadata.
- Create a property group XML file, and define the properties of the mediation primitive in the XML file. For your reference, the schema for this file is attached in the References section at the bottom of this document.
Generate the mediation metadata
Generate the mediation metadata (.mednode file) for the mediation primitive by launching a runtime workbench, and then using the Mediation Development view in the runtime workbench. The .mednode file contains the runtime representation of the mediationPrimitiveHandlers and must be placed at the root of the Java™ project created in Step 3.
Author Java code
Create a Java project, and write the code to implement your mediation primitive.
- Create a Java project
- Add library WebSphere ESB Server v7.5 to the build path of the project.
- Copy the .mednode file from the plug-in project to the root of the Java project.
- Create a Java class that extends com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.esb.ESBMediationPrimitive, and define a getter and a setter method for each property defined
in the property group file.
If : the getter and setter method names must correspond to the property names.For example, if a property name is value, the getter and setter methods must be named getValue() and setValue().
- Write your Java implementation code for the mediation primitive in the inherited mediate() method. The mediate method takes an InputTerminal and a DataObject. Use the InputTerminal only if you have multiple input terminals. The DataObject is your message. You can use the getters and setters in the DataObject interface to read and write the values in your messages, identified via an XPath expression. DataObject is part of the Service Data Object (SDO) emerging standard. This message parameter can also be cast to a ServiceMessageObject in the com.ibm.websphere.sibx.smobo package, part of the Service Message Object APIs. This interface is useful for accessing individual sections of the service message object, such as the body, context and headers. The example here will show you how to fire a message to an output terminal.DataObject See the Reference section at the bottom of this document for links to the Service Data Object and Service Message Object APIs.
Deploy the plug-in
Deploy your plug-in so that your mediation primitives appear in the Mediation Flow Editor palette:
- Set build properties for your plug-in project. Make sure the Binary Build properties include the mednodes, propertygroups and icons folders.
- Import the icons for your primitive into the plug-in project.
- Export the plug-in project as Deployable plug-ins and fragments option to the directory IIDInstallDir
- Shut down IBM Integration Designer.
- Restart IBM Integration Designer using the –clean option.
- Open a mediation flow component in the Mediation Flow Editor.
The icons for your primitive are in the palette.
- Drag the icon onto the canvas, and view the properties in the Properties view.
Deploy the primitives to the run time
To deploy your mediation primitives to the WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus or IBM BPM run time:
- Export the Java project
as a jar, for example myPrimitives.jar. In the root folder, select .mednode only, but keep the Java class
selected.
The .mednode files must be within the root of the deployed jar, not in a subdirectory.
- Select directory WAS_HOME/lib/ext where the WebSphere run time can access the classes at the right class loader scope.
Example
- Create a plug-in project
-
- Open the Plug-in Development perspective from Window > Open Perspective > Other and choose Plug-in Development from the list.
- Create a plug-in project from File > New > Plug-in Project.
- Enter com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.contribution as the project name. Keep the default options, and click Next.
- Clear the option to generate a Java class and click Finish.
- Edit plugin.xml
- In the Plug-ins view, open plugin.xml in the Plug-in Manifest
editor, and switch to the Extensions page.
- Click Add. In the New Extension wizard, clear Show only extension points from required plug-ins to view the list of plug-ins.
- Select com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveHandlers. Click Finish. When asked if you want to add the plug-in to the list of plug-in dependencies click Yes. An entry appears in the All Extensions list, with a mediationPrimitiveHandler under it.
- If you do not see a mediationPrimitiveHandler, you need to create one. Right-click com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveHandlers and select New > medationPrimitiveHandler. A medationPrimitiveHandler is added for the extension.
- Select the handler and set its properties as shown in the table:
Extension Element Details for mediationPrimitiveHandler extension Property name Value typeName CurrencyConverter typeNamespace mednode://mednodes/CurrencyConverter.mednode propertyDefinition propertygroups/CurrencyConverterPropertyGroup.xml implementationClass com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example .logic.CurrencyConverterMediation This is the Java project and class that is created when you author the Java code.
isTerminalTypeDeducible true The Extension Element Details should look like the following image:

The namespace must begin with mednode://mednodes.
- Add short and long description and three terminal categories for the handler by selecting it, right-clicking it and selecting them from the New menu.
