Create dynamic clusters
Overview
When creating a dynamic cluster, the workload of the cluster members is dynamically balanced based on performance information collected from the cluster members. Creating dynamic clusters enables application server virtualization.
Dynamic clusters expand and contract depending on the workload in the environment. Dynamic clusters work with autonomic managers, including the application placement controller and the dynamic workload manager to maximize the use of our computing resources. Dynamic clusters are required for many of the product autonomic functions, including high availability and service policies.
Before creating a dynamic cluster...
- We must have configurator administrative privileges.
- Verify that the application placement controller is enabled. The application placement controller is enabled by default. To enable...
-
Operational policies > Autonomic managers > Application placement controller

- Decide if we are going to use vertical stacking.
Vertical stacking can improve bottleneck conditions in deployed applications by enabling the placement controller to start more than one instance of the dynamic cluster on a node. With vertical stacking enabled, the autonomic managers limit the processor percentage used by each stacked instance. The general formula is 100%/max-number-of-stacked-instances. For example, if we configure three stacked instances, the workload is throttled to prevent any single instance form using more than 33% of the processor capacity.
- If we are creating a dynamic cluster of externally created middleware servers with assisted life-cycle management, create representations of these servers in the product environment before creating a dynamic cluster. All of these servers must have the same applications installed and have the same version of middleware software installed.
Deprecated feature: Assisted and Complete Lifecycle servers have been deprecated in WebSphere Application Server v9.0. Migrate WebSphere Liberty servers to a Liberty Collective configuration. There is no recommended migration action for other server types.depfeat
If we already have over 40 servers in our core group, we can use the coregroupsplit.py script to split our existing cell into multiple core groups.
Create a dynamic cluster
- Create the dynamic cluster.
In the administrative console, click...
- Servers > Clusters > Dynamic clusters > New
- Select the dynamic cluster server type.
The dynamic cluster server type determines the type of servers that are members of this dynamic cluster. Depending on the type, enter the name of the dynamic cluster on this panel or when we select the membership method.
- For some dynamic cluster types, we can select the membership method. The membership method defines how servers join the dynamic cluster as cluster instances.

Option Description Automatically define cluster members with rules We can Automatically define cluster members with rules if we are using servers with complete life-cycle management. With this option, we create a membership policy that defines the nodes on which cluster instances can be placed. Manually define cluster members If we are using servers with assisted life-cycle management, we can Manually define cluster members. With this option, we select existing servers to add to the dynamic cluster. The servers that we select must be homogenous: that is, they must be of the same server type, middleware server version, and have the same applications installed. To add a new middleware server to an existing dynamic cluster when one or more applications are targeted to the dynamic cluster, install the applications on the middleware server and target the applications to the server before we add the server as member of the dynamic cluster.
- Define the dynamic cluster members.
- If we selected Automatically define cluster members with rules in the previous step, use the subexpression builder to build a membership policy expression for our dynamic cluster. This expression is compared to all the nodes in the cell, selecting any nodes for which the subexpression is true.
- By default, the value of the Membership policy field is set to node_nodegroup = 'DefaultNodeGroup', which means that all of the nodes belonging to this node group are members of the new dynamic cluster. To modify the membership policy, click the Subexpression builder link under Edit rule.
- From the membership policy Subexpression builder window, modify the initial policy by setting the following options.
- Define the appropriate value for Logical operator as either AND or OR.
- Set the expression's operand value, which can be Nodegroup, Node name, Node host name and Node property.
- Choose the desired expression Operator.
- Enter the appropriate information in the value field, matching the chosen operand value, for the expression's operation.
- Click Generate subexpression.
- Click Append, which modifies the value of the Membership policy field
- To see where the new dynamic cluster members will reside, click the Preview membership link.
- Click Next.

