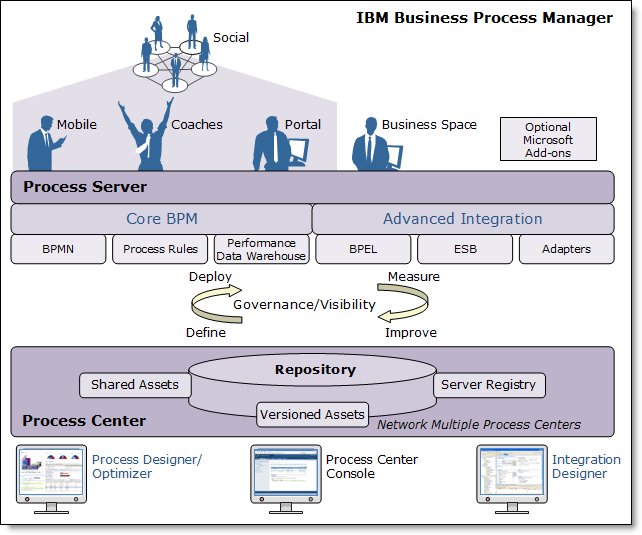
IBM Business Process Manager
IBM Business Process Manager (BPM) coordinates process steps across disparate applications and systems using alerts and a dashboard.
See also: IBM WebSphere Lombardi v7.2
IBM Business Process Manager V8.0 editions
| Edition | Phase | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced | Transformation | Complete set of capabilities with extended support for high-volume process automation. Built in SOA components. |
| Standard | Program | Multi-project improvement programs, with high business involvement |
| Express | Project | First projects: |
Components
| Process Center | Runtime environment that includes a repository for all process models, services, and other assets created via...
|
| Process Server | BPM runtime environment. Integrated with Process Center. The Business Performance Data Warehouse component aggregates process data for testing before formal deployment. |
| Process Designer | Available in all Business Process Manager editions. Graphics-oriented tooling for creating process models, reports, and services. We can call a service created in Integration Designer via an interface to access back-end systems or obtain customer data. Applications can be run on the Process Center server or saved to a snapshot and deployed on the Process Server. The same is true of services that are developed in Integration Designer and associated with process applications. |
| Integration Designer | Available in Business Process Manager Advanced Edition or as a stand-alone toolset. Complete integration development environment for those building integrated applications. Integration developers use it to call applications on Enterprise Information Systems, involve business processes across departments or enterprises, and invoke applications locally or remotely written in a variety of languages and running on a variety of operating systems. |
| Process Center Console | Location for users to create and maintain high-level library items such as process applications and toolkits. Provides a framework in which BPM analysts and developers can build their processes. Provides tools for maintaining the repository, including setting up the appropriate authorization for users and groups. |
| Process Admin Console | Administer process servers, including users and installed snapshots for each server. Provides tools to manage queues and caches. Includes the Process Inspector for managing process instances for process applications running on a specific process server. |
| Business Performance Admin console | Tools for managing the Performance Data Warehouses. Manage server queues and monitor server performance. |
| WebSphere Application Server administrative console | Administer applications, services, and other resources at a cell, node, server, or cluster scope. Use the console with stand-alone servers and deployment managers. |
| Business Process Choreographer Explorer and Business Process Archive Explorer | Client interfaces for managing Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) processes and human tasks created in IBM Integration Designer, work with your assigned tasks, view completed BPEL processes and human tasks that are in an archive database, or delete processes and tasks from the archive. |
| Business Space powered by WebSphere | Browser-based GUI for interacting with content from various products in the business process management portfolio. We can use Business Space to combine the content. Administer business processes, such as human task flows, modeling, and performance indicators. |
| Business Process Rules Manager | Web-based tool that assists the business analyst in browsing and modifying business rule values. The tool is an option of Process Server that we can select to install at profile creation time or after installing the server. |
| IBM WebSphere Operational Decision Management | Enables organizations to automate, govern, and improve operational decision making across business processes. We can integrate business rules and events from WebSphere Operational Decision Management into choreographed business processes in Business Process Manager. |
Ordering information
| Program name | PID number | Charge metric |
|---|---|---|
