Web Content Management - Basic architectures
We can set up the IWWCM (WCM) environment with a combination of authoring, staging, and delivery applications to support both test and production environments.
Two-stage environments
It is recommended that at least two separate WCM applications be used within a WCM environment.
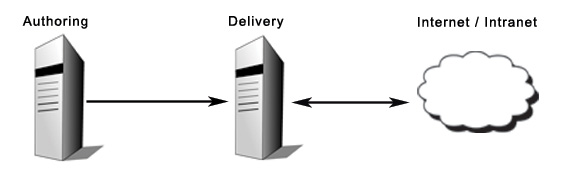
One WCM application is used to create and manage Web content. A second WCM application renders the site and delivers it to users, either via the WCM servlet, or via the WCM Rendering Portlet. No editing is performed on the delivery application. These could be installed on the same WAS, but would more often be installed on separate servers to improve performance.
- Syndication:
Syndication is used as the transport layer that replicates data from one WCM application to another.
- Database replication versus syndication:
When first creating a new WCM application, it is better to copy an existing WCM data repository database to a new server, enable the new WCM application to use the new data repository, and then enable syndication rather than trying to syndicate an entire site's data. You must be using the same type of database to be able to do this.
Three-stage environments
A third WCM application can be added between the authoring application and the delivery application. This server is used as a staging application.
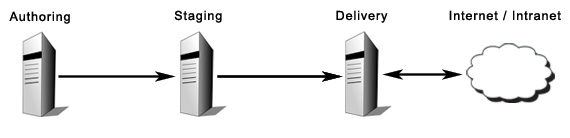
A staging application would mostly be used:
- To aggregate changes to a Web Site over time and push these aggregated changes to the delivery application in batches.
- To aggregate content from multiple authoring applications before syndicating to a delivery application.
Test and production environments
The basic architectures described above can be mirrored in two separate environments. The test environment can be used to test and review major changes to a Web Site, to test and review load-balancing, redundancy, caching and delivery strategies. Once successfully tested, these changes can be implemented in the production environment and delivered to end-users.
Parent topic:
Staging Web content to production