Overview of application placement
Dynamic application placement for Internet InterORB Protocol (IIOP), JMS, and HTTP request types is achieved through the cooperation of various product components. These components include dynamic clusters, the on demand router (ODR) and associated autonomic managers, and the application placement controller. The fluctuating volume of work requests for applications is dynamically met on the application server side by the application placement feature, which ensures the integrity of the defined business goals.
Application placement is a natural extension to the request flow prioritization feature. While the ODR and its associated autonomic managers ensure that the work flows appropriately according to the defined policy, the application placement feature ensures that the applications and the nodes that they run on are kept at appropriate levels to support the influx of work. In times of less work flow, the application instances that run within the resource pool are kept at a minimum. In times of significant work flow, the application instances that run are increased to keep pace with the requests.
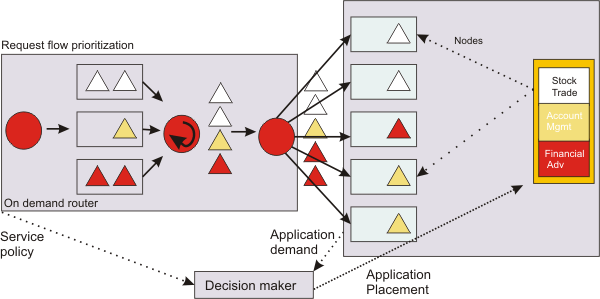
The following image shows the application placement process for a stock trading firm in times of less demanding workflow; that is, the request flow is during an off-peak hour. The ODR and its managers are controlling the incoming request flow prioritization. The decision making unit of the application placement function is made aware of the service policy for the incoming Universal Resource Identifier (URI) requests, as well as the demand level for the given application server resources. As a result, the application instances that run are comfortable for the given demand.
The following image shows a sudden increase in incoming URI requests occurs. For example, it is now lunch time and all online trade customers are now free to access the Web for personal use. The sudden work request fluctuation, which in other environments requires manual intervention to address, is handled by the autonomic features of dynamic operations.
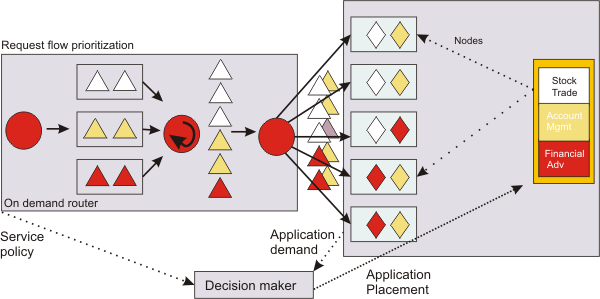
During times of more robust request flow, the application placement function must ensure that the business goals created for the many application URIs are met. As a result, the autonomic managers of dynamic operations must work together to bring a balance to the environment. You can see this balance achieved in the previous graphic. The work flow fluctuation is met by increasing the application instances that run on the available nodes, while balancing the service policy definitions. When the peak declines, the application placement function reduces the running number of application instances accordingly.
The functionality of dynamic application placement requires fundamental WebSphere® Virtual Enterprise components. Application placement requiresdynamic clusters and service policies. . Dynamic clusters are application deployment targets. Service policies are performance goals that are assigned to a specific application URI.
These components, when integrated with the autonomic managers, support dynamic application placement.
If you are using the WebSphere Extended Deployment Compute Grid component with the WebSphere Virtual Enterprise component, the dynamic application placement function with the job scheduler is supported. The application placement controller, along with the scheduler and autonomic request flow manager, provides overload protection of servers as long as both online and batch workloads are on dynamic clusters. This overload protection is not supported for static cluster members. Because batch jobs can consume a lot of processor capacity and run for a long period of time, the utilization limit might be exceeded. When the WebSphere Virtual Enterprise component is installed with the WebSphere Extended Deployment Compute Grid component, the application placement controller is consulted by the job scheduler during its endpoint selection process. The custom property, UseAPCEndpointSelection; value = false, can be configured on the job scheduler to disable the application placement controller and job scheduler integration. Use this custom property to disable the application placement controller during the job scheduler's endpoint selection process.
Application placement for WebSphere Virtual Enterprise is
more integrated with WebSphere eXtreme Scale in
V6.1.0.1 and later than in previous versions. In particular, before
stopping a dynamic cluster member that contains a data grid container, the
application placement controller contacts the data grid container to quiesce
any work that is being done, and moves any vital data to backup locations
as needed. Application placement also recognizes the replication zone concept
of data grid. The application placement controller ensures that when multiple
instances of a dynamic cluster are needed, the instances are placed across
multiple replication zones. For this functionality, the dynamic cluster must
be mapped to multiple replication zone node groups.
Related concepts
Overview of request flow prioritization
Related tasks
Configure dynamic application placement