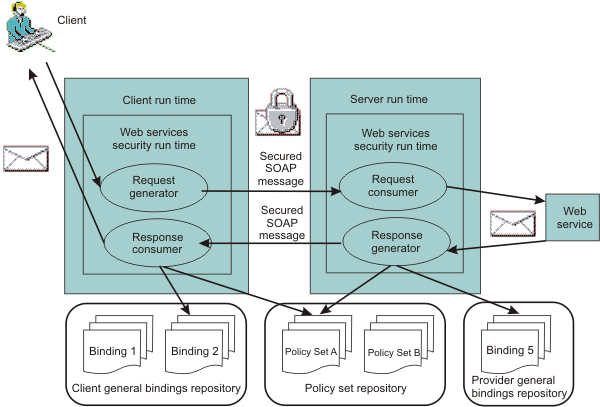
High-level architecture for Web Services Security
The Web Services Security policy is specified in the IBM extension of the web services deployment descriptors when using JAX-RPC, and in policy sets when using JAX-WS. A stand-alone JAX-WS client application may specify Web Services Security policy programmatically. Binding data that supports the Web Services Security policy are stored in the IBM extension of the web services deployment descriptors for both the JAX-RPC and JAX-WS programming models. The Web Services Security run time enforces the security assertions specified in the policy document, or in the application program, in that order.
IBM WebSphere Application Server supports JAX-WS and JAX-RPC. JAX-WS supports annotations. Use JAX-WS to develop new web services applications and clients. best-practices
WAS uses the Java EE Version 1.4 or later web services deployment model to implement Web Services Security. One of the advantages of deployment model is that we can define the Web Services Security requirements outside of the application business logic. With the separation of roles, the application developer can focus on the business logic and the security expert can specify the security requirement.
The following figure shows the high-level architecture model used to secure web services in WAS:
The WSS API can also be used to secure the message, as illustrated later in this section:
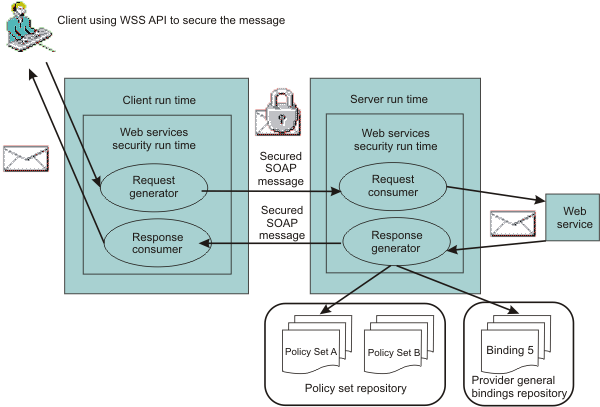
There are two sets of configurations on both the client side and the server side:
- Request generator
- Requirements for the outgoing SOAP message request. Requirements might involve generating a SOAP message request that uses a digital signature, incorporates encryption, and attaches security tokens.
- Request consumer
- Requirements for the incoming SOAP message request. Requirements might involve verifying that the required integrity parts are digitally signed; verifying the digital signature; verifying that the required confidential parts were encrypted by the request generator; decrypting the required confidential parts; validating the security tokens, and verifying that the security context is set up with the appropriate identity.
- Response generator
- Requirements for the outgoing SOAP message response. Requirements might involve generating the SOAP message response with Web Services Security; including digital signature; and encrypting and attaching the security tokens, if necessary.
- Response consumer
- Requirements for the incoming SOAP response. Requirements might involve verifying that the integrity parts are signed and the signature is verified; verifying that the required confidential parts are encrypted and that the parts are decrypted; and validating the security tokens.
WAS does not include security policy negotiation or exchange between the client and server. This security policy negotiation, as defined by the WS-Policy, WS-PolicyAssertion, and WS-SecurityPolicy specifications, are not supported in WAS.
The Web Services Security requirements defined in the request generator must match the request consumer. The requirements defined in the response generator must match the response consumer. Otherwise, the request or response is rejected because the Web Services Security constraints cannot be met by the request consumer and response consumer.
The format of the Web Services Security deployment descriptors and bindings are IBM proprietary. However, the following tools are available to edit the deployment descriptors and bindings:
- IBM assembly tools
- Use IBM assembly tools to edit the Web Services Security deployment descriptor and binding. Use the tools to assemble both web and EJB modules. For more information, read about assembly tools.
- WAS Administrative Console
- Use this tool to edit the Web Services Security binding of a deployed application.
Subtopics
- Web Services Security authorization models
- Security model mixture
- Web Services Security - Overview of platform configuration and bindings
- Default configuration
- Default implementations of the Web Services Security service provider programming interfaces
Related: