Uses of MQIPT
There are a number of potential uses for IBM MQ Internet Pass-Thru (MQIPT).
MQIPT can be used as a channel concentrator
By using MQIPT in this way, channels to or from multiple separate hosts can appear to a firewall as if they are all to or from the MQIPT host. This makes it easier to define and manage firewall filtering rules.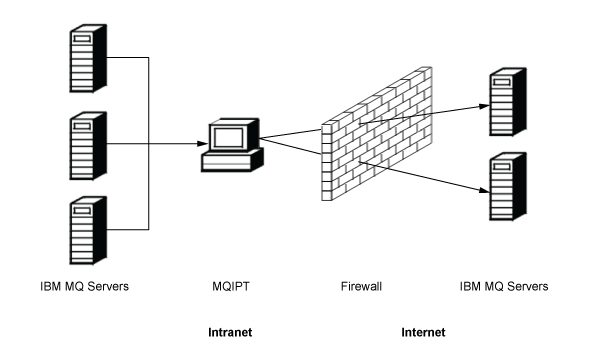
MQIPT can be placed in a DMZ to provide a single point of access
If MQIPT is placed within a DMZ firewall (a firewall configuration for securing local area networks), on a computer with a known and trusted internet protocol (IP) address, MQIPT can be used to listen for incoming IBM MQ channel connections which it can then forward to the trusted intranet; the inner firewall must allow this trusted computer to make inbound connections. In this configuration, MQIPT prevents external requests for access from receiving the true IP addresses of the computers in the trusted intranet. In this way, MQIPT provides a single point of access.
MQIPT can communicate by means of HTTP tunneling
If two instances of MQIPT are deployed in line, they can communicate by using HTTP. The HTTP tunneling feature enables requests to be transmitted through firewalls, by the use of existing HTTP proxies. The first MQIPT inserts the IBM MQ protocol into HTTP and the second extracts the IBM MQ protocol from its HTTP wrapper and forwards it to the destination queue manager.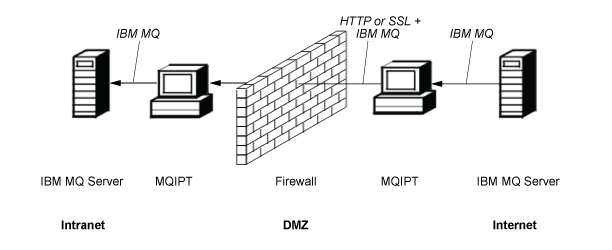
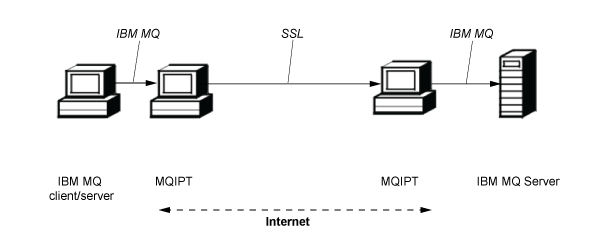
MQIPT can encrypt messages
If MQIPT is configured as in the previous example, requests can be encrypted before transmission through firewalls. The first MQIPT encrypts the data and the second decrypts it using SSL/TLS before sending it to the destination queue manager.