IBM BPM, V8.0.1, All platforms > Programming IBM BPM > Enterprise Service Bus programming > WebSphere eXtreme Scale
Common WebSphere eXtreme Scale scenarios
You can use WebSphere eXtreme Scale together with IBM BPM in a number of business situations.
Asynchronous aggregation scenario
Mediation flows provide areas of context to share data between mediation primitives.
For example, data can be shared between the request flow and the response flows of a mediation flow component by using the correlation context structure in the Service Message Object (SMO). By using the eXtreme Scale mediation primitives, data can be stored using a flow in one mediation module and retrieved in another flow, in a different module, a different server or even a different cell. Messages received in the mediation flow can be stored in a data grid, then processed together to create a single response.
In this scenario, a fictitious insurance company have a system that collects quotes from multiple insurance agents and aggregates them so that the best quote can be selected. Gathering the list of quotes can take a long time, so the insurance company want to be able to provide an up-to-date list of all quotes that have been received so far. By calling a mediation flow that stores each received insurance agent response in eXtreme Scale, the insurance company can run a separate mediation flow that retrieves all the quotes collected so far from eXtreme Scale, providing an up-to-date list.
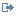
Figure 1. Asynchronous aggregation scenario request
flow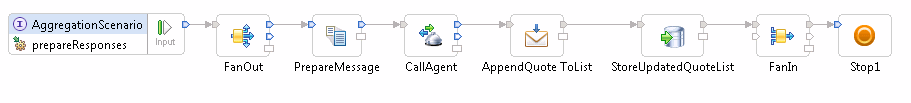
Figure 1.shows the mediation flow used to retrieve and store the insurance agent quotes. A Fan Out mediation primitive and a Fan In mediation primitive iterate through the list of insurance agents. The Mapping mediation primitive prepares the message and then the Service Invoke mediation primitive calls each insurance agent service in turn. As each response is retrieved, the Message Element Setter mediation primitive appends the quote to a list and the list is then stored in the eXtreme Scale cache using the WebSphere eXtreme Scale Store mediation primitive, overwriting any previous value. When all the insurance agents have been called, the flow is stopped.
Figure 2. Asynchronous aggregation
scenario response flow
Figure 2.shows the mediation flow used by the insurance company to retrieve the most recent list of insurance agent quotes. The WebSphere eXtreme Scale Retrieve mediation primitive retrieves the up-to-date list of insurance agent quotes, as stored by the previous mediation flow (which might still be running). The Mapping mediation primitive converts the results into the format required for the response message and the list of quotes is then returned.
Message collection scenario
The eXtreme Scale mediation primitives can be used to collect messages. By storing request or response messages in an object grid, a IBM BPM mediation flow can collect a number of messages into a single collection before processing that collection as a single entity.
A fictitious car insurance company provides an online quotation service through which a customer can provide details incrementally. Customers can provide their personal details, car details, and cover requirements separately at different times. The customer receives a quote when all three parts of the request are received.
Figure 3. Message collection scenario request flow
In Figure 3, the first Message Filter mediation primitive checks whether the inbound request contains all three parts required to provide a quote. If the inbound request is complete, then the retrieveQuote and sendQuote services are invoked, which sends an email containing an insurance quote to the customer. If the request is incomplete, then a WebSphere eXtreme Scale Retrieve mediation primitive checks for existing partial data in the data grid. If no match is found, then the partial data is stored using the WebSphere eXtreme Scale Store mediation primitive, after which the flow ends. The stored partial data is used when another partial request is received at a later time. If an existing partial request was found in the data grid, a transformation combines the inbound request and the retrieved data into a single request. The request is checked again for completeness. If the request is complete the quote is retrieved and sent to the customer. If the request is still not complete the partial data is stored in the data grid for later use.
Overloaded back-end scenario
A back-end service that receives many requests can become overloaded during peak times. If that back-end service provides information that is updated infrequently, and the returned information does not need to be up-to-date, then using an eXtreme Scale cache can help to reduce the load on the back-end service.
A service that provides information on requested items uses a database to retrieve the required data and build a response. At peak times the number of connections to the database might restrict throughput, which can cause delays. In this scenario IBM BPM makes use of eXtreme Scale by using a mediation flow containing the WebSphere eXtreme Scale Retrieve and Store mediation primitives.
Figure 4. Overloaded back-end scenario
request flow
Figure 4.shows the request flow with a WebSphere eXtreme Scale Retrieve mediation primitive configured to use a key defined in the input message to retrieve a cached value. If a value is found it is returned directly in the response.
If a value is not found in the cache, the back-end service is called.
Figure 5. Overloaded back-end scenario response flow
By using the WebSphere eXtreme Scale Store mediation primitive, future requests for the same item result in the response being retrieved from the data grid, preventing the back-end service from being called. This will help prevent the back-end service from becoming overloaded and might improve overall response times.
Related information: