Memory-to-memory topology: Peer-to-peer function
The basic peer-to-peer (both client and server function, or both mode) topology is the default configuration and has a single replica. However, we can also add additional replicas by configuring the replication domain.
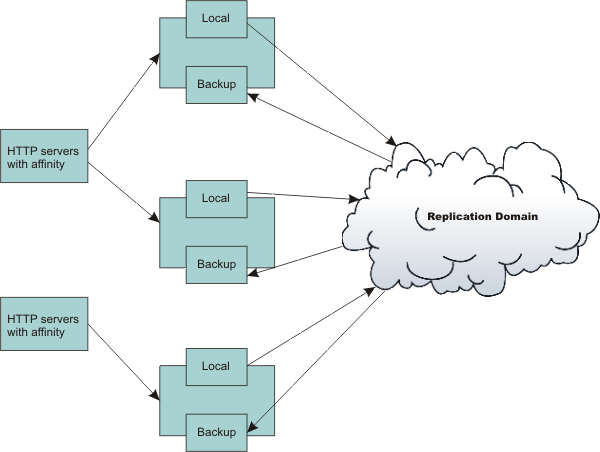
In this basic peer-to-peer topology, each server JVM can:
- Host the Web app leveraging the HTTP session
- Send out changes to the HTTP session that it owns
- Receive backup copies of the HTTP session from all of the other servers in the cluster
This configuration represents the most consolidated topology, where the various system parts are collocated and requires the fewest server processes. When using this configuration, the most stable implementation is achieved when each node has equal capabilities (CPU, memory, and so on), and each handles the same amount of work.
When using the peer-to-peer topology, that one session replication backup must run at all times for invalidation to occur. For example, if we have a cluster of 2 appservers, server1 and server2, that are both configured in the peer-to-peer mode and server2 goes down. All of backup information for server1 is lost and those sessions are no longer invalidated properly.
Related concepts
Memory-to-memory replicationMemory-to-memory topology: Client/server function
Memory-to-memory session partitioning
Related tasks
memory-to-memory replication for the peer-to-peer mode (default)Set memory-to-memory replication for the client/server mode