Message flow between service integration buses
An application connects to a bus, which is its local bus, and can exchange messages with other applications that connect to the same bus. To exchange messages with applications that connect to a different bus, that is, a foreign bus, you need a service integration bus link that connects the local bus to the foreign bus.
Applications that are connected to the local bus send messages to a destination on a foreign bus. The messaging engine on the local bus queues the messages on its link transmitter queue. For applications that use point-to-point messaging, there is one link transmitter queue and one link transmitter for each messaging engine in the sending bus. For applications that use publish/subscribe messaging, there is one link transmitter queue and one link transmitter for each topic space destination that is mapped to a topic space destination in the foreign bus.
Each link transmitter queue has a corresponding link receiver queue on the gateway messaging engine on the foreign bus. Each link receiver queue is served by a link receiver.
The link transmitter sends the messages over the service integration bus link to link receiver queues. Link receivers remove the messages from the link receiver queues and place them on the target remote queue points, which are on the gateway messaging engine on the foreign bus. Both point-to-point and publish/subscribe messaging in service integration use link transmitter queues.
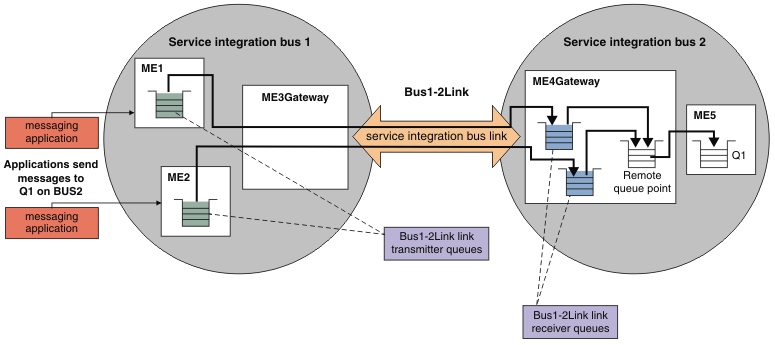
The following figure shows an example of the message flow from Service integration bus 1 to a foreign destination on Service integration bus 2 over a service integration bus link. One application is connected to the messaging engine ME1, and another application is connected to messaging engine ME2. The applications produce messages to send to Q1 on the foreign bus. Messages are queued on the link transmitter queue on each messaging engine, then transmitted through the gateway messaging engine and the service integration bus link to the link receiver queues on the gateway messaging engine in the foreign bus. From here, the messages are placed on to the target destination Q1. The target queue Q1 is on the messaging engine ME5. The link receiver in the gateway messaging engine ME4Gateway routes the messages to ME5 using a remote queue point.
Figure 1. Message flow between two service integration buses
Related
Configure exception destination processing for a link to a foreign bus
Manage messages in a link transmission queue for a connection between two buses
View messages in a link receiver queue for a connection between two buses