Session management
Browsers and e-commerce sites use HTTP to communicate. HTTP is a stateless protocol, which means that each command is run independently without any knowledge of the commands that came before it. Because it is a stateless protocol, sessions must be managed between the browser side and the server side.WebSphere Commerce supports two types of session management: cookie-based and URL rewriting.
The administrator can choose to support either only cookie-based session management or both cookie-based and URL rewriting session management. If WebSphere Commerce supports only cookie-based session management, customers' browsers must be able to accept cookies. If both cookie-based and URL rewriting are selected, WebSphere Commerce first attempts to use cookies to manage sessions. If the customer's browser is set to not accept cookies, then URL rewriting is used.
Cookie-based session management
When cookie-based session management is used, a message (cookie) containing user's information is sent to the browser by the web server. This cookie is sent back to the server when the user tries to access certain pages. The cookie allows the server to identify the user and retrieve the user's session from the session database, so that the user’s session is maintained. A cookie-based session ends when the user logs off or closes the browser. Cookie-based session management is secure and has performance benefits. Cookie-based session management is secure because it uses an identification tag that flows only over SSL. Cookie-based session management offers significant performance benefits because the WebSphere Commerce caching mechanism supports only cookie-based sessions, and not URL rewriting. Cookie-based session management is recommended for customer sessions.
For security reasons, cookie-based session management uses two types of cookies:
- Non-secure session cookie Used to manage session data. Contains an activity identifier that points to attributes such as the negotiated language, current store, and customer's preferred
currency at the time the cookie is constructed. This cookie can flow between the browser and server
under either SSL or non-SSL connection. There are two types of non-secure session cookies:
- A WebSphere Application Server session cookie is based on the servlet HTTP session standard. WebSphere Application Server cookies persist to memory or to the database in a multinode deployment. See the Session management support topic.
- A WebSphere Commerce session cookie is internal to WebSphere Commerce and does not persist to the database. All the cookies persist to memory except the persistent cookie. This configuration is the default. This configuration is required if URL rewriting is enabled.
- Secure authentication cookie
Used to manage authentication data. An authentication cookie flows over SSL and is time-stamped for maximum security. This cookie is used to authenticate the user whenever a sensitive command is run. For example, the DoPaymentCmd, which asks for a user's credit card number. There is minimal risk that this cookie might be stolen and used by an unauthorized user. Authentication code cookies are always generated by WebSphere Commerce whenever cookie-based session management is in use.
Both the session and authentication code cookies are required to view secure pages.
For cookie errors, the CookieErrorView is called:
- When the user logs in from another location with the same Logon ID, and multiple logon is not enabled.
- When the cookie is corrupted, tampered with, or both.
- If cookie acceptance is set to true and the user's browser does not support cookies.
Warning: Some browsers have features that preserve session cookies across browser sessions. One example is the Continue where I left off option that is provided by Google Chrome. Although these configurations are non-default, and require users to explicitly enable them, they can create privacy concerns when the browser is used in a public setting such as an Internet Cafe.
If the browser is configured to not destroy session cookies when it is closed, the cookies used for user identification and authentication remain active after the browser is restarted. In the case of a registered user, the user remains logged in. In the case of a guest user, all the assets associated to the user, such as pending carts, orders, or addresses, remain associated to the session in the browser. This behavior is caused by the browser not destroying session cookies, and it affects all sites that are accessed from the browser in the same way.
The default configuration for WebSphere Commerce is that when a user registers or logs in, the assets associated to the guest user before they login are transferred to the registered user account. These assets include addresses, orders, and interest items. This scenario might be a concern if the browser is shared and if it is configured to not destroy session cookies upon closure. For example, a guest user might place an order and close the browser. The following day, a different person might open the same browser and log in. Because the guest user session remains active, its assets, including the order that is placed and addresses used, are associated with the registered user that logged in.
The following options are available to avoid this scenario:
- Customize the MigrateUserEntriesCmd command, which is used to migrate addresses, orders and interest items from the current guest user session to the user that logs in. We can customize the command so that certain assets are not copied by replacing the method with an empty implementation.
- After a guest user places an order, automatically issue the Logoff command to reset the guest user session to the generic user.
Preserved session cookies to not present the same concern for registered users because these shoppers can use the Logoff link to clear their session information.
