The failover environment
The distributed session cache is most commonly used in a scenario where client requests are directed by a load balancing mechanism to two or more replicated WebSEAL servers.
The replicated servers are identical. They contain replica copies of the WebSEAL protected object space, junction database, and (optionally) dynurl database.
The client is not aware of the replicated front-end server configuration.
The load balancing mechanism is the single point of contact for the requested resource. The load balancer connects the client with an
available server.
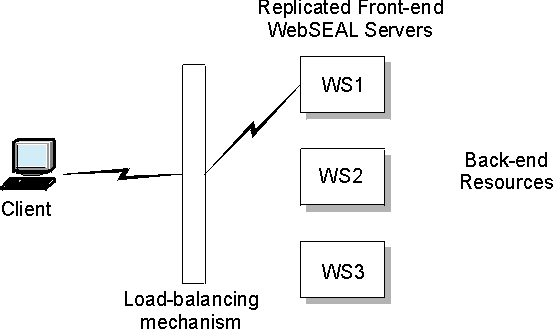
If the server where the client is connected suddenly becomes unavailable, the load balancer redirects the request to one of the other replicated servers. This action causes the loss of the original session-to-credential mapping. The client is new to this substitute server and is normally forced to login again.
The purpose of the distributed session cache is to prevent forced login when the WebSEAL server that has the original session with the client suddenly becomes unavailable. The distributed session cache enables the client to connect to another WebSEAL server, and create an authentication session containing the same user session data and user credentials. Whenever possible, configure load balancers to maintain session affinity. Session affinity provides improved performance, improved user experience, and makes WebSEAL configuration simpler.
Parent topic: Distributed session cache overview