Security tokens
Security tokens are always contained in a header. NeoLoad supports the following security tokens:
- Username token
- Timestamp token
- Encryption token
- Signature token
The  button makes it possible to add a security token.
button makes it possible to add a security token.
A security token can also be added by right-clicking on the request security profile tree and selecting Add a security token.
Username
This security token provides the associated request with LoginID / Password -type authentication.
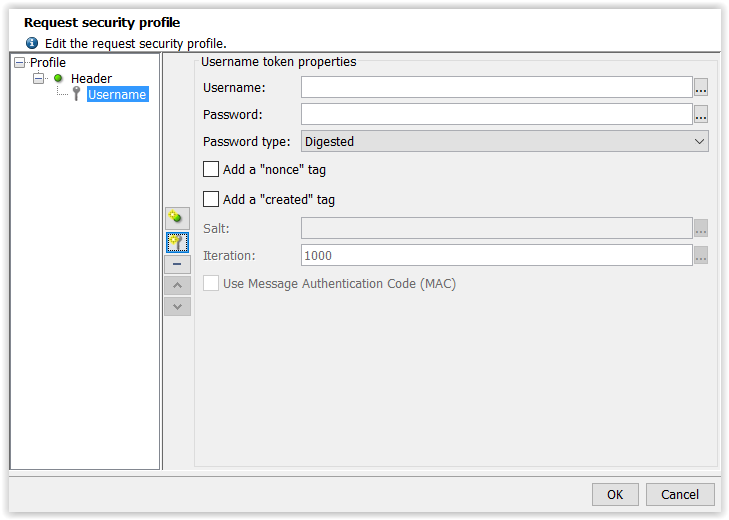
A username token has the following properties:
- Username: Security token ID.
- Password: Security token password.
- Password type: Type of password used by the security token.
Three types of password encryption are available:- Plain Text: The password is transmitted unencrypted.
- Digested: The password is hashed by the SHA1 algorithm.
- Derived: The password is hashed and salted by the SHA1 algorithm.
- Add a "nonce" tag: Adding a unique identifier to the token.
- Add a "created" tag: Adding a date of creation to the token.
This part is only valid if the password is hashed and salted. - Salt: Salt key.
- Iteration: Number of times the salt is applied to the SHA1 hash algorithm.
- Use a message ID: Adding a code certifying the message integrity.
Timestamp
This token provides the associated request with a lifespan.
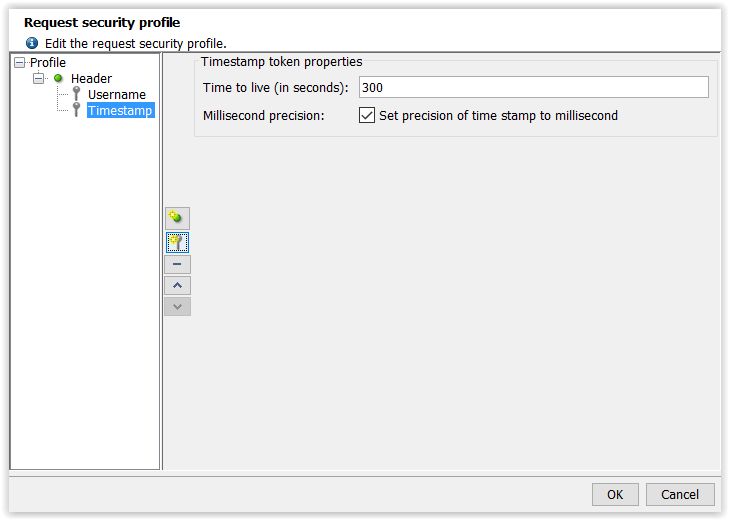
A timestamp token has the following properties:
- Time to live: Token lifespan in seconds.
- Millisecond precision: Forcing the server to take into account the token validity to the nearest millisecond.
Encryption
This token provides encryption for all or part of the associated SOAP request.
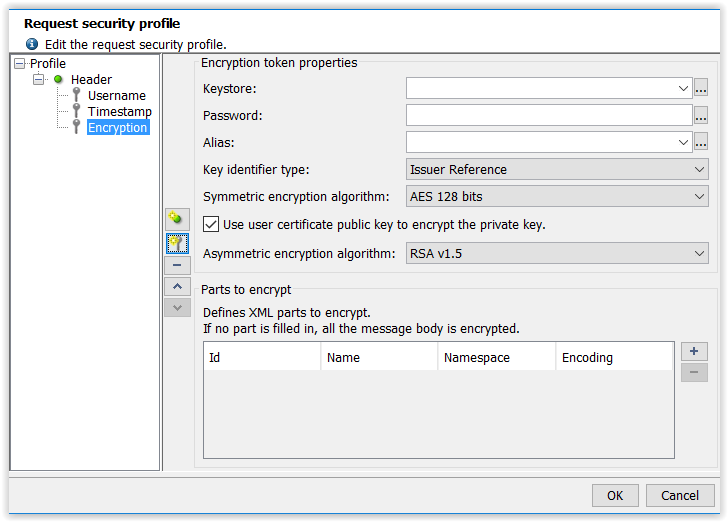
An encryption token has the following properties:
- Keystore: Keystore used by the token (the keystore may use variables). For more information about importing a new key store into NeoLoad, see Keystores Manager.
- Password: Keystore password (the password may contain variables).
- Alias: Alias of the key being used (the alias may contain variables).
- Key ID type: Key ID type sets the form that the information relating to the key takes. Basically, if the information is the key value and name or if it is just a reference to a key known to the server.
- Key name: Key name, only if the key is sent with the message.
- Key: Key value.
- Private key encryption algorithm: Private key encryption algorithm used to encrypt the request.
- Canonical formatting algorithm: Canonical formatting algorithm used. Canonical formatting modifies the XML message to eliminate the superfluous characters and thus obtain a standardized format for the message.
- Use the certificate public key to encrypt the key: Using the public key associated with the alias to encrypt the key.
- Public key encryption algorithm: the public key encryption algorithm used to encrypt the key.
- Id: ID of the XML tag to be encrypted.
- Name: Name of the XML tag to be encrypted.
- Namespace: Namespace of the XML tag to be encrypted.
- Encoding: the part of the XML tag to be encrypted.
Two choices are available: the entire tag, or just the tag content.
Signature
This security token provides a signature for all or part of the associated SOAP request.
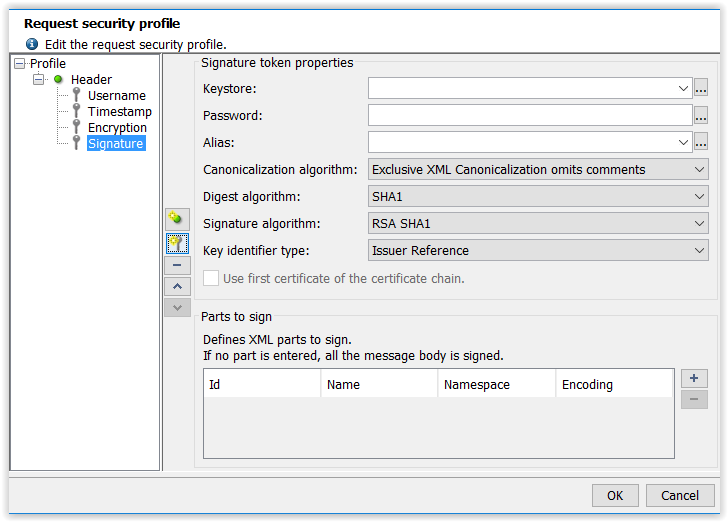
A signature token has the following properties:
- Key store: Keystore used by the token (the key store may use variables). For more information about importing a new key store into NeoLoad, see Keystores Manager.
- Password: Keystore password (the password may contain variables).
- Alias: Alias of the key being used (the alias may contain variables).
- Canonicalization algorithm: Canonical formatting algorithm used. Canonical formatting modifies the XML message to eliminate the superfluous characters and thus obtain a standardized format for the message.
- Signature algorithm: Algorithm used to generate the request signature.
- Key ID type: Key ID type sets the form that the information relating to the key will take; basically, if the information is the key or if it is just a reference to a key known to the server.
- Use the first certificate in the certificate chain: Using the certificate for the alias rather than the certificate chain to generate the signature.
A signature may be applied to parts of the SOAP request body only. To do this, it is necessary to specify which XML elements are to be signed. If no particular part is specified, the whole message body is signed.
- Id: ID of the XML tag to be signed.
- Name: Name of the XML tag to be signed.
- Namespace: Namespace of the XML tag to be signed.
- Encoding: Part of the XML tag to be signed.
Two choices are available: the entire tag, or just the tag content.