JDBC mediator exceptions
JDBC mediator exceptions either surface errors reported by the database, or indicate use of non-valid metadata in the attempt to instantiate the DMS.
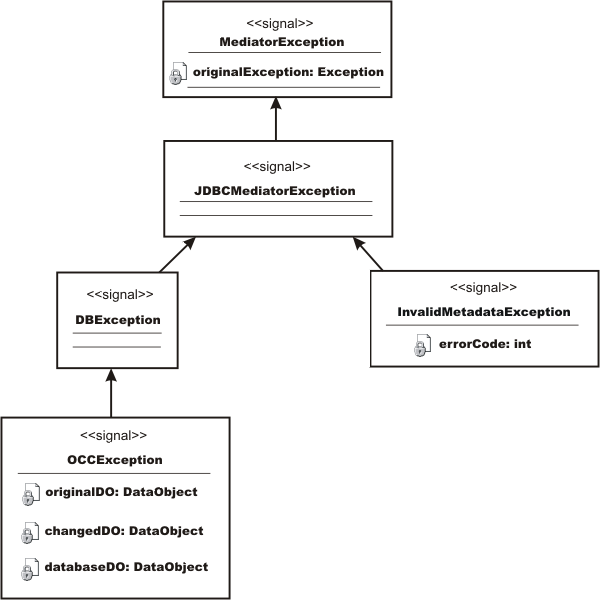
The Mediator exception is the root exception of all the data mediator services, and the JDBCMediator exception is the root exception for the JDBC DMS in particular.
The DB exception occurs when an error is reported by the database. This can occur several ways:
- when the connection being used has the AutoCommit property set to true, but the JDBC DMS is controlling the transaction and needs it to be set to false
- when an unsupported database is trying to be used
- when other backend database errors occur during commit or rollback.
An optimistic concurrency control (OCC) exception occurs when the applyChanges() operation results in an data collision. When this occurs, the exception contains the original row values, current row values, and the attempted row values. These values are used to help recover from the error.
An InvalidMetadata exception occurs for invalid metadata supplied to the JDBC DMS upon creation. This can happen when a query requires tables or columns that are not defined in the metadata, or when there are identical column names for different tables for the Oracle, Informix, and older supported versions of Sybase databases.
Example: Forcing OCC data collisions and JDBC mediator exceptions: The following example forces a collision to demonstrate detection and shows the exception that occurs as a result.
// This example assumes that a mediator has already
// been created and the first name in the list is Sam.
// It also assumes that the Customer table has an OCC
// column and the metadata has set this column to be
// the collision column.
DataObject graph1 = mediator.getGraph();
DataObject graph2 = mediator.getGraph();
DataObject customer1 = (DataObject)graph1.getList("CUSTOMER").get(0);
customer1.set("CUSTFIRSTNAME", "Bubba");
DataObject customer2 = (DataObject)graph2.getList("CUSTOMER").get(0);
customer2.set("BOWLERFIRSTNAME", "Slim");
mediator.applyChanges(graph2);
try
{
mediator.applyChanges(graph1);
}
catch (OCCException e)
{
// Since graph1 was obtained before graph2 and
// graph2 has already been submitted, trying to
// apply the same changes to graph1 causes
// this OCC Exception.
assertEquals("Sam", e.getOriginalDO(). getString("CUSTFIRSTNAME"));
assertEquals("Bubba", e.getChangedDO(). getString("CUSTFIRSTNAME"));
assertEquals("Slim", e.getDatabaseDO(). getString("CUSTFIRSTNAME"));
}