Configure the logger hierarchy
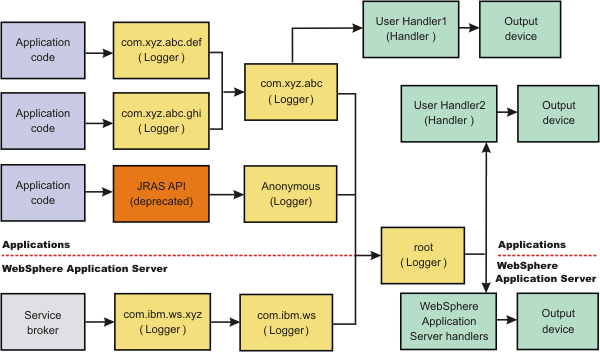
WebSphere Application Server handlers are attached to the Java root logger, which is at the top of the logger hierarchy. As a result, any request from anywhere in the logger tree can be processed by WebSphere Application Server handlers.
We can configure the application server to handle logs in many different ways. Configure the log settings based upon the configuration and the logging structure that best suits the needs.
- Forward all application logging requests to the WAS handlers. This behavior is the default.
- Forward all application logging requests to our own custom handlers. Set the useParentHandlers option to false on one of the custom loggers, and then attach the handlers to that logger.
- Forward all application logging requests to both WebSphere Application Server handlers, and the custom handlers, but do not forward WebSphere Application Server logging requests to the custom handlers. Set the useParentHandlers option to true on one of the non-root custom loggers, and then attach the handlers to that logger.True is the default setting.
- Forward all WebSphere Application Server logging requests to both WebSphere Application Server handlers, and the custom handlers. Logging requests are always forwarded to WebSphere Application Server handlers. To forward WebSphere Application Server requests to the custom handlers, attach the custom handlers to the Java root logger, so that they are at the same level in the hierarchy as the WAS handlers.
Example
The following example shows how these requirements can be met using the Java logging infrastructure:
Related tasks