Network Deployment (Distributed operating systems), v8.0 > Set up the application serving environment > Administer nodes and resources > Administer nodes remotely using the job manager
Job manager security
In a flexible management environment, a user ID must have the required authorization to use the job manager and to work with registered nodes.
Required security roles
You need the following roles to use the job manager:
| Administrative tasks | Required security roles |
|---|---|
| Register or unregister with the job manager | administrator |
| Submit a job | operator |
| Change the job manager configuration | configurator |
| Read the job manager configuration or job history | monitor |
If base (stand-alone) application server nodes that are managed by an admin agent are registered to a job manager, you need the following roles to use the admin agent and manage its nodes:
| Administrative tasks | Required security roles |
|---|---|
| Register or unregister a base (stand-alone) node with the admin agent | administrator |
| Work with the admin agent: | Administrative roles required for the operation being performed |
| Work with the administrative subsystem, such as registered nodes | Administrative roles required for the registered base node |
When a job runs on a target, the user must have privileges that include the role required for that job. For example, a job to create an application server requires a minimum configurator role on either the base node or WAS ND cell.
Basic security configuration
The admin agent and job manager support two different basic security configurations:
- Same security domain
In this configuration, all the cells in the topology share the same user registry, and therefore, the same security domain. The same is true of the admin agent and its registered base nodes, and also any job manager or WAS ND cells in the topology.
- Different security domains
In this configuration, all the cells are configured with different user registries, and therefore different security domains.
For the admin agent topology, when a user logs in to the JMX connector port of an administrative subsystem, or chooses the registered node from the administrative console, the authorization table for the base node is used.
For example, suppose User1
is authorized as administrator for the first base node, but is not authorized for the second node. User2 is authorized as configurator for the second node, but is not authorized for the first node. The Same user registry figure illustrates this example:
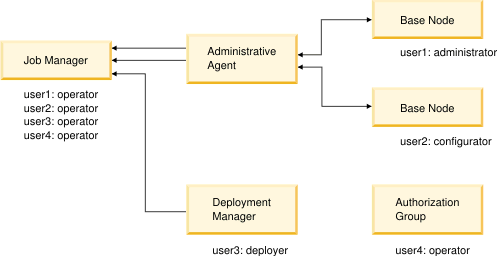
Further suppose User1
can log in to job manager as an operator with a user name and password.
User1 can also log in to the dmgr as a monitor with a user name and password. The Different user registry figure illustrates this example:
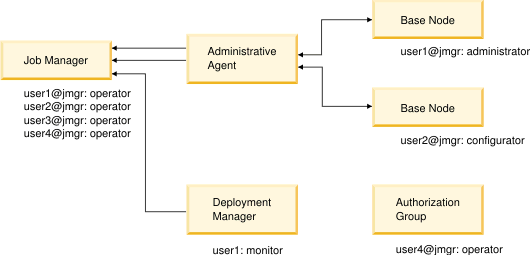
Although User1 has the same user name for both the job manager and the dmgr, User1 might as likely have different user names and passwords.
Transfer of security information
When the product transfers a job from the job manager to the admin agent, dmgr or host computer, the product also transfers security information about the job submitter. This transfer authenticates and authorizes the user while running the job. The following user security information might be passed with a submitted job:
- User name and password
When submitting a job, the user might specify a user name and password. When the job reaches the administrative subsystem or the dmgr, the user name and password are used to log in.
For the same user registry configuration, if John submits a job against the first base node, he can specify his user name and password as part of the job. The user name and password are used to log in against the first administrative subsystem, and the job runs. If John submits a job against the dmgr cell or the second base node, the job fails because John is not authorized.
For the different user registry configuration, John can submit a job against the dmgr cell, specifying his user name and password for the dmgr cell. When the job reaches the dmgr, login succeeds, and the job runs. If John submits a job against the base nodes, access is denied, and the job fails.
- Security token
If the user does not specify the user name and password with a job, the credential of the user is automatically persisted as a security token in the job database. The token contains the user security attributes, including groups. When a job is fetched, the token is used to authenticate and authorize against the administrative subsystem or the dmgr.
For the same user registry configuration, John can submit a job against the first base node without specifying user name and password. The job runs because John's credential is automatically propagated as a security token to the administrative subsystem, and used to authenticate and authorize him for the job. If John submits a job against the second base node or the dmgr cell, the job fails because his security token is not authorized in these two environments.
For the different user registry configuration, a user's security token does not automatically allow the submitted job to run against the administrative subsystem or the dmgr.
To enable a user token for a different realm, use the multiple security domain feature. First, establish the job manager realm as a trusted realm for the registered base nodes and the dmgr cell. In addition, import the access ID of the user from the job manager into the local authorization table and give the access ID a role. Then, the user can submit a job without passing user name and password.
Suppose John is an operator on the job manager, but his access ID is imported as an administrator in administrative authorization table of the first base node. Although John does not exist in the user registry of the base node, by passing the security token and the administrative authorization table definition, John is authorized as an administrator on the base node. John can submit a job for the first base node without having to specify a user name or password.
If John submits a job against the dmgr, the job fails. John's security token is from the job manager realm, and John's access ID has not been authorized for the dmgr. In this case, the administrator can export John's access ID from the job manager and import it to the dmgr. Or, John can submit a job passing user name and password that he had with the dmgr, which enables John to run jobs with monitor role.
The same mechanism works if the fine grained security feature is in use. We must be authorized in the authorization table for a new authorization group. The authorization table might also contain an external access ID.
Mixed registries configuration
In a more complex topology, where some cells share the same user registry and some cell do not, the following rules apply:
- We can always specify a user name and password during job submission if the target node or dmgr recognizes your user name and password.
- If the job manager and the target node or dmgr have the same user registry, then job submission does not require a user name and password. However, be authorized for the target node or dmgr.
- If the job manager and the target node or dmgr have different user registries, trusted realms have been established, and the access ID of the job submitter has been imported into the administrative authorization table of the target node or dmgr, then job submission does not require a user name and password.
Job manager
Administrative agent
Administrative roles
Administer nodes remotely using the job manager
Administer jobs in a flexible management environment using wsadmin.sh
Administer nodes and resources
Task overview: Securing resources