Creating a message-driven bean using annotations
You can use Java™ EE annotations to create a message-driven bean and add it to your project.
You need to have an EJB project created.
The main difference between a message-driven bean and a session bean is that a message-driven bean has no local or remote interface. Instead, it has only a bean class. To create a message-driven bean in your EJB project:
- In the Java EE perspective, click
File | New | Class.
- In the
Source folder field, select the source folder for the new bean.
- In the
Default package field, type the package name for the new bean, and click Finish.
- In the Java class editor, underneath the package declaration,
type @MessageDriven. You can see an error / quick fix
icon
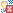 beside the @MessageDriven line.
beside the @MessageDriven line.
Tip: You can simply type @Mess and then press CTRL+Spacebar to see the options in content assistance:
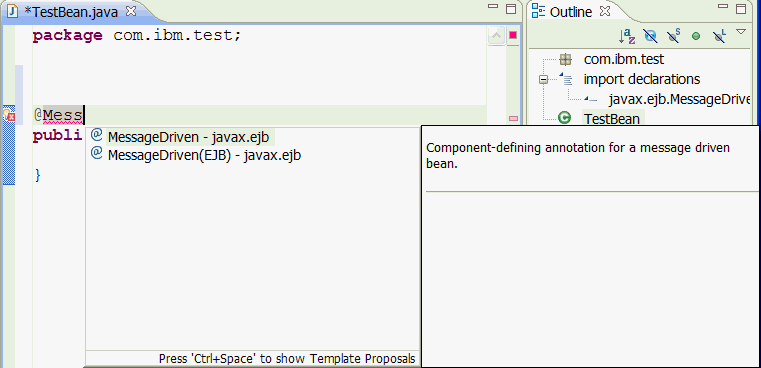
- You can see an error / quick fix icon
 beside the @MessageDriven line.
Right click the quick fix icon and select
beside the @MessageDriven line.
Right click the quick fix icon and select Quick Fix:
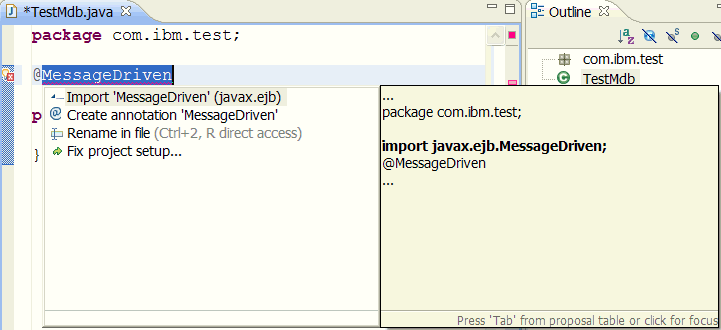
- Select
@MessageDriven(EJB) and the tools automatically add the dependency
import javax.ejb.MessageDriven;.
- In the Enterprise Explorer view, expand your
<Java project_name> | ejbModule, and your new MessageDriven bean Java class is listed under its package name.
- You can use the @MessageDriven annotation to specify properties
for the bean, including
- Destination type
- A durable subscription,
- A message selector
- An acknowledgment mode
- Destination type
- Creating a Session bean using annotations:
- The message-driven bean has to implement javax.jms.MessageListener
to produce or consume messages. Your message-driven bean class must implement
the javax.jms.MessageListener interface and the onMessage method, as shown
in this simple example:
@MessageDriven(mappedName = "jms/Queue") public class TestMessageBean implements MessageListener { ......... }After you add the implements MessageListener statement, the QuickFix option is to
Add unimplemented methods (javax.jsm.MessageListener.onMessage(). The onMessage method is added to your bean class:
public void onMessage(Message arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub }Your message-driven bean may implement a @PostConstruct callback method to create a connection, and a @PreDestroy callback method to close the connection. Use these methods if your bean produces messages or does synchronous receives from another destination.The bean class commonly injects a MessageDrivenContext resource, which provides some additional methods that you can use for transaction management. To configure a message-driven bean in its operational environment, you can use the @ActivationConfigProperty annotation. Here is an example of how you can configure a message-driven bean, using the @ActivationConfigProperty annotation:
@MessageDriven(activateConfig = {@ActivationConfigProperty(propertyName="destinationType", propertyValue="javax.jms.Queue"), @ActivationConfigProperty(propertyName="destinationName", propertyValue="jms/Queue") }) public class TestMessageBean implements MessageListener { ......... }The annotations @PostActivate and @PrePassivate can annotate a method as a lifecycle event callback in the Message-Driven Bean bean.
Related reference