Scenario 5: Interoperability with WebSphere Application Server Version 4
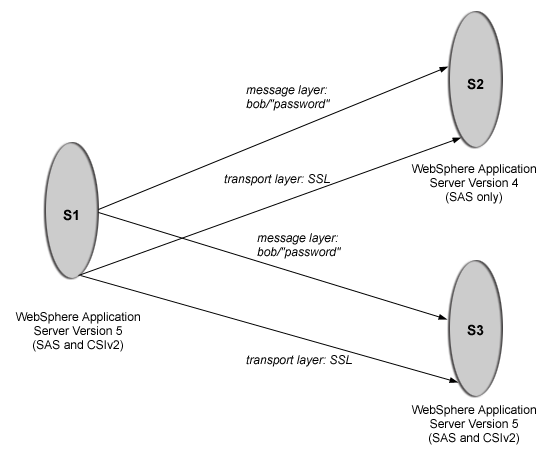
The purpose of this scenario is to show how secure interoperability can occur between different releases simultaneously while using multiple authentication protocols (Security Authentication Service (SAS) and Common Secure Interoperability Version 2 (CSIv2)).
For a WebSphere Application Server Version 5 server to communicate with a WebSphere Application Server Version 4 server, the WebSphere Application Server Version 5 server must support either IBM or BOTH as the protocol choice. By choosing BOTH, that Version 5 server also can communicate with other Version 5 servers that support CSI. If the only servers in your security domain are WebSphere Application Server Version 5, it is recommended that you choose CSI as the protocol because this prevents the IBM interceptors from loading. However, if there is a chance that any server will need to communicate with a previous release of WebSphere Application Server, select the protocol choice of BOTH.
Step 1: Configure S1
S1 requires message layer authentication with an SSL transport. The protocol for S1 must be BOTH. Configuration for incoming requests for S1 is not relevant for this scenario. To configure S1 for outgoing connections:
- Disable identity assertion.
- Enable user ID and password authentication.
- Enable Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
- Disable SSL client certificate authentication.
- Set authentication protocol to BOTH in the global security settings.
Step 2: Configure S2
WebSphere Application Server Version 4 only supports the SAS authentication protocol. There are no special configuration steps needed other than enabling global security on server (S2).
Step 3: Configure S3
In the administrative console, S3 is configured for incoming requests to message layer authentication and to accept SSL connections. Configuration for outgoing requests and connections are not relevant for this scenario.
- Enable identity assertion.
- Disable user ID and password authentication.
- Enable SSL.
- Disable SSL client authentication.
- Set authentication protocol to either CSI or BOTH.