Multiple-server bus with clustering
We can have a bus consisting of multiple servers, some or all of which are members of a cluster. When a server is a member of a cluster, it allows servers to run common applications on different machines. Installing an application on a cluster that has multiple servers on different machines provides high availability. If one machine fails, the other servers in the cluster do not fail.
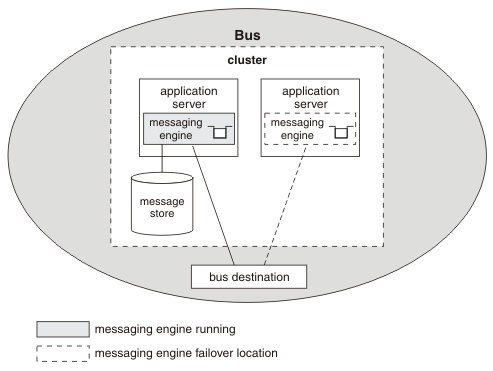
When we configure a server bus member, that server runs a messaging engine. For many purposes, this is sufficient, but such a messaging engine can run only in the server it was created for. The server is therefore a single point of failure; if the server cannot run, the messaging engine is unavailable. By configuring a cluster bus member instead, the messaging engine can run in one server in the cluster, and if that server fails, the messaging engine can run in an alternative server. See Bus member types and their effect on high availability and workload sharing.
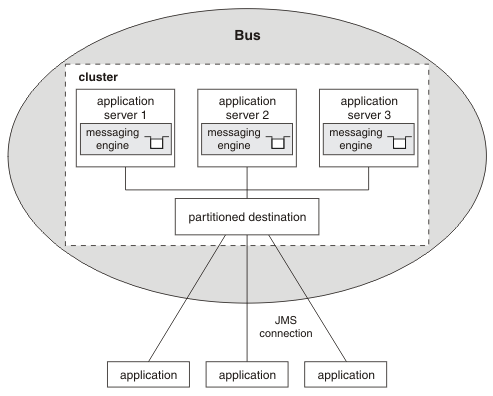
Another advantage of configuring a cluster bus member is the ability to share the workload associated with a destination across multiple servers. We can deploy additional messaging engines to the cluster. A destination deployed to a cluster bus member is partitioned across the set of messaging engines that the cluster servers run. The messaging engines in the cluster each handle a share of the messages arriving at the destination. This is a familiar concept to those with knowledge of cluster queues in IBM MQ. See Workload sharing.
To summarize, with a cluster bus member we can achieve high availability (through failover). We can also configure a cluster to achieve workload sharing or workload sharing with high availability, depending on the policies that we configure for the messaging engines. See Policies for service integration.
Service integration bus with clustered server
Service integration bus with partitioned destinations
Related: