Network Deployment (Distributed operating systems), v8.0 > Applications > Messaging resources > Interoperation with WebSphere MQ > Interoperation using a WebSphere MQ link
Message exchange through a WebSphere MQ link
Overview
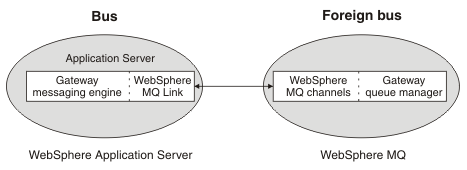
WebSphere MQ links connect WAS gateway messaging engines and WebSphere MQ network gateway queue managers:
- For the WAS service integration bus, the gateway queue manager appears as a foreign bus with links to the local bus.
- For the MQ gateway queue manager, the WAS service integration bus appears to be a remote queue manager.
Links appear to the gateway queue manager as message channels:
- sender channel
- receiver channel
- sender-receiver pair of channels
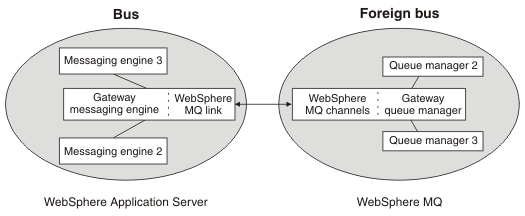
Other messaging engines on the same service integration bus can use the gateway messaging engine to send messages to, and receive messages from, the gateway queue manager on WebSphere MQ. In a similar way, the gateway queue manager receives messages from the WebSphere MQ link and routes them to other queue managers in the WebSphere MQ network. The gateway queue manager and the other queue managers to which it connects are together represented as a foreign bus when you configure the WebSphere MQ link.
A WebSphere MQ link cannot use cluster-sender and cluster-receiver channels to connect to multiple queue managers in a WebSphere MQ cluster. Even if the gateway queue manager is a member of a cluster, the WebSphere MQ link must still connect directly to the gateway queue manager. The gateway queue manager manages routing of messages to other queue managers in the cluster.
The figure below shows how messages exchanged between the gateway messaging engine and the gateway queue manager, can be sent and received by other messaging engines on the same bus and other queue managers connected to the gateway queue manager.
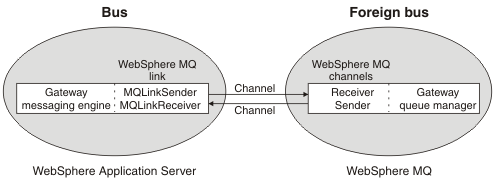
A WebSphere MQ link can have definitions for a WebSphere MQ link sender or a WebSphere MQ link receiver or both. The link sender and receiver emulate the behavior of WebSphere MQ sender and receiver channels. The MQ link sender therefore sends messages to the receiver channel of the gateway queue manager, and the MQ link receiver receives messages from the sender channel of the gateway queue manager.
The figure below shows the sender and receiver channels that enable the gateway messaging engine and the gateway queue manager to exchange messages.
The figure below shows how an individual message passes from the gateway messaging engine with a WebSphere MQ link, to the target queue in the WebSphere MQ network, and how a response message is returned over the WebSphere MQ link to a reply-to destination in WAS.
- A service integration JMS application sends a request message to a target destination, which is a JMS destination that points to a WebSphere MQ queue. The sending application includes the reply-to destination in a header field in the request message. The reply-to destination is a JMS destination that points to a service integration destination in the same service integration bus to which the sending application is attached.
- The messaging engine in the service integration bus uses the WebSphere MQ link to send the message to WebSphere MQ. WebSphere MQ puts the message on the target queue.
- The WebSphere MQ application receives the message from the queue, processes it, and sends a response to the reply-to destination. This application might be, but is not always, a JMS application.
Figure 5. Paths taken by a message and response exchanged between a messaging engine on a bus and a queue manager in WebSphere MQ

We can configure a publish/subscribe bridge on a WebSphere MQ link. The bridge allows subscribing applications connected to the service integration bus to receive messages from publishing applications connected to the WebSphere MQ network. The same publish/subscribe bridge allows subscribing applications connected to the WebSphere MQ network to receive messages from publishing applications connected to the service integration bus.
To specify service integration bus destination attributes for a WebSphere MQ queue, or to control access to a WebSphere MQ queue from service integration bus applications, then you can define a foreign destination to represent the WebSphere MQ queue.
To have service integration bus applications to use a different name for the WebSphere MQ queue then you can define an alias destination.
The WebSphere MQ link communicates with WebSphere MQ by using WebSphere MQ format and protocols.
WebSphere MQ link sender
Supported hardware and software
WebSphere MQ link receiver
Publish/subscribe messaging through a WebSphere MQ link
Interoperation using a WebSphere MQ server
Create a new WebSphere MQ link