Network Deployment (Distributed operating systems), v8.0 > New features > Overview and new features: Administering > Introduction: System administration
Welcome to basic administrative architecture
The basic administrative architecture consists of software processes called servers, topological units referenced as nodes and cells, and the configuration repository used for storing configuration information. The application server, node agent server, dmgr, admin agent, and job manager interact to perform system administration.
This topic discusses basic concepts in the administrative architecture to help you understand system administration in a WAS environment.
Servers perform the actual running of the code. Several types of servers exist depending on the configuration. Each server runs in its own JVM. The application server is the primary runtime component in all WAS configurations. All WAS configurations can have one or more application servers. In some configurations, each application server functions as a separate entity. No workload distribution or common administration among application servers exists. In other configurations, workload can be distributed between servers and administration can be done from a central point.
A node is a logical group of WAS-managed server processes that share a common configuration repository. A node is associated with a single profile. A node does not necessarily have a one-to-one association with a system. One computer can host arbitrarily many nodes, but a node cannot span multiple computer systems. A node can contain zero or more application servers.
The configuration repository holds copies of the individual component configuration documents that define the configuration of a WAS environment. All configuration information is stored in .xml files.
A cell is a grouping of nodes into a single administrative domain. A cell can consist of multiple nodes, all administered from a dmgr server. When a node becomes part of a cell (a federated node), a node agent server is created on the node to work with the dmgr server to manage the WAS environment on that node.
When a node is a stand-alone node, not part of a cell, the configuration repository is fully contained on the node. When a stand-alone node is registered with an admin agent, the configuration repository continues to be fully contained on the node. When a node is part of a cell, the configuration and application files for all nodes in the cell are centralized into a cell master configuration repository. This centralized repository is managed by the dmgr server and synchronized to local copies that are held on each node. The local copy of the repository that is given to each node contains just the configuration information needed by that node, not the full configuration that is maintained by the dmgr. When a dmgr is registered with a job manager, the dmgr continues to manage the centralized configuration repository.
WAS types
This section discusses the server types that interact to perform system administration.
- Application server
- The product provides functions that support and host user applications. An application server runs on only one node, but one node can support many application servers.
- Node agent
- When a node is federated, a node agent is created and installed on that node. The node agent works with the dmgr to perform administrative activities on the node.
- Deployment manager
- With the dmgr, you can administer multiple nodes from one centralized manager. The dmgr works with the node agent on each node to manage all the servers in a distributed topology. Application server nodes are federated with the dmgr before they can be managed by the dmgr.
- Administrative agent
- An admin agent provides a single interface to administer multiple unfederated application server nodes in environments such as development, unit test, or that portion of a server farm that resides on a single computer. Application servers nodes are registered with the admin agent before they can be managed by the admin agent.
- Job manager
- In a flexible management environment, a job manager enables you to submit administrative jobs asynchronously for application server nodes registered to admin agents and for dmgrs. Application server nodes that the admin agent or dmgr manage must be registered with the job manager before the job manager can manage them.
The following diagram depicts the concepts that are discussed in this topic.
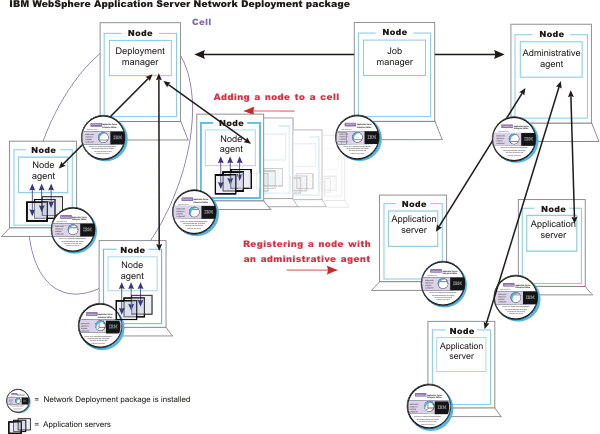
The concepts that are discussed in this topic form the basis of WAS administration.
More detailed descriptions can be found in other sections.
Administer nodes and resources
 Concept topic
Concept topic