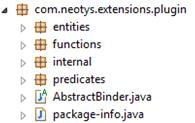
Data Format Extension API architecture
The Data Format Extension API architecture contains the following Java packages:
- entities is made of classes representing the request and response entities for the HTTP and WebSocket protocols.
- functions includes the Encoder, Decoder, and Namer functions.
- internal is used by NeoLoad to perform internal operations.
- predicates is made of classes which implement the com.google.common.base.Predicate interface. They help define the conditions for use.
The following classes diagram describes the architecture of the main API components.
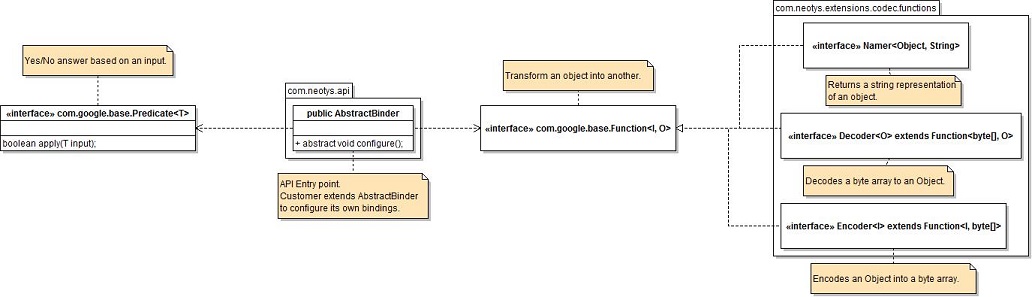
The API consists of classes, among which the main ones are the following:
- com.neotys.extensions.codec.functions.Decoder converts the binary content of a request or a response into a Java object.
- com.neotys.extensions.codec.functions.Encoder converts an object into binary content.
- com.neotys.extensions.codec.functions.Namer converts an object generated by a Decoder into a character string. It is used to name requests in NeoLoad.
- AbstractBinder acts as mediator. It links the classes above with conditions on requests and/or responses.
The API uses the Predicate and Function interfaces provided by the Google Guava library.
The API entry point is AbstractBinder is com.neotys.extensions.codec.AbstractBinder. This mediator makes it possible to link the implementations of the Decoder, Encoder and Namer Java interfaces with conditions for use. A condition for use is a Predicate. For more information about predicates, refer to the Google Guava documentation.