Configure Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC) with the application server
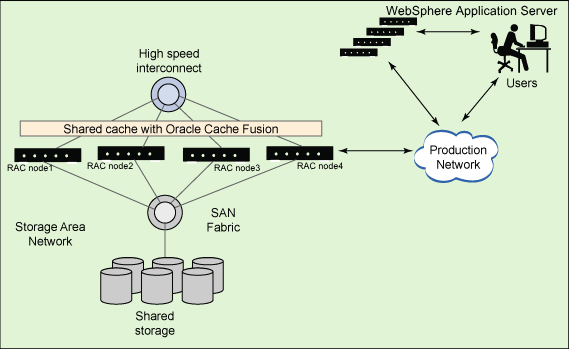
Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC) is a "share-everything" database architecture in which two or more Oracle RAC nodes are clustered together and share the same storage. The RAC nodes are connected together with a high-speed interconnect that enables fast communication between the Oracle nodes. The nodes can exchange various categories of data block ownership information during startup, lock information, exchange transaction information and data, and so on.
Use the Oracle JDBC driver, we can configure failover support, load balancing, or both, in an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) environment. Oracle RAC is an option of an Oracle database that brings together two or more computers to form a clustered database that behaves as a single system. In a RAC database, Oracle processes that are running in separate nodes access the same data from a shared disk storage. First introduced in Oracle Version 9i, RAC provides both high availability and flexible scalability.
A typical Oracle RAC cluster consists of the following:
- Cluster nodes - 2 to n nodes or hosts, running the Oracle database server.
- Network Interconnect - a private network used for cluster
communications and cache fusion. This is typically used for transferring
database blocks between node instances.
- Shared Storage - used to hold the database system and data files. The shared storage is accessed by the cluster nodes.
- Production network - used by clients and application servers to access the database.
The following figure depicts a typical configuration for Oracle RAC:
Here are two of the many features that Oracle RAC provides:
- Oracle Notification Service (ONS) allows for Oracle
RAC to communicate the status for the nodes, which are typically UP
and DOWN events, to the Oracle JDBC driver and the driver's connection cache. To take advantage of ONS, configure the application server to use Oracle's connection caching instead of the application server's connection pooling feature. Read the topic Configuring Oracle
connection caching in the application server for more information on this process.
- Distributed Transaction Processing (DTP) is a feature that was introduced in Oracle 10gR2. When this feature is enabled, Oracle will ensure that all in-flight prepared transactions that belong to a DTP service for failed RAC instances are pushed to disk. Then, Oracle will restart the DTP service on any of the RAC instances that are still operational.
For more information on Oracle RAC and how it works with the application server, refer to Build a high availability database environment using WebSphere middleware: Part 3: Handling two-phase commit in WebSphere Application Server using Oracle RAC on the developerWorks website.
- Configure a simple RAC configuration in an application server cluster.
- Configure Oracle connection caching in the application server.
- Configure two-phase commit distributed transactions with Oracle RAC.
Subtopics
- Configure a simple RAC configuration in an application server cluster
Oracle Real Application Cluster (RAC) is a "share-everything" database architecture that can provide high availability and load balancing. A typical configuration for an Oracle RAC contains two or more Oracle RAC nodes that are clustered together and share the same storage. - Configure Oracle connection caching in the application server
We can elect to configure an Oracle data source to use the Oracle connection caching feature instead of using the application server connection pooling. Connection caching for Oracle databases is similar to connection pooling in the application server. - Configure two-phase commit distributed transactions with Oracle RAC
Real Application Cluster (RAC) configurations for Oracle 10g have an inherent issue with the transaction manager when Oracle attempts to recover two-phase commit distributed transactions that span over multiple Oracle RAC nodes. A problem can occur when one node fails, and Oracle opens up the other surviving nodes for business before the Oracle RAC completes the necessary recovery action for the node that has failed. The application server's ability to maintain transaction affinity provides you the ability to circumvent this issue.
Related