- Select the short description and enter a short description for the primitive in the Body Text field: Currency Converter
- Similarly, add the following text for the long description: This primitive converts a value from the input message into the currency that is selected from a pre-defined list of currencies.
- Select each terminal and in the Details section on the right, set its type ( input, output and fail in this example). Enter a name for each terminal (in, out and fail in this example). If that the fail terminal must be named fail.
The All Extensions list should look like the following image:

- Add another extension to com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveUIContribution. An entry appears in the All Extensions list, with a medationPrimitiveUIContribution under it.
- If you do not see a medationPrimitiveUIContribution , you need to create one. Right-click com.ibm.wbit.sib.mediation.primitives.registry.mediationPrimitiveUIContribution and select New > medationPrimitiveUIContribution.
- Set the properties of medationPrimitiveUIContribution as shown
in the following table and save.
Extension Element Details for mediationPrimitiveUIContribution extension Property name Value mediationPrimitiveTypeName CurrencyConverter mediationPrimitiveTypeNamespace mednode://mednodes/CurrencyConverter.mednode paletteCategory My Primitives smallIcon icons/CurrencyConverterSmall.gif largeIcon icons/CurrencyConverterLarge.gif The properties under Extension Element Details should look like the following image:
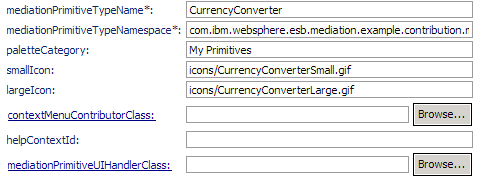
Place the primitive in a specific category by setting the paletteCategory property.
For example, to place a primitive in the My Primitives category, the property is set to My Primitives.
- Create required folders in the plug-in project
-
- Create a folder named icons in the plug-in project, and place your icons in it. The small icon (16x16) will appear on the palette. The large icon (24 x 24) will appear on the canvas.
- Create a folder named propertygroups in the plug-in contribution project, and create a property group XML file in this folder from File > New > Other > XML > XML File. Click Next.
- Ensure that the propertygroups folder is selected as the parent folder. Name the file CurrencyConverterPropertyGroup.xml and click Next.
- Choose to create an XML file from an XML template. Click Finish.
- Add properties to the XML file
- In CurrencyConverterPropertyGroup.xml , we will describe the properties of this new primitive, so as to derive the UI for the properties view Details page in the Mediation Flow editor. The Java class must have getter and setter methods
that correspond to each of these properties. See Elements of the properties xml file.
Add the required properties to CurrencyConverterPropertyGroup.xml by entering the following XML code:
<pg:BasePropertyGroups name="CacheReaderPropertyGroups" resourceBundle="ESBMediationExamples" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:pg="http://www.ibm.com/propertygroup/6.0.1"> <propertyGroup name="CurrencyConverterPropertyGroup" xsi:type="pg:BasePropertyGroup" > <!-- currency path using XPathProperty --> <property name="currencyPath" displayName="Currency Path" defaultValue="/body" required="true" propertyType="String" id="com.ibm.propertygroup.ext.ui.XPathPropertyContentAssist" xsi:type="pg:ConstraintSingleValuedProperty"> <qualifier name="propertyType" value="XPATH" xsi:type="pg:GenericPropertyQualifier" /> <description> An XPath expression to the input currency value. </description> </property> <property name="currencyRatesTable" displayName="Currency Rates" xsi:type="pg:TableProperty"> <description> Currency rates </description> <qualifier preferredHeight="100" xsi:type="pg:TableLayoutQualifier"> <column name="currency" preferredWidth="300" xsi:type="pg:TableColumnQualifier"/> <column name="currencyRate" preferredWidth="200" xsi:type="pg:TableColumnQualifier"/> </qualifier> <column name="currency" validValuesEditable="false" required="true" displayName="Currency" xsi:type="pg:ConstraintSingleValuedProperty"> <description> List of currencies </description> <validValue value="USD" displayValue="United States Dollars(USD)"/> <validValue value="CAD" displayValue="Canadian Dollars(CAD)"/> <validValue value="EUR" displayValue="Euro(EUR)"/> <validValue value="JPY" displayValue="Japanese Yen(JPY)"/> <validValue value="CNY" displayValue="Chinese Yuan(CNY)"/> </column> <column name="currencyRate" required="true" validValuesEditable="false" displayName="Rate" propertyType="float" xsi:type="pg:ConstraintSingleValuedProperty"> <qualifier name="promotable" xsi:type="pg:PropertyClassificationQualifier" /> <description> Exchange rate </description> </column> </property> </propertyGroup> </pg:BasePropertyGroups>
Save and close the file. Save the project.
