Programming model for JSP files and servlets (access beans)
An entity EJB can contain a large number of attributes. In most situations, these attributes are used by a JSP program to create an HTML output page.
As shown in the following figure, a servlet typically invokes a command (such as a request to an entity EJB) and then invokes the JSP program to display the result:
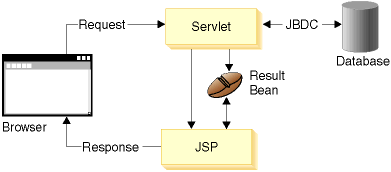
Depending on the results that get returned, the servlet may invoke a different JSP program. For the results bean associated with the JSP program, a call to retrieve an attribute should have the following characteristics:
- The call should be fast, because there can be many attributes that a JSP program needs to retrieve.
- The call should not cause an exception, because it will needlessly complicate the JSP logic.
A Java bean wrapper or EJB factory does not meet the requirement for the JSP programming model, because every call is a remote call that can throw a remote exception and bhas a long execution call path. A copy helper or data class resolves this problem.
An AccessBeanData interface class containing abstract representations of the getter and setter methods is generated when the access bean is created. The access bean class implements this interface, which can be used as a data object in a JSP that is independent of the access bean implementation. A data class containing getters and setters for the cache properties can also be generated. It extends the AbstractEntityData class.
Parent topic
Access beans
Related concepts
Access beansEJB access beans and client applications
Related tasks
Creating EJB access beansRelated reference
Example: Using access beans