Message-driven beans - listener port components
The WebSphere Application Server support for message-driven beans deployed against listener ports is based on JMS message listeners and the message listener service, and builds on the application server facility (ASF) support in the JMS provider.
From WebSphere Application Server Version 7, listener ports are stabilized. For more information, read the article on stabilized features. For information about the facilities available to aid migration of configuration information from a listener port to an activation specification for use with the WebSphere MQ messaging provider, refer to related tasks.
The main components of WAS support for message-driven beans are shown in the following figure and described after the figure:
Figure 1. The main components for message-driven beans
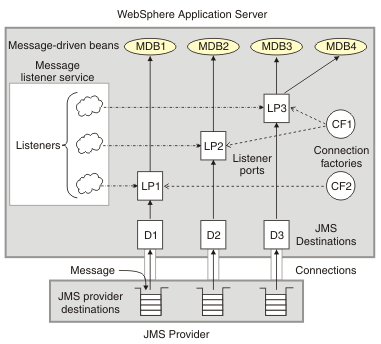
The message listener service is an extension to the JMS functions of the JMS provider and provides a listener manager, which controls and monitors one or more JMS listeners. Each listener monitors either a JMS queue destination (for point-to-point messaging) or a JMS topic destination (for publish/subscribe messaging).
A connection factory is used to create connections with the JMS provider for a specific JMS queue or topic destination. Each connection factory encapsulates the configuration parameters needed to create a connection to a JMS destination.
A listener port defines the association between a connection factory, a destination, and a deployed message-driven bean. Listener ports are used to simplify the administration of the associations between these resources.
When you deploy a message-driven bean, you associate the bean with a listener port. When a message arrives on the destination, the listener passes the message to a new instance of a message-driven bean for processing.
When an application server is started, it initializes the message listener service based on the configuration data. The message listener service creates a dynamic session thread pool for use by listeners, creates and starts listeners, and during server termination controls the cleanup of message listener service resources. Each listener completes several steps for the JMS destination that it is to monitor, including:
- Create a JMS server session pool, and allocating
JMS server sessions and session threads for incoming messages.
- Interfacing
with JMS ASF to create JMS connection consumers to listen for incoming messages.
- If specified, starting a transaction and requesting that it is committed (or rolled back) when the EJB method has completed.
- Processing incoming messages by invoking the onMessage() method of the specified enterprise bean.
Related tasks