ICEfaces polling
NeoLoad supports the open-source ICEfaces server and its commercial version, ICEfaces EE.
Versions 1.8.2a onwards of the ICEfaces server also feature an API that allows making use of the Push messages generated by the server itself as well as their associated timestamps. To be able to use the NeoLoad Push messages, the names of the ICEfaces beans and the beans associated timestamps must be published in the ICEfaces application.
The tested ICEfaces application is modified:
- Modifying the ICEfaces bean:
The Java file containing the ICEfaces bean must contain a method publishing the additional information. For example, the MyBean.java file might contain the following code:
public class MyBean implements Renderable {...
private GroupAsyncRenderer mybean;
private String renderInfo;
...
public String getRenderInfo()
{String currentRenderInfo = mybean.getLastRenderInfo();
if(!currentRenderInfo.equals(renderInfo))
{renderInfo = currentRenderInfo;
return currentRenderInfo;
} else {return "";
}
}
...
- Modifying the .jspx file:
The .jspx file containing the visual part of the content rendered in the browser must send back this information in the page. One idea is to send back the information in a hidden layer.
The code might take the following form:
...
<div id="hiddenDiv">
...
<ice:outputText value="MyBean #{MyBean.renderInfo}"/>...
</div>
...
After the recording, a User Path using the ICEfaces Push Framework is displayed as follows.
- Warning: At the end of recording, a dynamic parameter search must be launched for NeoLoad to be able to handle the ICEfaces dynamic session IDs and the JSF ViewState.
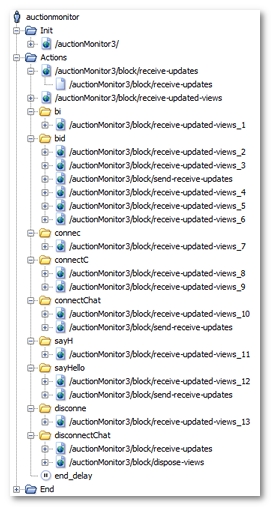
The following points should be noted:
- The ICEfaces polling is divided into two request categories: requests to the /receive-updated-views servlet and those to the /receive-updates servlet. This explains the large number of this type of requests.
- User clicks are represented by requests to the /send-receive-updates servlet.
- When a Container is added during entering, polling requests also are added. This explains the bi, connec... Containers.
Once processed by the NeoLoad Post-recording wizard, the User Path is modified as follows.

NeoLoad has made the following noticeable changes:
- The two categories of polling requests have been grouped together: requests with the form XXX/receive-updated-views on the one hand and those with the form XXX/receive-updates on the other hand. This reduces the number of requests considerably. If a Container becomes empty (as is the case with bi and connec here for example), it is automatically deleted. See Polling requests.
- The Variable Extractor viewsToUpdate has been placed on the first polling request (/auctionMonitor3/block/receive-updated-views for example), which retrieves the id's for the ICEfaces views to be updated. This is why the second polling request has been placed in a loop (loop_update_view for example), in order to issue an update request for each previously-extracted view.
- The request representing the ICEfaces Push channel (/auctionMonitor3/block/receive-updates for example) has been placed in a loop (polling_while), which continues to loop until the NL-stopPolling variable generated by NeoLoad becomes true. Lastly, the loop itself has been placed in a secondary execution thread using a fork action (push_fork for example).
- NeoLoad identifies the different types of message returned through the Push channel during recording, provided that the server being tested is version 1.8.2a or upwards and that the developers have published the required additional information. These different types of message are modelized by the Push messages (ClockBean for example).
- The polling_delay polling delay is the average of the time intervals between two polling requests in the original User Path.
- The variable modifier init_polling initializes the NL-stopPolling variable, with the false value, to have the polling function work on every Virtual User iteration.
- The stop_polling variable modifier stops the polling loop by modifying the value of the NL-stopPolling variable.