Browsers running on personal or mobile devices, such as phones or tablets, have the same issues as shoppers who use a browser in a public setting. These types of devices are not typically shared, so they do not present the same privacy concerns. However, shoppers on personal or mobile devices do not typically end the browser application after they browse a site, so session cookies are not destroyed. The options that are provided for protecting the privacy of shoppers in a public setting also apply to browsers that run on personal or mobile devices.
URL rewriting
WebSphere Commerce dynamic caching and URL rewriting cannot interoperate. If URL rewriting is enabled, then disable WebSphere Commerce dynamic caching.
With URL rewriting, all links returned to the browser or that get redirected have the session ID appended to them. When the user clicks these links, the rewritten form of the URL is sent to the server as part of the client request. The servlet engine recognizes the session ID in the URL and saves it for obtaining the proper object for this user. To use URL rewriting, HTML files (files with .html or .htm extensions) cannot be used for links. To use URL rewriting, JSP pages must be used for display purposes. A session with URL rewriting expires when the customer logs off.
Because URLs returned to the browser contain session IDs, another user with access to the browser history (for example, on a shared computer) might gain access to sensitive information exchanged during a session - if the session is left active. To prevent such unauthorized access, site developers can add a notice to their site to tell customers to always log off at the end of their visit so that their session ends, particularly on a shared computer.
WebSphere Commerce session cookies
The following table lists WebSphere Commerce session cookies. All of these cookies are considered essential for the operation of WebSphere Commerce. We cannot disable these cookies. Session cookies are not persistent.
| Cookie name | Description |
|---|---|
| _AN_CGID_COOKIE | Stores the categories visited by a user, which is later used by the following Analytics tags: Product tag, Cart tag, and Order tag. |
| REFERRER | The value of referer in the HTTP header. |
| WC_ACTIVEPOINTER non-secured session cookie | This cookie contains the value of the store ID of the session. This value is
used to select the store to run the command, if one is not specified on the URL.
|
| SESSION_COOKIEACCEPT | Checks whether the client browser accepts cookies. |
| WC_AUTHENTICATION_ID secured session cookie | WebSphere Commerce uses a secure authentication cookie to manage
authentication data. An authentication cookie flows only over SSL. For increased security, it has a
timestamp with a signature. This cookie is used to authenticate the user over SSL-connections.
|
| WC_GENERIC_ACTIVITYDATA non-secured session cookie | This cookie exists only if it is a generic user (-1002)
session. This cookie stores the session values such as store ID, language ID, and contracts.
|
| WC_SESSION_ESTABLISHED non-secured session cookie | This cookie is created on the first request that is processed by WebSphere Commerce run time. For example, a non-cache request.
|
| WC_USERACTIVITY_ID non-secured session cookie | This cookie is a user session cookie that flows between
the browser and server over both SSL or non-SSL connection. It
is used for user identification over non-SSL connections. It
contains user session values such as the session login time,
and session identifier information such as the user ID and
store ID.
|
| LTPA2 cookie WebSphere Application Server cookie | This cookie is used when WebSphere Commerce enabled for single sign-on with other WebSphere applications information center. |
| WC_EdgeCacheComponent_storeId | Used for Edge Caching. |
| WC_identitySignature | Management Center session cookie. |
| fulfillmentCenterId | Fulfillment center selected in Accelerator. |
| LtpaToken2 | WebSphere Application Server LTPA token used for single sign on. |
Note:
- All session cookies, except for WC_SESSION_ESTABLISHED, can be used in the Management Center preview environment. In the preview environment, the session cookie name is prefixed with WCP_. The cookies support sessions and users in the preview environment.
- The value of session cookies is encrypted using the session encryption key. See ../tasks/tsechangesessionkey.htm.
Store-level session management
The following diagram illustrates the WebSphere Commerce store level registration infrastructure and user session management in a multi-store environment. Store level registration uses access control roles to associate a customer with a store.
