Sample combined topology
A combined topology uses elements of other topologies to enhance availability, scalability, security, workload balancing, performance, and throughput. This topology requires WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment.
This figure shows an example of a combined topology:
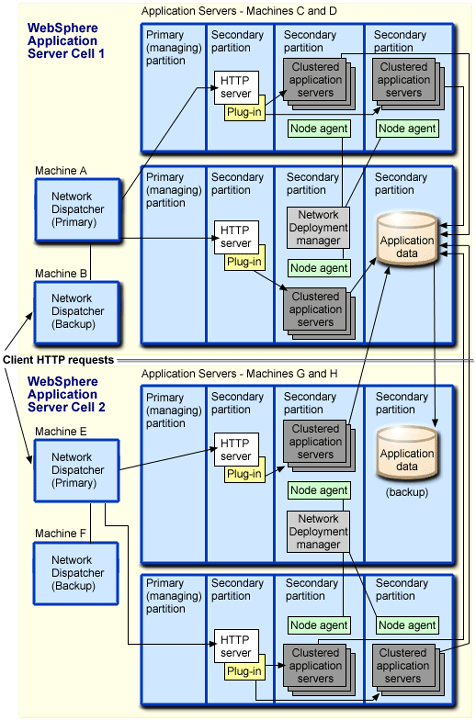
This sample topology includes these features:
- Two WebSphere Application Server cells. An application is deployed into both cells.
- You administer each cell separately. Each cell has its own set of XML configuration files and its own Network Deployment manager. Within each cell, the Network Deployment manager communicates with node agents in each partition to manage the application servers.
- One Network Dispatcher node in each cell (Machines A and D). Network Dispatcher distributes client HTTP requests among the two cells. Clients are presented with a single image of the application. You can also configure backup Network Dispatcher nodes for each cell, or configure one node to server both cells, and configure a second node as a backup.
- Four HTTP servers. One HTTP server is configured for each application server machine (Machines B, C, E, and F). You can also configure one HTTP server to for each cell, and configure a second HTTP server as a backup.
- Clustered application servers in secondary partitions on machines B, C, E, and F. Note identical applications are deployed in all partitions in both cells.
- This topology also shows the application database. Both cells in the topology share a common application database. The database uses data replication to enhance availability and avoid creating a single point of failure. For more information on high availability databases, see High availability database.
Note: Although the high availability database is included in this sample topology, it is not required to implement the topology.
Advantages and disadvantages of a combined topology
These are some of the advantages of a combined topology:
-
Provides isolation of hardware failure. If one cell goes offline due to hardware problems, the remaining cells can still process client requests.
-
You can perform hardware upgrades on a cell-by-cell basis during off-peak hours.
-
Provides isolation of software failure. When you deploy an application in two or more cells, any problems that occur within one cell are isolated, and the other cells continue to handle client requests. Process isolation allows you to maintain high availability in any of these situations:
- When you deploy a new application or a revision of an existing application. You can test the new application or revision in one cell while the other cells continue to process client requests.
- When you deploy a new version of WebSphere Application Server for iSeries. You can test the new version into in a live environment without interrupting service.
- When you apply fixes or patches to WebSphere Application Server for iSeries. You can perform hardware and software upgrades on a cell-by-cell basis during off-peak hours to avoid an interruption of service.
If a problem occurs with the new software, you can accomplish a rollback to a previous software version more quickly.
-
Improves performance. Running an application in multiple smaller cells can provide better performance than a single large cell because there is less interprocess communication in a smaller cell.
-
Improves workload balancing. In a combined topology you can use one or more of these workload management techniques:
- Use the WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment workload management (WLM) facility to distribute work among application server cluster members.
- Use Network Dispatcher to distribute client HTTP requests to each Web server.
For example, an application can manage workloads at the Web server level with Network Dispatcher and at the application server level with WebSphere workload management. Using multiple workload management techniques in an application provides finer control of load balancing.
The primary disadvantages of a combined topology are:
-
Deployment is more complicated than for a single administrative cell. Use a distributed file system that provides a common file mount point to make this task easier.
-
Multiple cells are more complicated to adminster because each cell is administered separately. To reduce this problem, you can use wsadmin scripts to standardize and automate common administrative tasks.