Distribution lists
Not supported on IBM MQ for z/OS . Distribution lists allow you to put a message to multiple destinations in a single MQPUT or MQPUT1 call. A single MQOPEN call can open multiple queues and a single MQPUT call can then put a message to each of those queues. Some generic information from the MQI structures used for this process can be superseded by specific information relating to the individual destinations included in the distribution list. Attention: Distribution lists do not support the use of alias queues that point to topic objects. If an alias queue points to a topic object in a distribution list, IBM MQ returns MQRC_ALIAS_BASE_Q_TYPE_ERROR.When an MQOPEN call is issued, generic information is taken from the Object Descriptor (MQOD). If you specify MQOD_VERSION_2 in the Version field and a value greater than zero in the RecsPresent field, the Hobj can be defined as a handle of a list (of one or more queues) rather than of a queue. In this case, specific information is given through the object records (MQORs), which give details of destination (that is, ObjectName and ObjectQMgrName).
The object handle (Hobj) is passed to the MQPUT call, allowing you to put to a list rather than to a single queue.
When a message is put on the queues (MQPUT), generic information is taken from the Put Message Option structure (MQPMO) and the Message Descriptor (MQMD). Specific information is given in the form of Put Message Records (MQPMRs).
Response Records (MQRR) can receive a completion code and reason code specific to each destination queue.
Figure 1 shows how distribution lists work.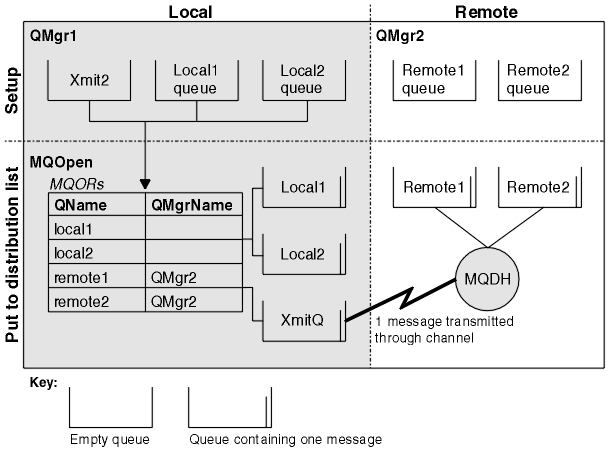
- Opening distribution lists
Use the MQOPEN call to open a distribution list, and use the options of the call to specify what we want to do with the list. - Put messages to a distribution list
To put messages to a distribution list, we can use MQPUT or MQPUT1.
Parent topic: Put messages on a queue