Store level registration
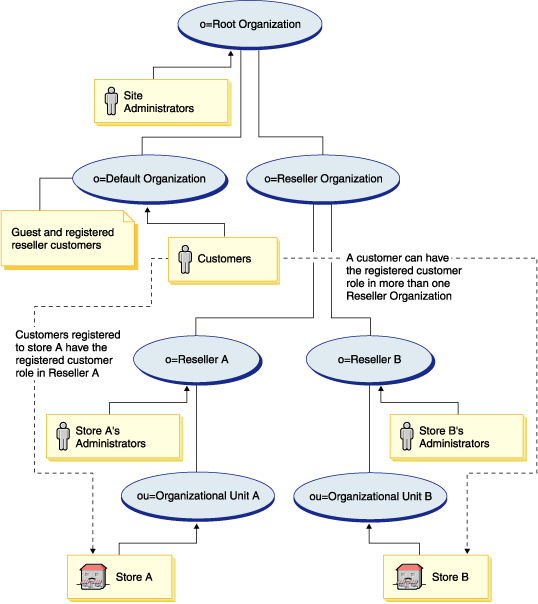
Users that shop at a store do not necessarily need to be a member of the store organization. However, they must play a shopping role (that is, they must be a Registered Customer) in the organization. Users that play an administrative role in an organization are associated with the organization by having an ancestral relationship with the organization.
For example, suppose that you have a store, Store A as in the preceding diagram. Also, suppose that Sue shops at Store A and Joe is an employee for Store A responsible for the administrative duties of running Store A. To model this scenario from an organizational perspective, Joe belongs under Store A's organization but Sue does not. Because Sue is not an employee of Store A, Sue is associated with Store A because she plays the shopping role in the Store A organization.
A store determines all of its registered customers by finding all the users that play a shopping role in the store organization. A user administrator of the store can then perform store wide activities, such as setting up a campaign for all the registered users in a store. The user administrator of the store can also take specific actions, such as resetting the password of a user that is registered to its store.
Refer to the previous diagram and consider the following scenario:
- Sue, who is a member of the Default Organization, has a shopping role in Reseller A's organization.
- Reseller A's parent organization is the Reseller Organization.
- Reseller A owns store A.
- Sue does not have an organizational role in Reseller B's organization.
- Reseller B owns store B.
- Sue logs in to Store A and shops as usual.
- When Sue accesses Store B, Sue is assigned a new session identity for Store B as a guest user.
- If she accesses Store A again, the information in her previous session identity for Store A is used by WebSphere Commerce to manage her session.
- The session identity for Store A would be reused for Store B if:
- Store A and Store B belong to the same organization.
- Sue has a role that is defined in both the Reseller A and Reseller B organizations.
Aurora starter store cookies
The following table lists Aurora starter store cookies.
| Cookie name | Description |
|---|---|
| analyticsFacetAttributes | The list of facets that the customer clicked, making this data available to the analytics tags in those pages. The cookie is continually updated until the customer starts a new search or starts a new session. |
| analyticsPreCategoryAttributes | Pre-category attributes used for Analytics. |
| analyticsSearchTerm | Search terms used for Analytics. |
| CompareItems_storeId | Catalog Entry IDs that are being compared. |
| priceMode | Display mode for showing prices in the storefront. |
| searchTermHistory | The history of terms searched. |
| signon_warning_cookie | Error key used to retrieve error messages. |
| WC_CartOrderId_storeId | Active Order Id for the store. |
| WC_CartTotal_orderId | Subtotal of order items (before tax and shipping), number of items, language, currency. |
| WC_DeleteCartCookie_storeId | Cookie to force refresh of other Mini Shopping Cart cookies. |
| WC_physicalStores | Physical stores that customer selects. |
| WC_pickUpStore | Pick-up store ID that customer selects. |
| WC_recurringOrder_orderId | Recurring order ID. |
| WC_ScheduleOrder_orderId_interval | Scheduled orders interval. |
| WC_shipTypeValue | Shipping type value: single or multiple. |
| WC_shipTypeValueOrderId | The orderId that corresponds to the Shipping type. |
| WC_SHOW_USER_ACTIVATION_storeId | Flag to show user activation message after user registration. |
| WC_OnBehalf_Role_storeId | Cookie to track the role of the user who started an on behalf session. |
| WC_Base_Text_Direction | This cookie is created when a shopper sets the Text
Direction in the Language and Currency panel. The cookie can be
used in HTTP and HTTPS.
|
See
- European Union Data Protection Directive and WebSphere Commerce cookies
- Use cookies for session management
- Use URL rewriting for session management
- Use JSP pages for URL rewriting
- Changing session management settings in the WebSphere Commerce configuration file (wc-server.xml)
- Enable multiple logon support for the same user