If TDI and MC4J are on different machines replace localhost with the TDI machine IP address.

- <TDI_home>\jars\3rdparty\others\log4j-1.2.15.jar
- <TDI_home>\jars\3rdparty\IBM\icu4j_4_2.jar
- <TDI_home>\jars\3rdparty\IBM\ITLMToolkit.jar
- Select Finish.
The Server API provides a JMX layer. It exposes all Server API calls through a JMX interface locally and remotely (through the JMX Remote API 1.0).
Please refer to the "Remote Server" chapter in the IBM TDI V7.1 Installation and Administrator Guide for information on how to switch on and setup the JMX layer of the Server API for local and remote access.
We can get a reference to the JMX MBeanServer object from the local Server JVM by calling
import com.ibm.di.api.jmx.JMXAgent; import javax.management.MBeanServer; ... MBeanServer jmxMBeanServer = JMXAgent.getMBeanServer();
The getMBeanServer() static method of the com.ibm.di.api.jmx.JMXAgent class will return an MBeanServer JMX object that represents an entry point to all MBeans provided by the JMX layer of the Server API. We can also register for JMX notifications with the MBeanServer object returned.
The getMBeanServer() method will throw an Exception if it is called and the JMX layer of the Server API is not initialized.
The remote JMX access to the Server API is implemented as per the JMX Remote API 1.0 specification.
We have to use the following JMX Service URL for remote access:
service:jmx:rmi://<TDI_Server_host>/jndi/rmi://<TDI_Server_host>:<TDI_Server_RMI_port>/jmxconnector
We need to replace <TDI_Server_host> and <TDI_Server_RMI_port> with the host and the RMI port of the TDI Server; for example, service:jmx:rmi://localhost/jndi/rmi://localhost:1099/jmxconnector
The sample code below demonstrates how a remote JMX connection can be established:
import javax.management.MBeanServerConnection;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnector;
import javax.management.remote.JMXConnectorFactory;
import javax.management.remote.JMXServiceURL;
...
JMXServiceURL jmxUrl = new
JMXServiceURL("service:jmx:rmi://localhost/jndi/rmi://localhost:1099/jmxconnector");
JMXConnector jmxConnector = JMXConnectorFactory.connect(jmxUrl);
MBeanServerConnection jmxMBeanServer = jmxConnector.getMBeanServerConnection();
Similarly to the local JMX access the MBeanServerConnection object is the entry point to all MBeans and notifications provided by the JMX layer of the Server API.
For example, we can list all MBeans available on the JMX Server:
Iterator mBeans = jmxMBeanServer.queryNames(null, null).iterator();
while (mBeans.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("MBean: " + mBeans.next());
}
The JMX layer wraps the Server API objects in MBeans. The access to the MBeans is however straightforward - we can directly look up an MBean through the MBeanServerConnection object.
There is no session object in the MBean layer (the session and the security checks are managed through the RMI session). The methods for creating, starting and stopping Config Instances that exist in the Server API Session object can be found in the DIServer MBean in the JMX layer.
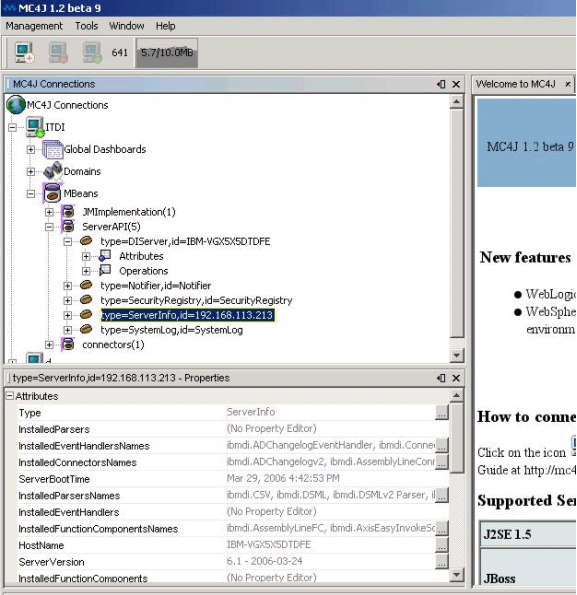
A list of the Server API MBeans available at some time on a TDI Server might look like this:
Each Config Instance or AssemblyLine is wrapped in an MBean. When the Config Instance or AssemblyLine is started the MBean is created automatically and it is automatically removed when the Config Instance or AssemblyLine terminates.
Refer to the JavaDoc of the Java package com.ibm.di.api.jmx.mbeans for all available MBeans, their methods and attributes.
The JMX layer of the Server API provides local and remote notifications for all Server API events (see Working with the System Queue.)
We have to register for JMX notifications with the Notifier MBean.
The JMX notification types are exactly the same as the Server API notifications:
This example describes how MC4J and TDI can be set up so that MC4J can be used to access the Server API JMX layer from MC4J.
Set the following properties in global.properties or solution.properties file (the long hexadecimal values may run off the side of this document):
## Server API properties
## ---------------------
api.on=true
api.user.registry=serverapi/registry.txt
api.user.registry.encryption.on=false
api.remote.on=true
api.remote.ssl.on=false
api.remote.ssl.client.auth.on=true
api.remote.naming.port=1099
# api.remote.server.ports=8700-8900
api.truststore=testserver.jks
{protect}-api.truststore.pass={encr}L79kdqak1afKdAyuCZBMi1GqY/DPfD1Ipo020CVAGx/OROE2JBUTgZxLjqADXSZJgM3dHg2aWlCRwB+is/WQa+dSVwT2hpA2kT11T7svqnIESYlcfbSg8xWxcNACdtHmdZoF7aKSJ1cunDAxNCk0xfvMN+hXV8GK/PrneMLs1YY=
## Specifies a list of IP addresses to accept non SSL connections from (host names are not accepted).
## Use space, comma or semicolon as delimiter between IP addresses. This property is only taken into account
## when api.remote.ssl.on is set to false.
## api.remote.nonssl.hosts=
api.jmx.on=true
api.jmx.remote.on=true
SSL is turned off for easy configuration.
Property api.remote.server.ports specifies which ports are used for the RMI services; this property can be used to change the default range (8700-8900) if there is a firewall between the server and the client, and the firewall requires this.
D:\TDI>ibmdisrv -d CTGDKD435I Remote API successfully started on port:1099, bound to:'SessionFactory'. SSL and Client Authentication are disabled. CTGDKD111I JMX Remote Server Connector started at: service:jmx:rmi://localhost/jndi/rmi://localhost:1099/jmxconnector.

If TDI and MC4J are on different machines replace localhost with the TDI machine IP address.

Now MC4J is connected to the TDI server.