|
|
High availability of the EJB container is achieved using a combination of the WebSphere server cluster support and workload management plug-in to the WebSphere ORB. Figure 2-7 shows horizontal and vertical scaling that is used for appserver redundancy to tolerate possible process and machine failures.
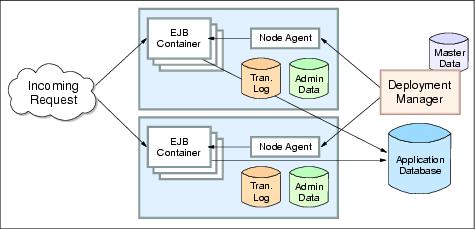
Figure 2-7 WebSphere EJB container failover
The mechanisms for routing workload-managed EJB requests to multiple cluster members are handled on the client side of the application. In WAS V6, this functionality is supplied by a workload management plug-in to the client ORB and the routing table in the LSD hosted in the Node Agent. The WLM failover support for EJBs is to maintain the routing table and to modify the client ORB to redirect traffic in case of a server failure.
The following is a list of possible failures for WebSphere processes:
- Expected server process failures, for example, stopping the server.
- Unexpected server process failures, for example, the server JVM crashes.
- Server network problems, for example, a network cable is disconnected or a router is broken.
- Machine problems, for example, a system shutdown, operating system crashes, or power failures.
- Overloading of EJB clients, for example, a denial of service attack, where the system is not robust enough to handle a large number of clients, or the server weight is inappropriate.