- Generate metadata
- Launch the runtime workbench from the PDE by following these steps:
- Create a new Eclipse application configuration and run it.
- From the main menu, select Run -> Run Configurations.
- In the Run Configurations page, right-click Eclipse Application and select New.
- Rename New_configuration to Runtime Workbench.
- From the Runtime JRE drop down list select jdk. This ensures that the runtime workbench is launched with the IBM Integration Designer 7.5 JRE that is installed in the Installation Directory\jdk (where Installation Directory is the directory in which IBM Integration Designer is installed).
- Click Apply, and then click Run. IBM Integration Designer launches a new IDE, which takes a few minutes.
- In the new IDE that is launched, click Window > Show View > Other > Mediation Development > Mediation Metadata Generation then click OK.
- The mediation primitives created are displayed here. Use this view to generate a .mednode file for your primitive. Select the primitives that you want and click Generate. A status of OK indicates that the .mednode file was successfully generated. Close the IDE.
- A file named CurrencyConverter.mednode is created in the mednodes folder of the plug-in project. You might need to refresh your view to see this file.
- Create a new Eclipse application configuration and run it.
- Author the Java Code
-
- Create a Java project from File > New > Project > Java > Java Project. Click Next. Enter the project name, com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.logic, and click Next.
- Switch to the Libraries page, and click Add library. Select Server Runtime and click Next. Select WebSphere ESB Server v7.5 and click Finish.
- Click Finish to complete the New Java Project wizard.
- Switch to the Java perspective.
- Copy CurrencyConverter.mednode from the plug-in project to the root of the Java project.
- Select the Java project
and click File > New > Class. Enter com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.logic as package name and CurrencyConverterMediation as class name. Click Finish. Replace the generated
code in the class with the following code. If that there will be errors in the code at this point.
package com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.logic; import com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.InputTerminal; import com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.MediationBusinessException; import com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.MediationConfigurationException; import com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.OutputTerminal; import com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.esb.ESBMediationPrimitive; import commonj.sdo.DataObject; /** * This mediation converts from one currency value to another currency value. */ public class CurrencyConverterMediation extends ESBMediationPrimitive { private static final String OUTPUT_TERMINAL_NAME = "out"; private String currencyPath; private CurrencyRate[] currencyRatesTable; /** * Default constructor. */ public CurrencyConverterMediation() { super(); } /** * @return Returns the currencyPath. */ public String getCurrencyPath() { return currencyPath; } /** * @param currencyPath * The currencyPath to set. */ public void setCurrencyPath(String currencyPath) { this.currencyPath = currencyPath; } /** * @return Returns the currencyRates. */ public CurrencyRate[] getCurrencyRatesTable() { return this.currencyRatesTable; } /** * @param currencyRates The currencyRates to set. */ public void setCurrencyRatesTable(CurrencyRate[] currencyRates) { this.currencyRatesTable = currencyRates; } /* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.Mediation#mediate(com.ibm.wsspi.sibx.mediation.InputTerminal, * commonj.sdo.DataObject) */ public void mediate(InputTerminal inputTerminal, DataObject message) throws MediationConfigurationException, MediationBusinessException { // retrieves the input currency value float inputCurrencyValue = message.getFloat(getCurrencyPath()); if (getCurrencyRatesTable() != null && getCurrencyRatesTable().length > 0) { // we only use the first available currency rate float currencyRate = getCurrencyRatesTable()[0].getCurrencyRate(); // converts to the new currency value float newCurrencyValue = inputCurrencyValue * currencyRate; // update the new currency value to the message message.setFloat(getCurrencyPath(), newCurrencyValue); } // gets the out terminal from the mediation services OutputTerminal outTerminal = getMediationServices().getOutputTerminal( OUTPUT_TERMINAL_NAME); if (outTerminal != null) { // fires the message to the out terminal outTerminal.fire(message); } } } - Create another class in the Java project.
