8.1.3 Destinations
With synchronous messaging, because there is no intermediary involved in the exchange of messages, the sending application must know how to connect to the receiving application. Once connected, there is no ambiguity to the intended destination of a message because messages can only be exchanged between the connected parties.
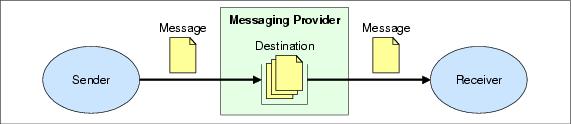
With asynchronous messaging, however, we need to introduce the concept of a destination. The need for a destination becomes apparent when we consider the fact that a single messaging provider can act as an intermediary for many applications. In this situation, the sending and receiving applications must agree on a single destination used to exchange messages. This destination must be specified when sending a message to the messaging provider, or receiving a message from the messaging provider.
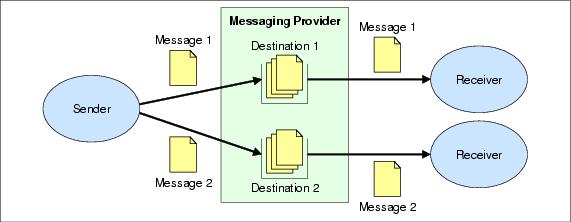
A sending application might need to exchange different messages with several receiving applications. In this situation, it would be normal for the sending application to use a different destination for each receiving application with which it wants to communicate.