Units of measure assets
Products can be sold, and inventory tracked, in a variety of quantity units, such as kilograms, inches, liters, and so on. Of these units, products can be ordered in minimum quantities, and by multiples of specific quantities.
The controller commands use the UOM (unit of measure) to specify the quantity unit. If a UOM parameter is not specified, then the customer's specified quantity is multiplied by the nominal quantity of the catalog entry in the CATENTSHIP database table. The result is known as the requested quantity.
The requested quantity is rounded up to the next highest quantity multiple for the catalog entry. For example, if the multiple is 2 kilograms and the requested quantity is 4.1 kilograms, the result of the rounding would be 6 kilograms. The rounded quantity is used when checking inventory, which has its own quantity unit. If the inventory quantity unit and the catalog entry quantity unit are different, there must be a conversion between the two units.
When Available to Promise (ATP) inventory is enabled (refer to the INVENTORYSYSTEM column of the STORE table), the inventory quantity unit is defined in the QUANTITYMEASURE column of the BASEITEM table. Otherwise, it is defined in the QUANTITYMEASURE column of the INVENTORY table.
The rounded quantity divided by the nominal quantity of the catalog entry is known as the normalized quantity. The normalized quantity is stored in the order item or the interest item, depending on the command being run. For example, if the rounded quantity is 6 kilograms and the nominal quantity is 2 kilograms, then the normalized quantity is 3.
When finding an offer for a catalog entry, the requested quantity can affect which offer gives the best price, and hence determines which offer will be used. For example, if the rounded quantity is 6 kg and there are two offers, one that specifies a price of $4.00 for the nominal quantity of 2 kilograms and a minimum quantity of 10 kilograms, and another that specifies a price of $4.50 for the nominal quantity of 2 kilograms and a minimum quantity of 2 kilograms, then only the second offer can be used.
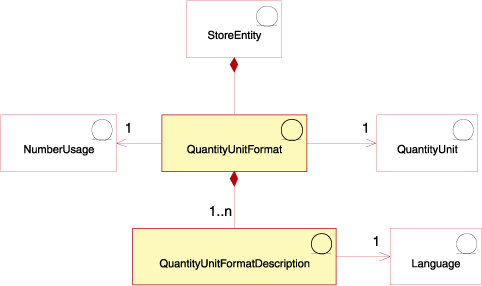
The following diagram illustrates the structure of units of measure in the WebSphere Commerce Server:
- Quantity unit and quantity unit format
-
A quantity unit is the unit of measurement used in the store, for example, kilograms, pounds, meters, inches, liters, and so on. The quantity unit format is how this quantity unit is formatted in the store, for example how many decimal places are used when displaying the quantity unit.
Each quantity unit format is part of only one store entity, but each store entity may have several quantity unit formats.
A quantity unit format can exist for each quantity unit and number usage, and may have one or more quantity unit format descriptions, depending on how many languages the store supports.
Quantity units defined in one store may be used by other stores. In order for one store to use quantity units defined in another store a store relationship of type com.ibm.commerce.measurement.format must be created between the stores. For more information, see Relationships between stores.
- Quantity unit format description
- A quantity unit format description describes how to format (for display purposes) a quantity amount in a particular quantity unit, in a particular language.
- Number usage
-
Number usage defines the way a number is used in an application. For example, by using number usage codes in your WebSphere Commerce code, you can choose the way you would like that number (currency or quantity) to be formatted or rounded. These codes (defined in the NUMBRUSG table) allow the number to be formatted according to the rules specified for that type of number usage in the CURFORMAT, CURFMTDESC, QTYFORMAT and QTYFMTDESC tables. This allows stores to format numbers in different ways to meet the requirements of a variety of situations.
Related tasks
Related reference