Price equations and constants in price rules
A price equation is a mathematical statement used in a price rule to calculate and output a price. For example, we can create a price equation that adds margins or distribution costs to prices in a price list. We can use the same price equation in more than one price rule so that the set of price rules is easier to maintain.
The following are examples of simple price equations we can create:
- Output Price = Cost * (1 + Margin)
- Output Price = Offer price + Markup
- Output Price = List price * 0.95
To use a price equation to calculate prices on the storefront:
- Create the price equation using the graphical equation builder in the Catalog Filter and Pricing tool.
- Create a price rule, and then include the price equation in the price rule using the Calculate Price action.
Here is an example: Figure 1. Price equation
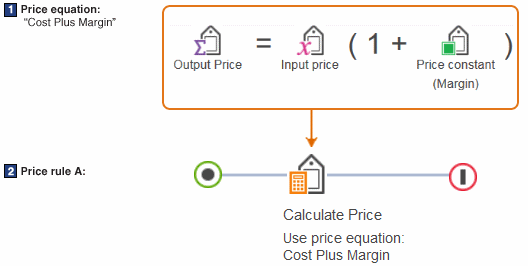
In Figure 1:
- 1 This is a price equation called "Cost Plus Margin," which adds a margin to prices in a "Cost" price list.
- 2 The "Cost Plus Margin" price equation is included in a price rule using the Calculate Price action.
When Price rule A is assigned to a contract, the price rule calculates the prices customers see on the storefront.
Independent and dependent price equations
We can create two types of price equations, depending on how you plan to reuse the equation:- Independent price equation
- A price equation that contains a price list. Figure 1 is an example
of an independent price equation because it includes the "Cost" price
list in the equation. All independent price equations must contain
a Price List icon, which specifies the price
list to use.
Create an independent price equation if you do not plan to reuse the equation with a different price list.
- Dependent price equation
- A price equation
that does not contain a price list. The
equation is dependent because it depends on an input
price. When we use a dependent equation in a price rule, a previous
action in the price rule flow must pass in a price to the equation,
as shown in the following example:Figure 2. Price equation (dependent)
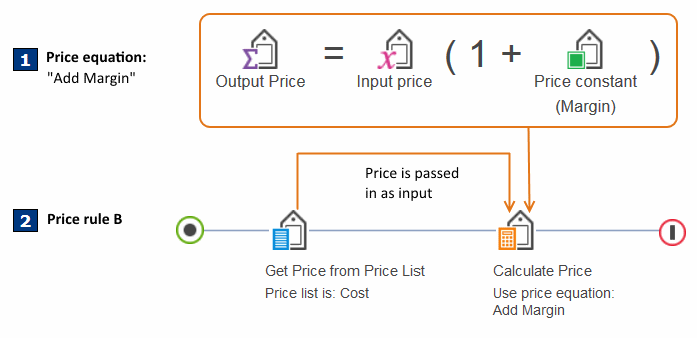
- 1 This is a dependent price equation called "Add Margin," which adds a margin to an input price. The Input Price icon represents a variable in the equation that must be passed a price. All dependent price equations must start with the with the Input Price icon.
- 2 Price rule B uses the "Add Margin" price equation. To provide an input price to the equation, the price rule passes in a price from the "Cost" price list.
Dependent price equations are more flexible because we can use them to perform the same calculation on different inputs. For example, in a different price rule, you could use an "Offer" price list instead of the "Cost" price list, but continue to use the "Add Margin" price equation.
A price list is only one means of passing an input price to a dependent price equation. We can use other price rule actions to pass in an input price, such as a Nested Price Rule action or an independent Calculate Price action. Place the action that passes in the price to the left of the Calculate Price action containing the dependent price equation (as shown in Figure 2).
Constants in price equations
A price constant is a number, a percentage, or a price that you intend to use over and over to calculate prices. We can create a price constant, and then use the constant in one or more price equations, or in a Comparison Condition. If you change the value of the constant, our changes automatically apply wherever the constant is used, saving you time. Here are a couple of examples:- Example 1: A pricing
manager uses the following price equation
to add a 30% margin to her costs:

The pricing manager can create a constant to represent the margin value in this equation, rather than specifying 0.3 directly in the equation. The revised price equation now looks like this:

This constant can be used in any other equation that adds the same margin to a price. Later, if the pricing manager wants to change the margin to 0.4, she can change it once in the constant, and all price equations that use the constant will automatically use the margin value 0.4.
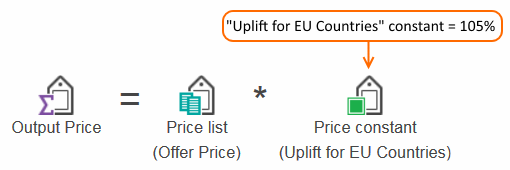
- Example 2: A pricing manager needs to include an uplift on prices
for a European Union (EU) site. The uplift is typically 5%, but the percentage can change over time. To make managing the uplift percentage
easier, the pricing manager creates a constant called "Uplift for
EU Countries" and uses the constant in price equations that require
the uplift, as shown here:
The format of a constant can be:
- Numeric (a number)
- Percentage
- Currency (a price, which can be represented in different currencies). Currency constants are useful when we want to use the same constant regardless of the currency the price equation must handle. For example, we can specify a value of 5.00 in Euros and 4.00 in British Pounds.
When choosing the format of your constant (Numeric, Percentage, or Currency), think carefully about how we are going to use the constant in your calculation or comparison. Here are a few tips:
- If the constant is a percentage, always multiply by the percentage constant in your price equation, for example, Price * 110%. Do not add a percentage constant, for example, Price + 10%.
- To add or subtract a monetary amount to or from a price, use the currency constant, for example, Price + $5. It does not make sense to add or subtract a numeric constant, for example, Price + 5, because the price has a unit and the numeric constant does not.
- It does not make sense to multiply by a currency constant, for example, Price * $5.
- If we are comparing constants in the Comparison Condition, the two constants must be the same format. For example, it does not make sense to compare a numeric constant to a currency constant.