Enter com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.logic as package name and CurrencyRate as class name.
Click Finish. Replace the generated code in the new class with the following code, after which all errors should go away.
package com.ibm.websphere.esb.mediation.example.logic; /** * Data object for currency rates table property. */ public class CurrencyRate { private String currency; private float currencyRate; /** * */ public CurrencyRate() { super(); } /** * @return Returns the currency. */ public String getCurrency() { return currency; } /** * @param currencyPath * The currency to set. */ public void setCurrency(String currency) { this.currency = currency; } /** * @return Returns the currencyRate. */ public float getCurrencyRate() { return currencyRate; } /** * @param currencyRate * The currencyRate to set. */ public void setCurrencyRate(float currencyRate) { this.currencyRate = currencyRate; } }
- Deploy the plug-in
-
- Open the build.properties file of the plug-in project in the Build Properties Editor, and make sure that the icons , mednodes and propertygroups folders are selected under Binary Build.
- Export the project as Deployable plug-ins and fragments.
Select to export as a directory structure and specify the destination
directory IIDInstallDir.
When you export the plugin, a plugins directory will be created under the destination directory. Your plugin will be placed in IIDInstallDir\plugins
- Deploy the Java project to the UTE by exporting it as a jar to IIDInstallDir\runtimes\bi_v75\lib\ext, if you intend to test your primitive in a mediation flow.
- Shutdown IBM Integration Designer and start it using the -clean option.
- Open a mediation flow component in the Mediation Flow editor.
The icon for the CurrencyConverter mediation primitive is in the palette

.
- Drag the icon for your primitive onto the canvas, and view the properties in the Properties view Details tab.

- Deploy to the run time
- Export the Java project as a jar, for example myPrimitives.jar. In the root folder, select .mednode only, but keep the Java class selected. Export the jar to WAS_HOME/lib/ext.
References
For information on the service message object and mediation flow APIs, see the Reference
section in the  WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus information.
WebSphere Enterprise Service Bus information.
For information on Service Data Object APIs, see  http://help.eclipse.org/help32/topic/org.eclipse.emf.ecore.sdo.doc/references/javadoc/org/eclipse/emf/ecore/sdo/package-summary.html.
http://help.eclipse.org/help32/topic/org.eclipse.emf.ecore.sdo.doc/references/javadoc/org/eclipse/emf/ecore/sdo/package-summary.html.
Elements of the properties xml file
You must create a properties definition XML file to define the properties of your mediation primitive. This XML file must conform to the schema defined in Mediation primitive property group schema definition. The following are the typical steps to author the properties definition XML file.
- Defining propertyGroups:
Each properties definition XML file must contain one and only one propertyGroups element that contains a sequence of zero or more propertyGroup elements.
<pg:BasePropertyGroups name="myGroups" resourceBundle="mypackage.myProperties">
Attributes of propertyGroups Attribute Description name Name of the property group. This name will not be displayed in the Mediation Flow Editor. resourceBundle The resource bundle that will be loaded to interpret a string value. This is used for globalization. - Defining propertyGroups elements
Each propertyGroup element is represented as a horizontal tab page within the Details page of the Properties view. Each propertyGroup can contain multiple properties. A property can be a standard property or a custom property.
<propertyGroup name="myGroup" xsi:type="pg:BasePropertyGroup">
Attributes of propertyGroup Attribute Description name Name of the property group. If there is more than one propertyGroup, each propertyGroup element is rendered as tab page in the Details page. The name attribute becomes the name of the tab page. - Defining simple standard properties
IBM Integration Designer supports the following property types:
- ConstraintSingleValuedProperty - can have only one value with constraints defined (that is, passwordProperty must be at least 8 characters long and contain at least one number to be valid)
- ConstraintMultiValuedProperty - contains multiple values with some constraints defined (that is, logTypeProperty must be either INFO, DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR or any combination of the four to be valid)
- TableProperty - multiple columns each of which is a single valued property ConstraintSingleValuedProperty (that is, two-dimensional array each column being limited by constraints defined as for a ConstraintSingleValuedProperty type)
The following standard properties have been predefined in the propertygroups schema definition. Both properties have the same attributes.