| IBM Business Process Manager Advanced | 5725-C94 | Processor Value Unit (PVU) |
| IBM Business Process Manager Standard | 5725-C95 | PVU |
| IBM Business Process Manager Express | 5725-C96 | PVU |
| IBM Business Process Manager Tools and Add-ons | 5725-C97 | Authorized User Application Instance |
Warranty Reporting Example
The warranty reporting example leverages...- IBM Business Process Manager
- IBM WebSphere Operational Decision Manager
- IBM Cognos Business Intelligence
- IBM Rational tooling
- IBM Solution for Collaborative Lifecycle Management
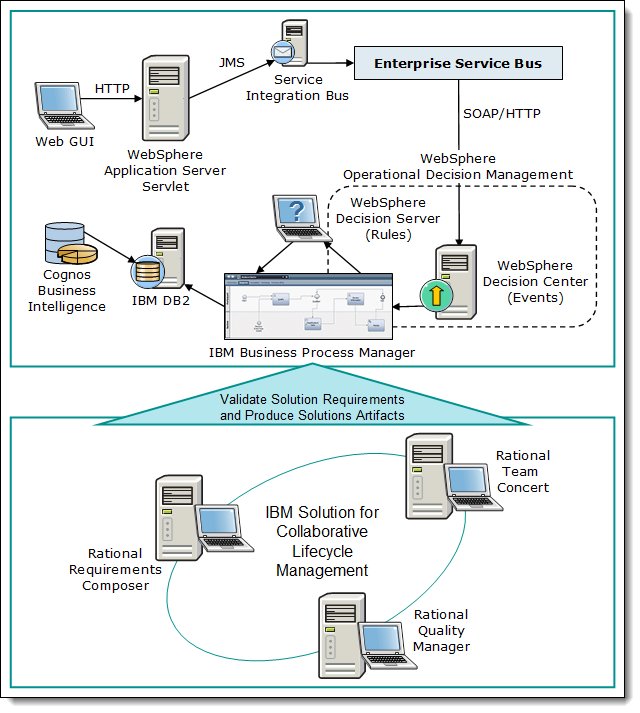
WebSphere Operational Decision Management
WebSphere Operational Decision Management is the decision management solution that defines the rules for the warranty application. In the warranty reporting solution, decision management capabilities are combined with Business Process Manager to incorporate business rules through a Decision Service.

Business Process Manager Advanced
Business Process Manager models the warranty business process, which manages the core business process flow of the solution and acts as the choreographer of process steps and activities. BPM also integrates with events and decision management in WebSphere Operational Decision Management to manage the integration between process components and events, database, and decision management components.
Cognos Business Intelligence
Cognos Business Intelligence is used to elicit insight through the creation of reports that are gathered from the data and events collected by the warranty reporting system.
Deploy a process
Process center
After modeling, designing, and implementing a business process solution, the next step in the business process application lifecycle is the deployment of the application to a runtime server.
The Process Center is used for the following tasks:
- Management of runtime process servers
The Process Center maintains a list of online and offline process servers that represent your deployment target. These servers can be classified as test, staging, or production servers.
- Deployment to online process servers
The Process Center console is used to deploy snapshots of process applications to process servers (test, stage, or production servers).
- Creation of deployment packages for offline-server deployments
From the Process Center, we can create deployment packages for process application snapshots. Deployment packages are required to deploy to an offline process server.
IBM BPM supports the concept of environments. Each environment is used for a specific purpose that is determined by the type of the environment.
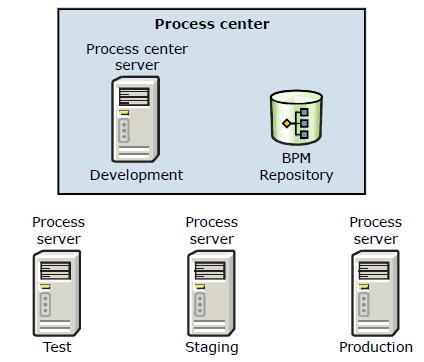
Process Center server (development environment)
The Process Center Server acts as the development environment and is automatically assigned the development environment type. The development environment is the only environment where we cannot specify the environment type, and in contrast to other environment types, we can have only one environment as the development environment.
Process servers (test, staging, and production environment)
Apart from a development environment, a typical BPM setup contains one or more runtime servers. It should at least contain a production environment, but usually contains additional environments for special purposes.

If you create profiles using manageprofiles.sh, then specify the environment type using the parameter...
-
-environmentType
Unlike the Process Center Server, Process Servers need to be associated with the Process Center during or after the creation of the server (profile creation). Runtime servers can be configured as:
- Online server/connected server
Directly connected to the Process Center. Application deployments to online servers can be performed from the Process Center console. Usually, test and staging environments are configured as online servers.
- Offline server
Not connected to the Process Center. Usually, production environments are configured as offline servers.
Automatic deployments during development
When modeling and implementing a business process, BPM analysts and solution developers use the Process Designer and Integration Designer tools to create the solution. These tools are connected to the Process Center containing the development environment: the Process Center Server.
Deployments to a Process Center Server occur automatically when:
- You run, or .play back,. a process in Process Designer

- You change dependencies in Process Designer, such as add a dependency, remove a dependency, or change the version of a dependency
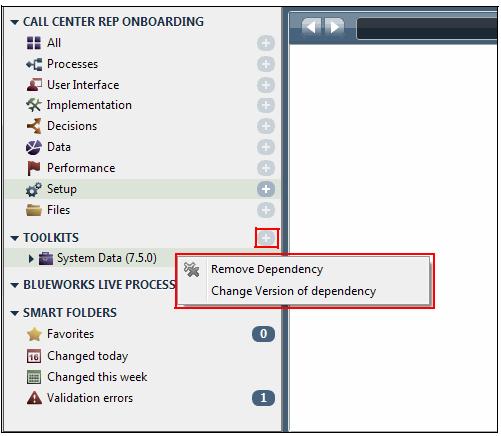
- When we publish the application from Integration Designer

Manual deployments to runtime servers
In contrast to the development environment, where deployments to the Process Center Server are performed automatically, deployments to runtime Process Servers need to be initiated manually. Specific versions (snapshots) of a process application are deployed to a runtime server at a specific point in time. This process is done either from the Process Center console for deployments to online Process Servers or through scripts for deployments to offline Process Servers.
Process application
In IBM Business Process Manager V7.5, applications are developed as process applications by the BPM solution developers. A process application is a container for process models and their implementations. It can contain the following artifacts:
- Process artifacts (from Process Designer)
- Business process models (business process definitions)
- Coaches
- Services required to implement activities or to integrate with other systems
- Toolkits that the process application depends on
- Integration artifacts (from Integration Designer)
- Monitoring artifacts (from Integration Designer)
- . Monitor models
- Other items required to run the process
Process application snapshot
Process application snapshots record the state of the items within a process application at a specific point in time and represent a specific version of your process application. The snapshot contains all the components that are part of the process application and the dependent toolkits.
Process application snapshots can be created from the Process Center console or in the Process Designer view. The snapshots are managed from the Process Center console and represent the deployment unit that gets deployed to online and offline process servers. We can deploy process application snapshots to process center servers (development environment) and to process servers (test, staging, or production environment). To deploy to a stand-alone process server, you must take a snapshot of the process application, because this artifact is the only artifact that we can deploy to process servers.
Business level application
If you have IBM Business Process Manager V7.5 Advanced and your process application contains not only artifacts from Process Designer but also artifacts from WebSphere Integration Developer, then a business level application (BLA) is created under the covers. It is a container for the process application and its assets (for example, monitor models). In addition, each snapshot of such an advanced process application has its own BLA.You do not see BLAs in the Process Center, but many of the administration tasks for a snapshot, such as stop or start, are technically done at the level of the BLA. This action allows for a quicker and simpler administration of the snapshot and all of its assets.
BLAs are also relevant in the context of deployment. BLAs that represent the tip of a process application or that represent a concrete snapshot of a process application can be deployed.
Snapshots: Besides snapshots for process applications, we can also create snapshots for toolkits. Toolkit snapshots are only deployed when you deploy a process application snapshot that depends on this toolkit snapshot. This way, the owners of the process applications can decide whether they want to use the new version of the toolkit.
Tip
The tip is a special snapshot containing the most recent content of the process application. When your BPM analysts and solution developers change a process application, the changes are automatically saved to the Process Center repository at the tip of the working track. This situation means that the tip is the only snapshot where we can change contents. This configuration is useful during development, and for that reason the tip can be run only on the development environment (the Process Center Server). Tips cannot be deployed to all other environments (to Process Servers). The deployment of a tip to a Process Center Server happens automatically in your development environment when people change the artifacts. For this reason, this chapter focuses on the deployment of process application snapshots.Track
Tracks can be compared to branches in version control systems. Tracks allows parallel development to occur with isolation from changes in other tracks. Tracks are especially important in the context of fixing problems in a version of a process application that is already deployed to production. By using tracks, the development on a new version can continue in parallel to fix the problems in an older version. Tracks do not support merging capabilities. When a developer fixes a problem in a track, the fix also needs to be applied to the main track so that it is included.
Managing BLAs: BLAs are created automatically for process applications/process application snapshots under the covers. Do not manage BLAs manually using the WebSphere Application Server administrative console.
Putting it all together using an example
The figure below shows the Process Center repository with different artifacts. It contains two process applications with different snapshots. Each process application snapshot represents a deployment unit and can be deployed to a Process Server.
While process application A exists only in the main or default track, an additional track (track Y) was created for process application B for bug-fixing purposes. Snapshots for both tracks of process application B exist and can be deployed to a server.
The process center repository also contains a toolkit (toolkit A) that has two versions or snapshots. The dotted lines in Figure 6-7 show the dependencies between the snapshots of process application A and toolkit A:
- Snapshot 1.0.0 of process application A uses snapshot 1.0.0 of toolkit A.
- Snapshot 1.0.1 of process application A uses snapshot 2.0.0 of toolkit B.
See also
- IBM Business Process Manager cookbook
- Scaling BPM Adoption: From Project to Program with IBM Business Process Manager
- IBM Business Process Manager Advanced detailed system requirements
- IBM Redbooks publication: Scaling BPM Adoption: From Project to Program with IBM Business Process Manager
- Business Process Manager product page
- Business Process Manager announcement letter
- Business Process Manager Sales Manual
- Business Process Manager information center
- Business Level Application (BLA)
- IBM WebSphere Lombardi v7.2