Destination mediation
A destination can be configured with one or more mediations that refine how messages are handled by the destination. For example, a mediation can modify the actual message, or redirect the message to another destination or sequence of destinations, or both.
A mediation can process messages through message transformation, subsetting, aggregation, disaggregation, and using a selection of destinations (but not consumers) to which the message can be forwarded.
When a message arrives at the mediation point, the mediation consumes the message and can transform, subset, aggregate or disaggregate the message. The message is then either forwarded to another destination or returned to the same destination. If the message is returned to the same destination, it goes to the queue point, where it can be consumed by the messaging application. This process is shown in the following figure:
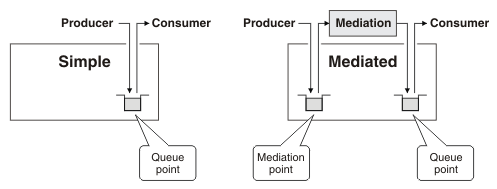
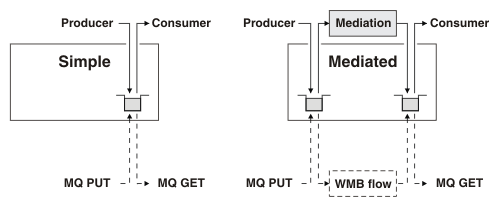
We can configure a destination so the mediation point or the queue point, or both are IBM MQ queues. If both are IBM MQ queues then an IBM MQ application can act as an external mediation as shown in the following figure:
Related: