Delegation
Delegation is a process security identity propagation from caller to called object. The EJB Specification only supports delegation (RunAs) at the enterprise bean level. But an IBM extension allows specifying the delegation at the enterprise bean method level. This allows you to specify a different RunAs role for different methods within the same enterprise beans.
WebSphere Application Server supports the following types of delegation:
-
RunAs client identity
A servlet or enterprise beans propagate the client (remote user) identity when other enterprise beans are invoked:
-
RunAs specified identity
A servlet or enterprise beans propagate a specified identity in the corresponding deployment descriptor when other enterprise beans are invoked:
-
RunAs system identity
(IBM extension) An enterprise bean propagates the server ID when it invokes other entity beans: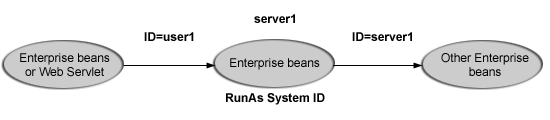
The RunAs Specification is specified in the deployment descriptor (the ejb-jar.xml file in the EJB module and the web.xml file in the Web module). The IBM extension to the RunAs specification is set in the ibm-ejb-jar-ext.xmi file. There is also an IBM-specific binding file for each application that contains a mapping from the RunAs role to the user. This is specified in ibm-application-bnd.xmi file.
The settings in these files are read by the run time during application startup.
The delegation process
The following figure illustrates the delegation mechanism as implemented in the WebSphere Application Server security model.
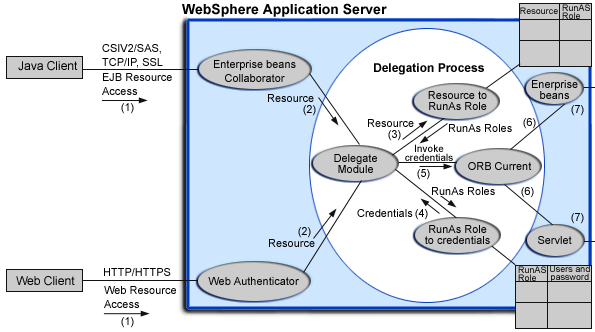
Two tables help in the delegation process:
-
Resource to RunAs Role mapping table
Use the Resource to RunAs Role mapping table to get the role that is used by Servlet or enterprise beans to propagate to the next enterprise beans call. -
RunAs Role to User ID and Password mapping table
Use the RunAs Role to User ID and Password mapping table to get the user ID that belongs to the RunAs role and its password.
The delegation process occurs as follows:
- A client requests access to an enterprise bean or Web resource.
- The client is successfully authenticated and authorized.
- The delegation module consults the Resource to RunAsRole mapping table to get the RunAs role.
- The delegation module consults the RunAs role to user ID and password mapping table to get the user that belongs to the RunAs role.
- The user ID and password is used to create a new credential using the authentication module (not shown in the figure). The resulting credential is stored in the ORB Current as invocation credential.
- When servlets and enterprise beans invoke other enterprise beans, the invocation credential is retrieved from the ORB Current.
- The subsequent enterprise beans are called.