Secure sockets layer (SSL)
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol provides transport layer security: authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality, for a secure connection between a client and server in the WebSphere Application Server. The protocol runs above TCP/IP and below application protocols such as Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), and Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP), and provides trust and privacy for the transport data.
ecure Sockets LayerDepending upon the SSL configurations of both the client and server, various levels of trust, data integrity, and privacy can be established. Understanding the basic operation of SSL is very important to proper configuration and to achieve the desired protection level for both client and application data.
SSL can be effective in securing an enterprise environment. Some of the security features provided by SSL are as follows:
Data encryption Prevent the exposure of sensitive information while data flows across the network. Data signing Prevents unauthorized modification of data while data flows across the network. Client and server authentication Ensures that you communicate with the appropriate person or machine.
SSL is used by multiple components within WebSphere Application Server to provide trust and privacy. These components are the built-in HTTP transport, the Object Request Broker (ORB), and the secure LDAP client.
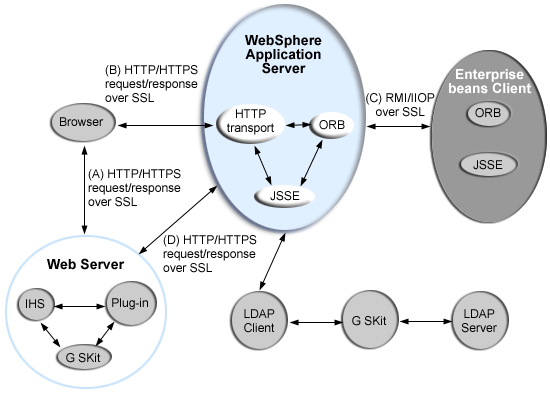
In this figure:
- The built-in HTTP transport in WebSphere Application Server accepts HTTP requests over SSL from a Web client like a browser.
- The Object Request Broker (ORB) used in WebSphere Application Server can perform Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (IIOP) over SSL to secure the message.
- The secure LDAP client uses LDAP over SSL to securely connect to an LDAP user registry and is present only when LDAP is configured as the user registry.
WebSphere Application Server and the IBMJSSE provider
The SSL implementation used by the WebSphere Application Server is IBM Java Secure Sockets Extension (IBM JSSE). The IBM JSSE provider contains a reference implementation supporting SSL and TLS protocols and an application programming interface (API) framework. The IBM JSSE provider also comes with a standard provider, which supplies RSA support for the signature-related JCA features of the Java 2 platform, common SSL and TLS cipher suites, hardware cryptographic token device, X.509-based key and trust managers, and PKCS12 implementation for a JCA keystore.
A graphical tool called IBM Key Management Tool (iKeyman) also is provided to manage digital certificates. With this tool, you can create a new key database or a test digital certificate, add CA roots to the database, copy certificates from one database to another, as well as request and receive a digital certificate from a CA. For more information, see IBM Key Management Tool.
Configure JSSE is very similar to configuring most other SSL implementations (for example, GSKit); however, a couple of differences are worth noting:
- JSSE supports both signer and personal certificate storage in an SSL key file, but it also supports a separate file called a trust file. A trust file can contain only signer certificates. You can put all of your personal certificates in an SSL key file and your signer certificates in a trust file.
- JSSE does not recognize the proprietary SSL key file format (.kdb files), which is used by the plug-in. Instead, it recognizes standard file formats such as Java keystore (JKS). Use the iKeyman utility to manage .jks files. For iSeries, use the Digital Certificate Manager (DCM) to manage .kdb files. For more information about DCM, see these topics in the iSeries Information Center:
There are also certain limitations with using Java Secure Socket Extension (JSSE):
- Customer code using JSSE and Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) APIs must reside within a WebSphere Application Server environment. This includes applications deployed in WebSphere Application Server and client applications in the J2EE application client environment.
- Only com.ibm.crypto.provider.IBMJCE, com.ibm.jsse.IBMJSSEProvider, com.ibm.security.cert.IBMCertPath, and com.ibm.crypto.pkcs11.provider.IBMPKCS11 are provided as the cryptography package providers.
- Interoperability of the IBMJSSE implementation with other SSL implementations by vendors is limited to tested implementations. The tested implementations include Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS), BEA WebLogic Server, IBM z/OS, IBM AIX, and IBM OS/400.
- Hardware token support is limited to supported cryptographic token devices. (Note: No hardware cryptographic devices are supported for iSeries.)
- The SSL protocol of Version 2.0 is not supported. In addition, the JSSE and JCE APIs are not supported with Java applet applications.