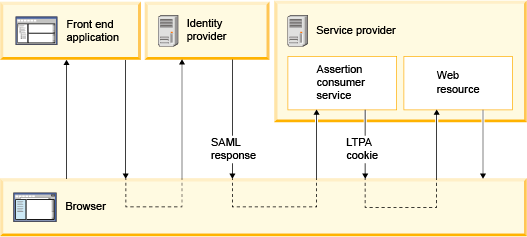
SAML single sign-on scenarios
- User accesses a front end web application, which redirects user to SAML 2.0 Identity Provider (IdP).
- User authenticates to IdP.
- IdP redirects user to Assertion Consumer Service (ACS) in SP by sending SAML response over HTTP POST inside a hidden form.
- SAML Service Provider (SP) processes SAML response and creates WebSphere security context.
- SP adds LTPA cookie to HTTP response and redirects request to web resource or business application.
- WAS intercepts request, and maps LTPA cookie to security context and authorizes user access to the requested web resource.
- WAS sends HTTP response back to user.
The following images shows the SAML SSO flow:
The WebSphere SAML service provider...
- ...supports single sign-on with multiple identity providers.
- ...supports options for identity assertion and mapping the assertion identity to the user registry of the service provider.
- ...can map or assert SAML token attributes to the realm, principal, unique Id, and group, and set them into the service provider security context.
- ...provides a plug point to allow for customized identity mapping.
- ...has an option to retrieve the group membership of the identity from the registry of the service provider and populate the security context.
- ...provides an IdP selection filter to route the request back to the proper IdP if the request did not come from the IdP.
- ...supports both RSA-SHA1 and RSA-SHA256 signature algorithms.
- ...preserves the SAML token in the subject of the service provider for access by the application, and makes it available for a downstream authenticated EJB or Web Service call.
- ...allows a business application URL to act as an AssertionConsumerService URL, so the IdP can send a SAMLResponse directly to the business application URL.
The WebSphere SAML trust association interceptor (TAI) allows auditing of key SAML assertions, including Issuer and NameID.
SAML SSO features:
- Assertion consumer service (ACS) in WebSphere SAML service provider:
ACS is a secured servlet that accepts a SAML protocol message and establishes the security context. An ACS URL has a predefined ContextRoot as samlsps, and a URL has the following format:
- https://host:port/samlsps/<any uri pattern>
The SAMLResponse received by the ACS will be intercepted by TAI, and upon successful validation, the request is redirected to the target application service.
Any business service that implements the POST method can act as an ACS. Using a target business servlet as an ACS is preferred, as it reduces one round trip between the browser and the service provider server.
- Multiple security domain support:
An ACS is deployed in an application security domain, and it is expected that the ACS reside in the same security domain as the business application. If the ACS and target business application (RelayState) are in different security domains, the following are some recommended options:
- Process the SAMLResponse in the security domain of the ACS.
- Reconfigure the ACS to have the same domain as the business application.
- Use the target business service as the ACS.
- Process the SAMLResponse in the security domain of the ACS.
- Multiple single sign-on partners:
The WebSphere SAML TAI supports multiple ACS and IdP single sign-on (SingleSignOnService) partners. One SSO partner is defined as one ACS URL, and can have multiple SingleSignOnService objects. With the existence of multiple SSO partners, each SSO partnership is uniquely identified by an ACS URL.
Each SSO partner can have its own validation rules, mapping rule from assertion to subject, or a rule to start the SSO with its own IdP. For example, one SSO partner can handle ID assertion, which consists of generating a WebSphere platform subject without calling into the user registry. Another SSO partner can perform a local user registry lookup. Another example is that one SSO partner handles SSO with one IdP, and another SSO partner handles SSO with a different IdP.
- Bookmark style SSO and TAI filter:
Consider a bookmark style SSO which traditionally fits into an SP-initiated SSO. The user accesses the business application without authenticating to the IdP first. The WebSphere SAML TAI can be configured to initiate an SSO. Each SSO partner configuration contains an IdP login application and a routing filter. Each filter defines a list of selection rules that represent conditions that are matched against the HTTP request to determine whether or not the HTTP request is selected for an SSO partner. The filter rule is a combination of HTTP request header, referrer data, and target application name. The WebSphere SAML TAI runtime environment checks the user request against all filter rules to uniquely identify the SSO partner, and redirects the request to the selected IdP login application. The TAI filter allows an IdP-initiated SSO to provide similar functionality as the combination of an SP-initiated SSO and an IdP discovery service.
- Identity mapping and security context management:
The WebSphere SAML TAI provides a rich and flexible identity mapping, and can be classified as follows:
- Identity assertion: Map the SAML assertion to the WebSphere platform
subject without a local registry. Typical ID assertion scenarios include:
- Default: use NameID as principal, issuer as realm, selected attribute as group members.
- Customized: configure SAML attribute as principal, realm, accessID, and group members.
- Map NameID from the IdP against the user registry of the service provider, and build the subject from the registry. The following scenarios
are supported:
- Directly map the SAML NameId to the local registry.
- Provide a plugin point for custom mapping, and then use a new user to build the subject.
- Map NameID to the user registry, and fall back to ID assertion.
- Directly map the SAML NameId to the local registry.
- Combination of ID assertion and local registry:
In addition to ID assertion, TAI searches parent groups of the asserted groups in the user registry of the service provider, and includes the parent groups into the subject. For example, authorization is granted to parent groups, but the identity provider does not know the parent group names.
- Identity assertion: Map the SAML assertion to the WebSphere platform
subject without a local registry. Typical ID assertion scenarios include:
WebSphere Application Server supports IdP initiated SAML web SSO only.
The following specifications or scenarios are out of scope:
- Enhanced Client or Proxy (ECP) Profile
- Identity Provider Discovery Profile
- Single Logout Profile
- Name Identifier Management Profile
- Artifact Resolution Profile
- Assertion Query/Request Profile
- Name Identifier Mapping Profile
- SAML Attribute Profiles
Related information:
Step by step guide to implement SAML 2.0 for Portal 8.5
Profiles for the OASIS
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0
Bindings for the OASIS
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0
Assertions and Protocols
for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0