Seller assets
A Seller is a user within WebSphere Commerce. The Seller supervises the overall store objectives and management, in addition to tracking the store sales. A Seller sells the goods and services to the customer. The Seller role is equivalent to a merchant and has access to all WebSphere Commerce Accelerator capabilities.
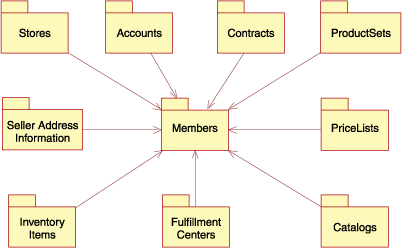
The following diagram illustrates the assets that a Seller requires to maintain a store and to sell to customers.
 relationships." usemap="#FPMap0"/>D
relationships." usemap="#FPMap0"/>D
- Users
- The WebSphere Commerce system contains members. Each member is assigned a role, such as Customer Service Representative for the store, or Receiver at a warehouse. The Seller role can maintain the following assets in order to sell to customers:
- Stores
- Contracts (or at least the WebSphere Commerce default contract)
- Product sets
- Price lists
- Catalogs
- Fulfillment centers
- Inventory items
The diagram highlights the relationship between a member (Seller) and the Seller assets; that is, a Seller can have the assets listed above to maintain a store and the assets need to have a Seller for deployment.
- Stores
- A WebSphere Commerce online store is comprised of a set of HTML and JavaServer Pages files, as well as tax, shipping, payment, catalog and other database assets, which are contained in a store archive. A store also contains store data, which is the information populated into the WebSphere Commerce database to allow a store to function.
- A store can set up business accounts for customers to allow them to purchase from the store. An account contains the following information:
- The account name, which is often the name of the organization with which the customer is associated. This organization has defined contracts with the store, stipulating terms for the customer to shop at the store. For example, the organization IBM may have contracts with the ABC Office Supplies Company.
- The representative name, which is the name of the representative organization within the Seller's organization that is responsible for the account.
- The number of contracts that belong to the account.
- Contracts
- Typically, in WebSphere Commerce, all customers must shop under a contract. Each account between the customer and the Seller must be associated with one or more contracts (or at least a defaultcontract for non-registered customers or customers to shop at the store, or if you want customers to be able to purchase products not covered by other contracts). A contract allows the customer to purchase products from a store at a specified price for a specified period of time, under terms and conditions, and business policies, stipulated in the contract. The Seller deploys the contract so that customers can buy from the store.
The Buyer in a contract can be a user, an organization, or a member group. In the case of the user, the Buyer is considered the customer. In the case of an organization, which is defined as a Buyer in a contract, then any child of this organization can act as a Buyer for the contract. In the case of a member group, any user in the member group can act as a Buyer for the contract.
- Product sets
- Product sets provide a mechanism for a Seller to categorize online catalogs into logical subsets so that a Seller can allow various customers to take advantage of different catalog views. Furthermore, a Seller can create a contract for a customer and stipulate that the customer can only purchase products under a predefined product set.
- Price lists
- A price list is associated with the price a Seller offers or presents to a customer. A Seller can list different prices for the same product to different customers. In WebSphere Commerce, a price offer is also known as a trading position and represents the price of a catalog entry and criteria that the customer must satisfy in order to qualify for that price.
In WebSphere Commerce, an Offer object is part of a TradingPositionContainer, which is owned by a member. A TradingPositionContainer contains TradingPositions, and can be made available to all customers, or to only customers in certain groups through the trading agreements or contracts. Sometimes a TradingPositionContainer is referred to as a price list. There are two kinds of price lists: a standard price list which contains the base prices for the products in the store catalog or a custom price list which specifies the list of products and their customized prices.
In some business models, you may have multiple standard price lists, which could be based on either cost, or on list prices.
- Catalogs
- A WebSphere Commerce store uses at least one online catalog to showcase the goods and services that the Seller offers for sale. Typically, an online catalog contains prices, images, and descriptions of the items for sale. An online catalog may also present merchandise into distinct categories to facilitate navigation.
Each store in the WebSphere Commerce system must have a master catalog, which is used for catalog management. The master catalog is the central location to manage a Seller's merchandise; it is the single catalog containing all products, items, relationships, and standard prices for everything that is for sale in the store. If a Seller has more than one store, the master catalog can be shared between these stores.
- Fulfillment centers
- Fulfillment centers are used by stores as both inventory warehouses and shipping and receiving centers. A Seller may have one or many fulfillment centers.
From a WebSphere Commerce Server perspective, a FulfillmentCenter object is separate from the Store object. It manages product inventory and shipping. To ship an order, the fulfillment center relies on a ShippingMode object that is specified by the customer. The ShippingMode object indicates the shipping carrier and method of shipping for fulfilling orders. In a fulfillment center, the ShippingArrangement object indicates that a Store object has arranged with a FulfillmentCenter object to ship products using a certain ShippingMode.
- Inventory items
- Inventory items include anything that can be physically accounted for in a Seller's fulfillment center. The WebSphere Commerce system defines specific types of inventory that can be fulfilled, such as items, products, SKUs, bundles, and packages; but these are all considered inventory. Products are configured for fulfillment using the Product Management tools on WebSphere Commerce Accelerator.
- Seller address information
- Information about the Seller's address is important for several parties within an order. For example, fulfillment centers require this information for shipping inventory. Likewise, customers require this information to contact the Seller of any order inquiries.