- If we selected Manually define cluster members, the action you take depends on what kind of servers are in our dynamic cluster.
- If the server type is application server, choose an existing static cluster to convert to a dynamic cluster.
- If the server type is an externally created middleware server with assisted life-cycle management, select servers from the list, and add them to our dynamic cluster. Before we add assisted life-cycle servers, be sure that they are the same type, middleware server version, and have the same set of applications installed.
Before adding a new middleware server to an existing dynamic cluster when one or more applications are targeted to the dynamic cluster, install the applications on the middleware server and target the applications to the server.
- Deploy your unmanaged application to the middleware server.
- Define the deployment target for the application. In the administrative console, click...
- Applications > All applications > unmanaged_app_name
Select the target and click Add.
- Click Apply and save the changes.
- If we selected Automatically define cluster members with rules in the previous step, use the subexpression builder to build a membership policy expression for our dynamic cluster. This expression is compared to all the nodes in the cell, selecting any nodes for which the subexpression is true.
- Select a dynamic cluster server template.
We can select a dynamic cluster server template only for dynamic clusters that consist of servers with complete life-cycle management. We can choose an existing predefined template, or create our own server templates to use when we create our dynamic cluster. Read about creating server templates.
If the configuration consists of mixed versions of WAS Network Deployment, specifically the deployment manager is at a higher version than the version of the node, we cannot use a predefined server template to create a dynamic cluster. If we are running a v6.1 node and a v7.0 deployment manager, for example, we can create a static cluster of servers on the node, and then convert the static cluster to a dynamic cluster.
Deprecated feature: The defaultXD and defaultXDZOS server templates used when creating a dynamic cluster are deprecated. Use the default or defaultZOS server template instead.depfeat
- Specify dynamic cluster-specific properties.
- Define the minimum number of cluster instances.
The default minimum number of instances is one instance and the maximum default is no limit on instances. If a minimum value is excessive, performance degradation might occur.
- Define the maximum number of cluster instances. The default value has no limit on the number of cluster instances.
- Determine whether to enable vertical stacking. When we configure vertical stacking, more than one dynamic cluster instance can start on the same node.
- Specify an isolation preference for the dynamic cluster.
- Define the minimum number of cluster instances.
- Save the changes to the master configuration.
-
Finish > Save
- Select the mode of operation...
-
Servers > Clusters > Dynamic clusters > dynamic_clusters > operational_mode > Set mode
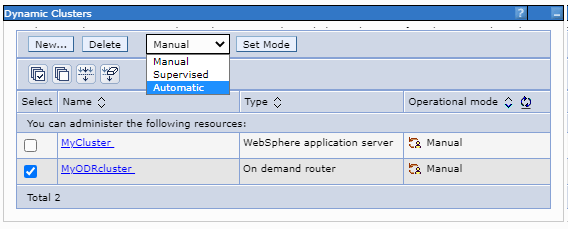
To use dynamic application placement, click Automatic or Supervised as the mode of operation.
(ZOS) If we have nodes that run on z/OS systems, use dynamic clusters in supervised or automatic mode. To prevent Intelligent Management from automatically starting a cluster member on a logical partition (LPAR) hosting a dynamic cluster when the LPAR processor is too busy, then we must define the cpuUtilizationThreshold custom property. In this scenario, the product starts the cluster member only if transaction demand requires additional cluster members and the processor utilization on the LPAR is less than the cpuUtilizationThreshold value.
When the dynamic clusters start, at least one instance of each dynamic cluster in the environment becomes available as soon as possible. Multiple instances on the same node can start concurrently if we have multiple processors on the same node. For example, if we have two processors on a node, two instances can start concurrently. The application placement controller continues to start instances evenly across the nodes for all the dynamic clusters until the minimum number of instances for each dynamic cluster is reached.
Specify that exactly two servers are started when the dynamic cluster is running
Click
-
Keep multiple instances started at all times
Click...
-
Limit the number of instances that can start
...and set the Number of instances value to 2.
Limit the number of started servers to five. Stop servers when no activity occurs
Click...
-
Stop all instances during periods of inactivity
Set the maximum number of instances by clicking...
-
Limit the number of instances that can start
...and set the Number of instances value to 5.
Keep at least one instance active. Support an unlimited number of instances to start
Click...
- Keep one instance started at all times
- Do not limit the number of instances that can start
What to do next
- To edit dynamic cluster settings, click...
- Servers > Clusters > Dynamic clusters > dynamic_cluster_name
To make changes to all of the members of the dynamic cluster, edit the dynamic cluster server template. Click Server template.
- Deploy an application to our dynamic cluster.
- Monitor performance with reports and operations tabs.
-
Servers > Clusters > Dynamic clusters > dynamic_cluster_name
Click the Reports tab or the Operations tab.
- If we are using supervised mode, the autonomic managers generate recommended actions and runtime tasks upon which we can act.
To view all the runtime tasks that the supervised operating mode created...
-
System administration > Task management > Runtime tasks
To avoid monitoring the runtime tasks queue, we can define e-mail notification. Create an e-mail notification profile by clicking...
-
System administration > Task management > Notifications
- If we are using automatic mode, we can prevent servers from starting or restarting during the cell shutdown by adding commands to disable the application placement controller and health controller to the script used to stop the cell. For example, we might add the following lines to your script:
- wsadmin -profile PlacementControllerProcs.jacl -c "disable"
wsadmin -profile HmmControllerProcs.jacl -c "disable"
Remember: To change the server ports after the server has been created, change the ports on each server instance. We cannot change the ports through the dynamic cluster template. Because multiple servers can be on the same node by configuring vertical stacking, the ports must be unique for each server instance.
Subtopics
- Create a static cluster of ODRs
- Create a dynamic cluster of ODRs
- Dynamic clusters
- createDynamicCluster.jacl script
- appEditionRename.py script
- coregroupsplit.py script
- deleteDynamicCluster.jacl script
- Intelligent Management: dynamic cluster administrative tasks
- Intelligent Management: dynamic cluster custom properties
- Intelligent Management: static clusters versus dynamic clusters
- Dynamic cluster isolation
- Configure application lazy start
- Configure vertical stacking
- HTTP session rebalancing
Related: