Planning for multiple clusters
Multiple clusters are sets of servers that are managed together within a single administrative domain known as a cell, and participate in workload management. IBM WAS Network Deployment provides the ability to manage many appservers and appserver clusters within a single administrative domain, or cell. The single cell has the following advantages:
- A single administration User Interface (Administrative Console)
- A single administrative scripting client (wsadmin)
- Shared resources at the cell, node, or server scope
- Replication domains for sharing application data, state information, and caches
- Work load management at the Web server level providing a single server identity for all applications hosted across the cell, enabling ease of collaboration between applications while building a rich end-user application experience
An administrator's goal is to manage as many WebSphere Portal and portal-based products within the same managed cell as possible, to take advantage of these administrative and runtime features.
WebSphere Portal provides the ability to federate multiple, independently configured portals into the same cell. While there are limitations to this support, this allows multiple clusters to be managed together, where one portal may be providing different applications or services than another portal. With a common server identity through the Web server, these services and applications can integrate seamlessly at the browser through the latest in Web 2.0 technology (for example through the use of Ajax and REST services).
How multiple clusters work in a single cell
A cell’s configuration has the notion of scope, which controls the visibility of that resource to other resources and appserver instances. An example of a resource might be a data source definition, or a WebSphere variable definition. Scopes are typically defined as being one of the following:
- Cell
- All resources defined at this scope are visible to all other resources defined in the cell, and are thus configured globally available
- Node
- A cell has one or more nodes, and each node is named and matches with some WAS profile on some physical server. All resources defined at this scope are visible only to other resources defined in this same node, including any server definitions
- Server
- A node has one or more server definitions. All resources defined at this scope are visible only to that server. No other server or node can make use of these resources
- Cluster
- A resource defined at a cluster scope is visible to all cluster members, or server instances, in this cluster, but is not visible to any other servers in the same nodes
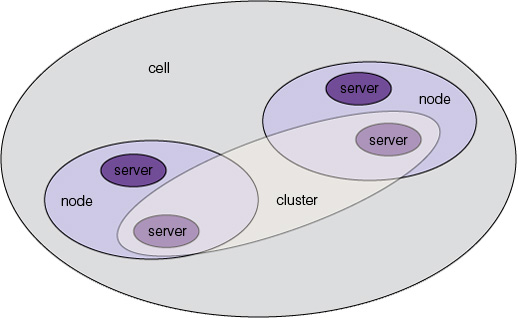
Resources defined within a circle, in the above diagram, can be seen by all other resources defined within that circle and any other scopes defined within that circle.
Within this concept of scope, an important point is that all enterprise applications are cell-scoped. In other words, there can only be one enterprise application with a given name in the cell. If multiple servers and clusters, or multiple clusters require the use of that enterprise application, they must share it.
IBM WebSphere Virtual Enterprise offers the ability manage multiple editions of the same enterprise application, including the mapping of these editions to different servers and clusters, or to different clusters. WebSphere Portal, however, does not currently exploit this feature.
Typically, when installing an enterprise application that will be shared across multiple clusters, the administrator simply installs the EAR into the cell’s management server, Deployment Manager, and then maps the application to the target clusters where it will run. Since WebSphere Portal installs several enterprise applications as part of its basic configuration and typically before any cluster is defined, special steps have to be followed to ensure that these infrastructure applications are appropriately shared when multiple WebSphere Portal clusters are defined within the same cell. And by extension, since these are infrastructure applications, all WebSphere Portal-based clusters must be at the same version.
Since portlets are enterprise applications of a special type, it is possible, but not always appropriate, to share portlets across multiple clusters. Many portlets (for example WebSphere Portal administration) are considered part of the infrastructure, and as a result can be shared across multiple clusters. Most end-user application portlets will be specific to certain clusters and will be installed as such.
The J2EE security configuration for the cell is shared by all servers and clusters managed in the cell. Therefore, each server and cluster must share the same underlying user repository against which users are authenticated when using any application hosted by any server and/or cluster in that same cell.
Supporting multiple clusters in the same cell involves:
- A common security model, including user repositories, for every cluster
- Some number of common enterprise applications and portlets, that must be made common as part of the federation and clustering process
- Installing portlets into certain clusters, or across clusters, as appropriate
- Understand how to tell if enterprise applications are shared between clusters
- Defining other resources at the appropriate scope, depending on the usage goals
Limitations
- All portal clusters must be at the same maintenance levels
- Because WebSphere Portal is made up of several enterprise applications, and because these applications are tightly coupled to the underlying services and infrastructure, all portal-based clusters in the same cell must be at the same service level.
- Process Server
- In the case where multiple clusters need access to a common WebSphere Process Server, the server should be centralized within its own cluster, and the client install option of WebSphere Process Server should be used in conjunction with WebSphere Portal to allow remote access to the central process server cluster.
- WebSphere Virtual Enterprise Static clusters
-
Use the WebSphere Virtual Enterprise On Demand Router (ODR) to balance workload across multiple clusters. See Routing requests across clusters for information about ODR.
You cannot install WebSphere Virtual Enterprise on i5/OS.
See also:
Parent topic:
Cluster
Related concepts
Understand configuration options for process integration