Vertical scaling sample topology
Vertical scaling refers to setting up multiple application servers on a single machine. Use clusters to create additional application server processes on a single physical machine. This topology requires WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment.
This figure shows an example of a vertical scaling topology:
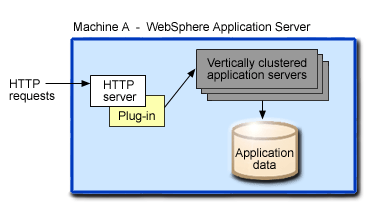
In this sample topology, multiple cluster members of an application server work together to implement vertical scaling on Machine A. You can also combine vertical scaling with other high availability techniques and configurations to improve availability, performance, and throughput.
Advantages and disadvantages of vertical scaling
Vertical scaling offers the following advantages:
-
Potentially more efficient use of the machine's processing power. Each application server runs in a single Java virtual machine (JVM) process. Some applications may create contention points on resources scoped to the JVM. For some applications, the use of multiple clustered servers, each with its own JVM process, improves availability by reducing the overall contention.
Use vertical scaling only if you need to. Clustering can increase the memory requirements of the application, and decrease performance. WebSphere Application Server for iSeries performs well with a single JVM. Vertical clustering is necessary only with some types of applications, or in the event of contention points in the JVM.
Vertical scaling provides a straightforward mechanism for creating multiple instances of an application server (and multiple JVM processes) on a single physical machine. This enables the application server to make the best possible use of the processing power of the host machine.
-
Load balancing. Vertically clustered application servers can use workload management to improve availability, performance, and throughput.
-
Process failover. A vertical scaling topology provides failover support among application server cluster members. If one application server fails, the other application server cluster members on the machine continue to process client requests.
The primary disadvantage of single-machine vertical scaling topologies is that the host machine becomes a single point of failure in the system. To eliminiate this risk, you can implement vertical scaling in a multiple machine topology, or use horizontal scaling.
Configure a vertical scaling topology
Before you implement vertical scaling, decide how many cluster members to create. These are some factors to consider as you plan for a vertical scaling topology:
-
The application design: Applications that use more components require more memory, which limits the number of cluster members that you can run on a machine.
-
The hardware environment: Vertical scaling is most beneficial on machines with large amounts of memory and processing power. However, eventually the overhead of running more cluster members cancels out the benefits of adding them.
To set up a vertical scaling topology, use the administrative console to configure a set of application server cluster members that reside on your iSeries server. See Clusters and clustering for more information on clustering an application server.
The best way to ensure good performance in a vertical scaling configuration is to tune a single application server for throughput and performance, then incrementally add cluster members if needed. In general, a single application server on iSeries is adequate to process most workloads. Test performance and throughput as you add each cluster member. Always monitor memory use when you are configuring a vertical scaling topology to ensure additional memory requirements do not cause excessive paging on a machine.