Standard properties and their attributes Property Attribute Description - ConstraintSingleValuedProperty - A single-valued property with various user input validation rules
- ConstraintMultiValuedProperty - Multi-valued property. All values share the same type
name / displayName Name is the identifier of a property. DisplayName is used as a label preceding the property input control. description Displayed as tooltip text propertyType Defines the value type (String / Boolean / Float / Integer) defaultValue The default value of the property hidden Defines whether the property is hidden or shown readOnly Defines whether the property is read only required Indicates that the property requires a value sensitive If value type is String, this attribute determines whether it is case sensitive validValuesEditable Defines whether a user is allowed to enter a value which is different from values defined by validValues validValues A list of valid values pattern (optional) If the value type is String, the editor will do a pattern match to validate user input maxLength (optional) If the value type is String, the editor will limit the size that user can input minValue / maxValue (optional) If the value type is Integer or Float, the editor will perform a range check on user input. validValueGeneratorClass Points to a class which is responsible for dynamically generating valid values.. The class must implement the interface com.ibm.propertygroup.ext.api .IValidValuesGenerator - Defining a table property
Each table property can consist of multiple columns, each of which is a single-valued property, such as ConstraintSingleValuedProperty.
<property name="filters" displayName="%displayname" xsi:type="pg:TableProperty"> <column name="pattern" required="true" .../> <column name="terminalName" required="true" .../> </property>
- Defining a custom property
The implementation class must implement com.ibm.propertygroup.ext.ICustomProperty
<property name="myCustomProperty" class="MyCustomImpl" xsi:type="pg:CustomProperty">
- Defining properties to decide if cloning is necessary
Mediation primitives can provide information to the WebSphere ESB run time which allows it to decide whether a clone is necessary at various points in the flow, this information takes the form of mediation primitive parameters. These parameters are:
- sibxMayChangeMessage A mediation primitive parameter that indicates to the run time whether a primitive can modify the message during processing. If the message is not modified during processing (such as the Logger mediation primitive) then the WESB run time will not clone the message before invoking this primitive.
- sibxOnlyFireAtEnd A mediation primitive parameter that indicates to the run time whether a primitive will guarantee to only fire its output terminals at the completion of its work. This allows the run time to avoid a message clone on terminal fire.
- sibxNoChangeOnFailure A mediation primitive parameter that indicates to the run time that a primitive will leave the original SMO message unmodified should it have any failure. A good example of the use of this is in the Mapping primitive. This primitive works on a serialized version of the SMO right up until the end of its processing when it copies that serialized version over the original message. This means, the Mapping primitive can make use of the original SMO on failure since it has a copy of it for the full life of its processing, thus negating the need to the WebSphere ESB run time to do the same.
Usage examples:
<!-- private property which tells the engine if the mednode might change the message --> <property name="sibxMayChangeMessage" hidden="true" defaultValue="false" propertyType="String" xsi:type="pg:ConstraintSingleValuedProperty"> </property>
<!-- private property which tells the engine if the mednode has finished updating the message by the time it fires its output terminal(s) --> <property name="sibxOnlyFireAtEnd" hidden="true" defaultValue="true" propertyType="String" xsi:type="pg:ConstraintSingleValuedProperty"> </property>
- Adding qualifiers to properties
The property model already described is neutral to any UI rendering mechanism or processing infrastructure. However, in certain scenarios, some UI or runtime-dependent information must be presented.
For example, you might want to define the table layout for a table property. Or you might want to instruct the run time to perform special handling when processing certain properties. A qualifier is introduced to serve this purpose. You can attach as many qualifiers to a property as you want, provided they are valid for the UI and the run time.
For example, you can attach a TableLayoutQualifier to a TableProperty.
<property name="filters" xsi:type="pg:TableProperty"> <qualifier preferredHeight="100" xsi:type="pg:TableLayoutQualifier"> <column name="pattern" preferredWidth="100" xsi:type="pg:TableColumnQualifier"/> <column name="terminalName" preferredWidth="200" xsi:type="pg:TableColumnQualifier"/> </qualifier> ... </property>
- Adding the properties promotion qualifier
If you want to designate the property to be promotable, which means that the value of the property value can be changed at run time, add this qualifier:
<qualifier name="promotable" xsi:type="pg:PropertyClassificationQualifier" />